[wpb_childpages parent_page_id=”17224″ post_type=”topic” post_status=”publish” sort_pages=”post_name” title=”Subtopics” style=”#topicNav{height: 350px;}”]
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a severe psychiatric condition that occurs in the aftermath of a traumatic event. It involves constant flashbacks, nightmares, and uncontrollable thoughts about the trauma that can leave you in a state of extreme fear. Treatment of PTSD is extremely important for you to be able to better manage your symptoms and regain control over your life.
Treatments For PTSD
The primary objectives of PTSD treatment are to limit the impact of its physical and emotional symptoms, enhance the patient’s ability for daily functioning, and improve the overall quality of life. Treatment for PTSD typically involves psychotherapy, medication, or a combination of both [mfn] Hetrick, S. E., Purcell, R., Garner, B., & Parslow, R. (2010). Combined pharmacotherapy and psychological therapies for post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). The Cochrane database of systematic reviews, (7), CD007316. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD007316.pub2 [/mfn].
A 2003 study [mfn] Grinage B. D. (2003). Diagnosis and management of post-traumatic stress disorder. American family physician, 68(12), 2401–2408. [/mfn] found that around 46% of patients with PTSD can improve within a period of 6 weeks with psychotherapy. Moreover, 62% of people experience improvement after receiving medication. Unfortunately, about 50% of people with PTSD do not receive treatment.
Here are some of the most popular methods of treating PTSD.
I. Psychotherapy
Psychological interventions [mfn] Sripada, R. K., Rauch, S. A., & Liberzon, I. (2016). Psychological Mechanisms of PTSD and Its Treatment. Current psychiatry reports, 18(11), 99. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11920-016-0735-9 [/mfn] are regarded as first-line treatment [mfn] Bajor, L. A., Ticlea, A. N., & Osser, D. N. (2011). The Psychopharmacology Algorithm Project at the Harvard South Shore Program: an update on posttraumatic stress disorder. Harvard review of psychiatry, 19(5), 240–258. https://doi.org/10.3109/10673229.2011.614483 [/mfn] for PTSD and in some cases [mfn] Sareen J. (2014). Posttraumatic stress disorder in adults: impact, comorbidity, risk factors, and treatment. Canadian journal of psychiatry. Revue canadienne de psychiatrie, 59(9), 460–467. https://doi.org/10.1177/070674371405900902 [/mfn], have been found to be more effective than pharmacotherapy.
Some of the commonly used psychotherapeutic techniques for PTSD treatment include
A. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive behavioral therapy is possibly the most effective treatment [mfn] Harvey, A. G., Bryant, R. A., & Tarrier, N. (2003). Cognitive behaviour therapy for posttraumatic stress disorder. Clinical psychology review, 23(3), 501–522. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0272-7358(03)00035-7 [/mfn] for PTSD and is specifically recommended for victims of assault, combat, and mixed traumas. A form of CBT known as trauma-focused cognitive behavioral therapy (TF-CBT [mfn] de Arellano, M. A., Lyman, D. R., Jobe-Shields, L., George, P., Dougherty, R. H., Daniels, A. S., Ghose, S. S., Huang, L., & Delphin-Rittmon, M. E. (2014). Trauma-focused cognitive-behavioral therapy for children and adolescents: assessing the evidence. Psychiatric services (Washington, D.C.), 65(5), 591–602. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ps.201300255 [/mfn]) is considered especially beneficial for treating PTSD. Around 66% of patients [mfn] Bradley, R., Greene, J., Russ, E., Dutra, L., & Westen, D. (2005). A multidimensional meta-analysis of psychotherapy for PTSD. The American journal of psychiatry, 162(2), 214–227. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.162.2.214 [/mfn] respond effectively to TF‐CBT.
Prolonged exposure therapy [mfn] Asukai N. (2015). Seishin shinkeigaku zasshi = Psychiatria et neurologia Japonica, 117(6), 457–464. [/mfn] is one of the well-known methods of this therapy technique. It involves recalling painful details about the traumatic event and exposing yourself to external reminders of the trauma under the guidance of a therapist, to eventually gain control over your emotions and reactions.
Research [mfn] Lancaster, C. L., Teeters, J. B., Gros, D. F., & Back, S. E. (2016). Posttraumatic Stress Disorder: Overview of Evidence-Based Assessment and Treatment. Journal of clinical medicine, 5(11), 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm5110105 [/mfn] provides ample evidence of the high efficacy of exposure-based methods for PTSD treatment.
Cognitive processing therapy [mfn] Chard, K. M., Ricksecker, E. G., Healy, E. T., Karlin, B. E., & Resick, P. A. (2012). Dissemination and experience with cognitive processing therapy. Journal of rehabilitation research and development, 49(5), 667–678. https://doi.org/10.1682/jrrd.2011.10.0198 [/mfn] is another type of CBT that is especially helpful in addressing related symptoms of depression, anxiety, and guilt in PTSD.
Read More About CBT Here
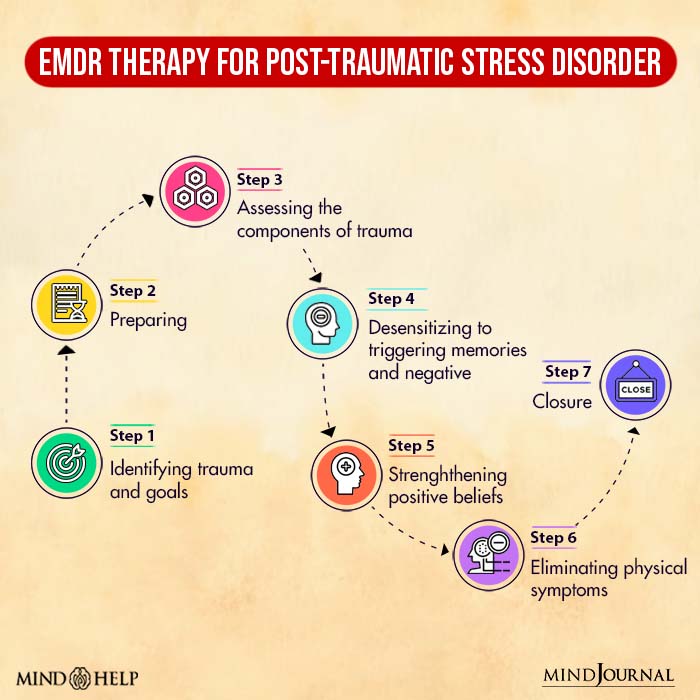
B. Eye Movement Desensitisation and Reprocessing (EMDR)
Eye Movement Desensitisation and Reprocessing is a form of PTSD therapy that requires you to remember aspects of the traumatic event while making rhythmic eye movements [mfn] Shapiro F. (2014). The role of eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) therapy in medicine: addressing the psychological and physical symptoms stemming from adverse life experiences. The Permanente journal, 18(1), 71–77. https://doi.org/10.7812/TPP/13-098 [/mfn].
The rapid eye movements aim to create an effect similar to how the human brain processes memories while sleeping. The aim of EMDR therapy is to create positive associations with previously disturbing memories.
EMDR has been found to produce faster results than trauma-focused CBT in post-traumatic stress disorder treatment.
C. Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT)
The assumption underlying ACT [mfn] Orsillo, S. M., & Batten, S. V. (2005). Acceptance and commitment therapy in the treatment of posttraumatic stress disorder. Behavior modification, 29(1), 95–129. https://doi.org/10.1177/0145445504270876 [/mfn] is that people often attempt to intentionally suppress intrusive thoughts and memories in PTSD. An acceptance and commitment therapist encourages you to face your thoughts and feelings and accept them for what they are while helping you to eventually come to terms with the trauma.
D. Hypnotherapy
Hypnosis-based treatment methods [mfn] Rotaru, T. Ș., & Rusu, A. (2016). A Meta-Analysis for the Efficacy of Hypnotherapy in Alleviating PTSD Symptoms. The International journal of clinical and experimental hypnosis, 64(1), 116–136. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207144.2015.1099406 [/mfn] have also proven to be quite effective in alleviating PTSD symptoms. However, further research is required to fully understand its advantages.
E. Other Therapies
Several other PTSD treatment approaches exist apart from the ones we just discussed, such as
- Brief Eclectic Psychotherapy [mfn] Gersons, B. P. R., Nijdam, M. J., Smid, G. E., & Meewisse, M.-L. (2020). Brief eclectic psychotherapy for PTSD. Casebook to the APA Clinical Practice Guideline for the Treatment of PTSD., 139–161. https://doi.org/10.1037/0000196-007 [/mfn]
- Couple and Family therapy [mfn] Suomi, A., Evans, L., Rodgers, B., Taplin, S., & Cowlishaw, S. (2019). Couple and family therapies for post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). The Cochrane database of systematic reviews, 12(12), CD011257. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD011257.pub2 [/mfn]
- Brief Psychodynamic Therapy [mfn] Krupnick, J. L. (2002). Brief psychodynamic treatment of PTSD. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 58(8), 919–932. https://doi.org/10.1002/jclp.10067 [/mfn]
II. Medications
There is as such no medication specifically indicated for PTSD treatment. Certain drugs may however be prescribed for symptom relief. Some of the most prescribed medications for post-traumatic stress disorder include [mfn] Stein, D. J., Ipser, J. C., & Seedat, S. (2006). Pharmacotherapy for post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). The Cochrane database of systematic reviews, 2006(1), CD002795. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD002795.pub2 [/mfn]
- Antidepressants such as SNRIs and SSRIs [Read more]
- Anti-anxiety drugs such as benzodiazepines
- Mood stabilizers
- Antipsychotics
- Beta-blockers
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI) along with serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRI) like venlafaxine [mfn] Stein, D. J., Seedat, S., van der Linden, G. J., & Zungu-Dirwayi, N. (2000). Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in the treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. International clinical psychopharmacology, 15 Suppl 2, S31–S39. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004850-200008002-00006 [/mfn], are considered the first-line drugs [mfn] Mann, S. K., & Marwaha, R. (2022). Posttraumatic Stress Disorder. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559129/ [/mfn] for PTSD. However, antidepressants may increase suicidal behavior in patients below 24 years of age. Pharmacological agents like prazosin [mfn] Singh, B., Hughes, A. J., Mehta, G., Erwin, P. J., & Parsaik, A. K. (2016). Efficacy of Prazosin in Posttraumatic Stress Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. The primary care companion for CNS disorders, 18(4), 10.4088/PCC.16r01943. https://doi.org/10.4088/PCC.16r01943 [/mfn] are usually prescribed as a treatment for PTSD nightmares.
Medical treatment often goes hand-in-hand with psychotherapy.

Takeaway
If you are suffering from severe post-traumatic stress disorder and finding it challenging to function in everyday life, seeking professional help is extremely important.
A qualified and experienced healthcare professional can help you figure out the best PTSD treatment plan with minimal side effects to ensure a fast recovery. With the right kind of help, it can be possible for you to experience a significant improvement in your symptoms within a few weeks.
At A Glance
- PTSD treatment can involve both psychotherapy and medication.
- Some common psychological interventions for PTSD include cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR).
- Medications such as antidepressants may also be prescribed for the symptomatic treatment of PTSD.
- Certain alternative methods of treatment for PTSD include yoga, tai chi, acupuncture, and psychedelics.
- Seeking professional help can help in effective and fast recovery from PTSD.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can psychedelic drugs cure PTSD?
Psychedelic treatment [mfn] Krediet, E., Bostoen, T., Breeksema, J., van Schagen, A., Passie, T., & Vermetten, E. (2020). Reviewing the Potential of Psychedelics for the Treatment of PTSD. The international journal of neuropsychopharmacology, 23(6), 385–400. https://doi.org/10.1093/ijnp/pyaa018 [/mfn] for PTSD involving drugs such as psilocybin and cannabinoids has recently risen in popularity, although it is not legal everywhere in the world. Experts suggest exercising caution [mfn] Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Treatment with Psychedelic Drugs. (n.d.). NYU Langone Health. Available from: https://med.nyu.edu/departments-institutes/population-health/divisions-sections-centers/medical-ethics/education/high-school-bioethics-project/learning-scenarios/ptsd-treatment-psychedelics#:~:text=Risks%20of%20Approving%20Psilocybin%20to%20Treat%20PTSD&text=A%20bad%20trip%20has%20the [/mfn] when using these methods as they can sometimes scar people, doing more harm than good.
2. Is there a definitive cure for PTSD?
With the appropriate help, it is possible to completely recover from PTSD using a variety of methods. However, PTSD treatment demands a certain amount of time, effort, and patience to be fully effective.
3. What is the best type of therapy to treat PTSD?
Exposure-based therapies are considered to be the most effective PTSD treatment.
4. How do you treat PTSD without medication?
There are several psychotherapeutic methods (for example, CBT) to treat PTSD which are often found to be more effective than medical treatment.
5. How do you treat PTSD at home?
PTSD usually requires professional help to be treated. However, some self help strategies such as meditation, exercise, and healthy diet can hasten the process of recovery.
6. Can PTSD go away without treatment?
Sometimes, PTSD symptoms can diminish on their own without treatment. However, for long term recovery, therapy or medication is often crucial.

Leave a Reply