Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) is a common and chronic condition marked by persistent, excessive worry about a variety of everyday topics. Unlike the occasional anxiety many experience in response to specific events, individuals with GAD feel anxious nearly every day, often struggling to remember the last time they felt relaxed. This relentless anxiety can significantly impair their daily functioning and overall quality of life.
What is Generalized Social Anxiety Disorder?
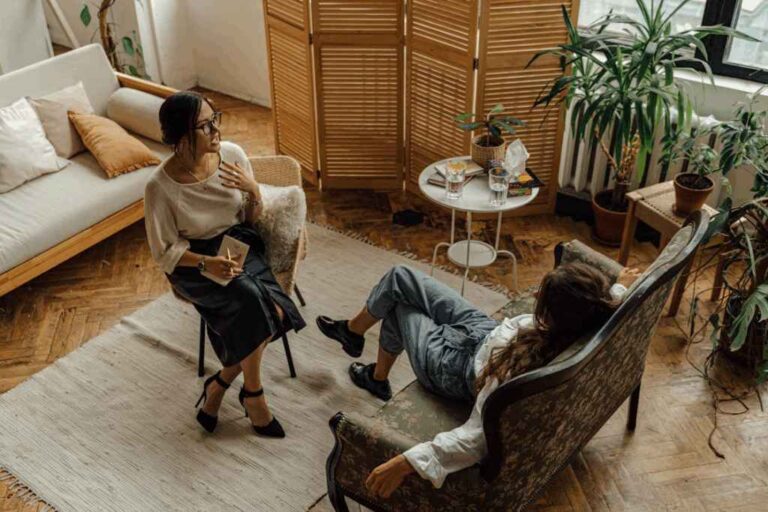
Generalized Social Anxiety Disorder, often confused with or considered as part of GAD, specifically relates to the overwhelming worry and self-consciousness about everyday social situations. The fear typically stems from a concern about being judged or negatively evaluated by others. This can be a debilitating condition that leads to avoidance of social interactions, severely impacting personal and professional relationships.
Understanding Generalized Anxiety Disorder
GAD sufferers often exhibit a variety of physical and psychological symptoms. Physically, they might experience fatigue, headaches, muscle tension, or trouble sleeping. Psychologically, the disorder manifests as difficulty concentrating, restlessness, and an uncontrollable feeling of worry. These symptoms can be persistent and fluctuate in intensity, sometimes peaking during periods of stress.
The exact causes of GAD are not fully understood but are believed to be a combination of genetic, environmental, and developmental factors. For instance, a person who has a family history of anxiety is at a higher risk of developing GAD. Traumatic experiences and a background of long-term stress or changes can also trigger or worsen the condition.
Strategies to Overcome Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Overcoming GAD involves several therapeutic strategies and lifestyle adjustments. Here are some effective approaches:
1. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT):
This is a form of psychological treatment that helps patients understand the thoughts and feelings that influence behaviors. CBT is highly effective for GAD, as it teaches individuals to recognize and challenge the irrational beliefs and fears that fuel their anxiety.
2. Medication:
Certain medications, such as antidepressants and anti-anxiety drugs, can help manage the symptoms of GAD. These are often used in conjunction with therapy to provide better outcomes.
3. Lifestyle Changes:
Regular physical activity, adequate sleep, and a balanced diet can significantly reduce anxiety levels. It’s also beneficial to limit caffeine and alcohol intake, as these can exacerbate anxiety symptoms.
4. Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques:
Practices such as yoga, meditation, and deep-breathing exercises can help calm the mind and reduce the physical symptoms of anxiety.
5. Support Networks:
Talking with friends or joining a support group can provide emotional support and decrease feelings of isolation associated with GAD.
Living with Generalized Anxiety Disorder is challenging, but with the right treatment and strategies, individuals can regain control of their lives and reduce the impact of this disorder. It’s important for those suffering to seek help from healthcare professionals to tailor a treatment plan that suits their specific needs.