Holistic health or holistic healing encompasses a broad range of treatments, dietary supplements, lifestyle changes, among others to bring about a change in our quality of life and health. It is a broad term which involves complementary and alternative medicine (CAM).
Types Of Holistic Treatments
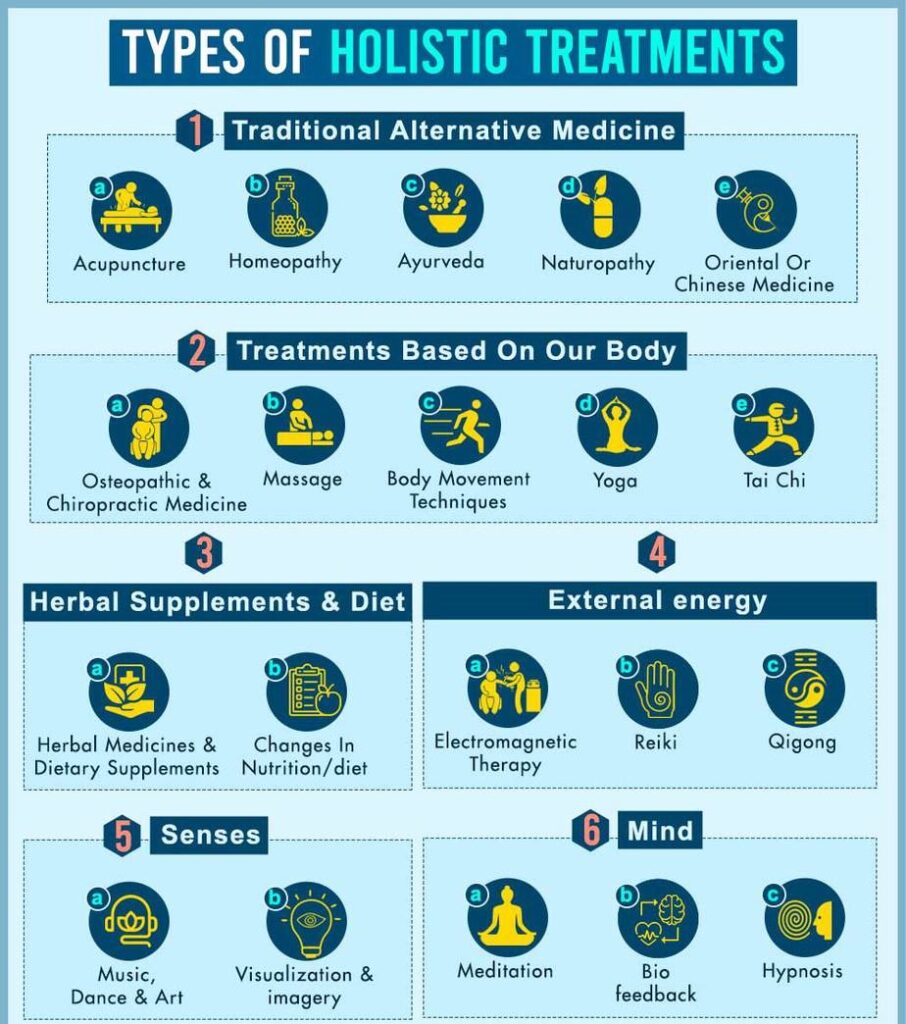
Holistic health treatments involve numerous approaches. The knowledge of some of these treatments has been carried forward from ancient times when primitive man used to depend on the forces of nature and our body’s own healing capacity in order to fight diseases. A lot of different areas make up the broad term of holistic healing that we now use today. These treatments are different from conventional methods used like in allopathy and conventional medicine. A study [mfn] Tabish S. A. (2008). Complementary and Alternative Healthcare: Is it Evidence-based?. International journal of health sciences, 2(1), V–IX. [/mfn] states that these are a “group of diverse medical and health care systems, practices, and products that are not presently considered to be part of conventional medicine.”
A lot of these treatments or therapies as most of them are, overlap one another in terms of treatments and methods used. Here are 6 major categories of holistic healing:
1. Traditional Alternative Medicine
Practices in traditional alternative medicine have been used since centuries. It is based on beliefs, theories, skills, practices and experiences, which were indigenous to China and India. Since then, alternative [mfn] Kisling LA, Stiegmann RA. Alternative Medicine. [Updated 2020 Jul 27]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538520/ [/mfn] medicine has found its way into modern societies and a lot of countries across the world, especially Australia, China and India believe in its benefits. The common types of alternative medicine are:
A. Acupuncture
Acupuncture is a type of treatment where needles [mfn] Kawakita, K., & Okada, K. (2014). Acupuncture therapy: mechanism of action, efficacy, and safety: a potential intervention for psychogenic disorders?. BioPsychoSocial medicine, 8(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.1186/1751-0759-8-4 [/mfn] are used to insert in a person’s skin. The fine needles are used in different areas of our body, also known as pressure points. There is a growing amount of research which suggests that it might actually be beneficial in pain management. A 2014 study [mfn] Kawakita, K., & Okada, K. (2014). Acupuncture therapy: mechanism of action, efficacy, and safety: a potential intervention for psychogenic disorders?. BioPsychoSocial medicine, 8(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.1186/1751-0759-8-4 [/mfn] indeed found out that “acupuncture in the treatment of chronic musculoskeletal pain have clearly demonstrated the efficacy and safety of acupuncture therapy.”
It is based on the traditional Chinese way of healing and suggests that our life force, also known as “Qi” in Chinese, is balanced by the “Yin” and “Yang” in our body. This life force is supposed to flow inside our body, which can be accessed through 350 different pressure points in our body. Inserting needles into these specific pressure points are supposed to help in treating illness and other ailments in the body. Acupuncture is a popular method of holistic health and is used by a lot of nations worldwide.
B. Homeopathy
Homeopathy is a system of medicine and is based on an age-old belief that the body is capable of healing itself. The practitioners of homeopathy are called homeopaths. Homeopaths or homeopathic doctors use natural [mfn] Merrell, W. C., & Shalts, E. (2002). Homeopathy. The Medical clinics of North America, 86(1), 47–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0025-7125(03)00071-3 [/mfn] substances in tiny amounts and administer it to their patients. They believe that these substances can stimulate the healing process in our body.
Homeopathy was first established in Germany and since then has found recognition in various parts of the world. The basic principle of homeopathy is that “like cures like.’’ This essentially means that when foreign bodies bring about symptoms in a healthy person, those same substances in small amounts can cure illnesses with similar symptoms. The substances are diluted using water or alcohol.
A lot of homeopathic medicines come in the form of liquid drops, gels, lotions, tablets and even sugar pellets. Usually, homeopathic treatments are customized according to the patients and their requirements.
C. Ayurveda
One of the oldest methods of holistic healing in the world is Ayurveda [mfn] Jaiswal, Y. S., & Williams, L. L. (2016). A glimpse of Ayurveda – The forgotten history and principles of Indian traditional medicine. Journal of traditional and complementary medicine, 7(1), 50–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcme.2016.02.002 [/mfn]. It is based on the intrinsic belief of holistic health that optimal health is a result of a balance [mfn] Chauhan, A., Semwal, D. K., Mishra, S. P., & Semwal, R. B. (2015). Ayurvedic research and methodology: Present status and future strategies. Ayu, 36(4), 364–369. https://doi.org/10.4103/0974-8520.190699 [/mfn] between the mind, body and soul. The main goal of Ayurveda is not to fight symptoms or cure diseases, but to promote good health in individuals. Practitioners of Ayurveda believe that all humans are made of the basic elements found in our universe.
They are fire, air, water, earth and space. These elements get combined in our body to form three energies or life forces. They are called “doshas” [mfn] Travis, F. T., & Wallace, R. K. (2015). Dosha brain-types: A neural model of individual differences. Journal of Ayurveda and integrative medicine, 6(4), 280–285. https://doi.org/10.4103/0975-9476.172385 [/mfn] . These doshas are responsible for the well being of our body. These doshas are Kapha dosha which represents earth and water, Vata dosha which represents air and space and finally Pitta dosha which signifies water and fire.
Ayurveda believes that each individual has a unique mix of all these doshas. However, some of them can be more powerful than others. Each of these doshas tend to control a different body function [mfn] Telles, S., Pathak, S., Kumar, A., Mishra, P., & Balkrishna, A. (2015). Ayurvedic doshas as predictors of sleep quality. Medical science monitor : international medical journal of experimental and clinical research, 21, 1421–1427. https://doi.org/10.12659/MSM.893302 [/mfn] within us. It is believed that our health ailments and chances of falling sick are dependent on the balance of these doshas in our body. Ayurvedic treatments are also customized according to different people.
Ayurvedic practitioners take into account the different factors of each individual like their physical state, their emotional state and their spiritual state. Practitioners use a combination of ancient ayurvedic herbs [mfn] Kumar, S., Dobos, G. J., & Rampp, T. (2017). The Significance of Ayurvedic Medicinal Plants. Journal of evidence-based complementary & alternative medicine, 22(3), 494–501. https://doi.org/10.1177/2156587216671392 [/mfn] like ashwagandha, gokshura, tulsi, etc., examples of which can be found in ancient Indian texts and manuscripts. Most practices are based on blood purification, medicinal oils, herbs, herbal powders and tablets, massages with essential oils, laxatives and even enemas.
D. Naturopathy
Naturopathy [mfn] Fleming, S. A., & Gutknecht, N. C. (2010). Naturopathy and the primary care practice. Primary care, 37(1), 119–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pop.2009.09.002 [/mfn] is a system of medicine, under holistic health which first originated in Europe in the 19th century. It is a type of alternative treatment which involves pseudoscientific practices. These practices are seen as non-invasive, self-healing and natural. Naturopathy consists of a variety of treatments and therapies like acupuncture, exercise, changes in nutrition and diet, herbal massages, homeopathy, stress reduction, psychotherapy and even counseling.
The objective [mfn] Smith, M. J., & Logan, A. C. (2002). Naturopathy. The Medical clinics of North America, 86(1), 173–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0025-7125(03)00079-8 [/mfn] of naturopathy, just like holistic healing, aims to treat the person as a whole, which consists of the body, mind and the spirit. It tries to rectify the root cause of an ailment, rather than just focusing on the symptoms itself. A lot of naturopathic remedies are also created using a combination of herbs mentioned in the Ayurvedic system of healing and also homeopathic and chiropractic practices.
E. Oriental or Chinese medicine
This system of medicine, as the name suggests, had its origin [mfn] Lu, A. P., Jia, H. W., Xiao, C., & Lu, Q. P. (2004). Theory of traditional Chinese medicine and therapeutic method of diseases. World journal of gastroenterology, 10(13), 1854–1856. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i13.1854 [/mfn] thousands of years ago in China. It is used to diagnose, treat and prevent the onset of diseases. The concept of Oriental medicine is based on the belief that there is a vital life force in our body called “Qi [mfn] Flowers J. (2006). What is qi?. Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine : eCAM, 3(4), 551–552. https://doi.org/10.1093/ecam/nel074 [/mfn] ’’. This “Qi” is responsible for our physical, emotional, mental and spiritual well-being. Any imbalance to this vital life force tends to cause diseases. A 2004 study [mfn] Lu, A. P., Jia, H. W., Xiao, C., & Lu, Q. P. (2004). Theory of traditional Chinese medicine and therapeutic method of diseases. World journal of gastroenterology, 10(13), 1854–1856. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i13.1854 [/mfn] states that “Chinese medicine focuses on the integrity of human body and the close relationship with its social and natural environments.” It believes that we humans are just a smaller part of our entire universe and we are connected with nature. It tries to maintain a balance between diseases and health in individuals.
Practices involved in Oriental medicine are also customized according to the individual and their own unique requirements, thus forming the basis of holistic health of an individual. It makes use of acupuncture, cupping therapy, massage, moxibustion (burning of herbs near the body), herbal supplements and also through changes in diet, nutrition and exercise. Herbal remedies in Oriental medicine range from commonly used herbs like ginger, garlic, green tea along with other traditional herbs native to China.
Read More About Holistic Health Here
2. Treatments based on our body
Treatments concerned with our body are based on the healing power of touch. It is believed that when a person falls ill, the illness affects all parts of the body. Thus, if other body parts can be treated and brought back to their original state of well-being, then the body can focus on healing the site where the illness has occurred. Techniques and treatments concerned with our body use manual manipulation like massages and chiropractic treatments. Treatments concerned with our body are:
A. Osteopathic and chiropractic medicine
Osteopathic treatments [mfn] Campbell, S. M., Winkelmann, R. R., & Walkowski, S. (2012). Osteopathic manipulative treatment: novel application to dermatological disease. The Journal of clinical and aesthetic dermatology, 5(10), 24–32. [/mfn] are based on the belief that all the bones, ligaments, muscles and tissues in our body should work together in harmony. This helps to achieve an optimum physical condition of the body where there is absence of any illness or diseases. Some osteopathic [mfn] Steel, A., Sundberg, T., Reid, R., Ward, L., Bishop, F. L., Leach, M., Cramer, H., Wardle, J., & Adams, J. (2017). Osteopathic manipulative treatment: A systematic review and critical appraisal of comparative effectiveness and health economics research. Musculoskeletal science & practice, 27, 165–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.math.2016.10.067 [/mfn] treatments use manual manipulation techniques like massaging and stretching therapies, which are believed to ease tension in the body and increase mobility.
Chiropractic treatments [mfn] Salehi, A., Hashemi, N., Imanieh, M. H., & Saber, M. (2015). Chiropractic: Is it Efficient in Treatment of Diseases? Review of Systematic Reviews. International journal of community based nursing and midwifery, 3(4), 244–254. [/mfn] focus on the relationship between our muscles, skeleton and our nerves. Most of the treatments are targeted towards the patient’s spinal cord, as chiropractic treatments believe this is where all our nerves originate from. Chiropractors use hands and other devices to make adjustments in our joints. It is a popular method for getting relief from pain. Nowadays chiropractic treatments have gained popularity as a beneficial method in holistic health as most people believe it to be an effective method in pain management.
B. Massage
Massage therapies are used to embrace wellness and also treat health conditions. It involves applying pressure and massaging the tissues and muscles in our body. It was one of the earliest techniques used by man for getting relief from pain. The masseur or masseuse is usually a licensed professional who uses his/her hands or fingers for rubbing, pressing and stretching our muscles and joints. Massage therapies are often used with a combination of essential oils and lotions.
A 2016 study [mfn] Field T. (2016). Massage therapy research review. Complementary therapies in clinical practice, 24, 19–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctcp.2016.04.005 [/mfn] found out that “massage therapy has been shown to have beneficial effects on varying conditions including depression, autism, skin conditions, arthritis, fibromyalgia, hypertension, asthma, multiple sclerosis, HIV and breast cancer.” There are different types of massage therapies, which differ in their application of pressure and using certain massaging tools for deeper penetration. Some types of popular massage therapies in holistic health include Swedish massage, deep tissue massage, Balinese massage, among others.
C. Body movement techniques
Movement therapies can refer to a wide range of Western and Eastern practices which are used to promote mental, physical, emotional and spiritual well-being. Movement therapies focus on the mobility of the body. It is based on the belief that all of our bodies have a unique sense of movement. People tend to lose mobility in some parts of their body due to an injury [mfn] Phuphanich, M. E., Droessler, J., Altman, L., & Eapen, B. C. (2020). Movement-Based Therapies in Rehabilitation. Physical medicine and rehabilitation clinics of North America, 31(4), 577–591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmr.2020.07.002 [/mfn] or illness. Also, toxins in our body tend to get accumulated inside when there is not enough physical motion or exercise. A movement therapist works to help a person tap into their sense of movement again. Movement therapies include yoga, Tai Chi, Qigong, dance, among other techniques which focus on physical exercise and activities.
D. Yoga
Yoga [mfn] Stephens I. (2017). Medical Yoga Therapy. Children (Basel, Switzerland), 4(2), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/children4020012 [/mfn] originated in ancient India and comprises mental, spiritual and physical practices. It is more of a practice than a treatment in holistic health, as it does not intend to cure or prevent any diseases. It is associated with the general well-being of the human body. A 2012 study [mfn] Büssing, A., Michalsen, A., Khalsa, S. B., Telles, S., & Sherman, K. J. (2012). Effects of yoga on mental and physical health: a short summary of reviews. Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine : eCAM, 2012, 165410. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/165410 [/mfn] found out that “yoga may have potential to be implemented as a beneficial treatment “ for mental and physical health. Styles of yoga comprise of meditation, physical exercises and breathing techniques.
Yoga is believed to promote a healthy body and mind, physical strength, flexibility and calmness. There are six branches of yoga [mfn] Brems, C., Colgan, D., Freeman, H., Freitas, J., Justice, L., Shean, M., & Sulenes, K. (2016). Elements of yogic practice: Perceptions of students in healthcare programs. International journal of yoga, 9(2), 121–129. https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-6131.183710 [/mfn] known as hatha yoga, karma yoga, raja yoga, tantra yoga, bhakti yoga and jnana yoga. The main philosophy of yoga is that our human body comprises chakras or energy points [mfn] Ross C. L. (2019). Energy Medicine: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Global advances in health and medicine, 8, 2164956119831221. https://doi.org/10.1177/2164956119831221 (Retraction published Glob Adv Health Med. 2021 Apr 13;10:21649561211012196) [/mfn] . This determines how people live their life and imbalances between these chakras can cause physical symptoms of diseases.
E. Tai Chi
Tai chi [mfn] Webster, C. S., Luo, A. Y., Krägeloh, C., Moir, F., & Henning, M. (2015). A systematic review of the health benefits of Tai Chi for students in higher education. Preventive medicine reports, 3, 103–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmedr.2015.12.006 [/mfn] had its origin in China and is based on traditional Chinese martial arts. It is also known as meditation in motion. It consists of a series of breathing techniques and movements, which are performed in a slow and fluidic manner. Each of the Tai Chi postures tend to flow or transition to the next without stopping. This ensures that your body is in a constant state of motion. There are various styles of Tai Chi, which incorporates different methods like physical movements and breathing techniques.
Also, different forms of Tai Chi are concerned with different benefits, like health [mfn] Huston, P., & McFarlane, B. (2016). Health benefits of tai chi: What is the evidence?. Canadian family physician Medecin de famille canadien, 62(11), 881–890. [/mfn] aspects or even martial arts training. Tai Chi is considered to be safe for people including elderly persons. This is because it does not require much physical strength and also is non-exhaustive. The benefits of Tai Chi in holistic health are improvements in physical well-being, mobility of joints, improvements in mental and emotional states, improved energy, body flexibility and balance.
3. Herbal supplements and diet
Holistic healing methods also comprises a lot of herbal supplements and changes in diet and nutrition. It believes in the healing power of certain herbs which can prevent ailments and can also strengthen our immune system. Nutritional and dietary deficiencies are one of the leading causes of ailments in individuals. This form of holistic healing is concerned with such dietary and nutritional practices which can fulfill the nutritional intake of our body and can also prevent the onset of diseases.
A. Herbal medicines and dietary supplements
Herbal medicines [mfn] Firenzuoli, F., & Gori, L. (2007). Herbal medicine today: clinical and research issues. Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine : eCAM, 4(Suppl 1), 37–40. https://doi.org/10.1093/ecam/nem096 [/mfn] , the use of medicinal plants for treatment of diseases, fall under a category of alternative healing called herbalism in holistic health. It is concerned with the use of plants which are revered for their medicinal [mfn] Vickers, A., Zollman, C., & Lee, R. (2001). Herbal medicine. The Western journal of medicine, 175(2), 125–128. https://doi.org/10.1136/ewjm.175.2.125 [/mfn] properties. These plants are obtained from nature and some are specific to some regions only. These herbal medicines are obtained from plants which have been long used by men for their supposed medicinal benefits and uses.
These plants are often mentioned in Ayurvedic forms of healing. The ancient Chinese and Indians made use of some medicinal plants, evidence of which can be found in the vedas. These plants are often crushed into powders, made into tablets or used in cooking. Some of these plants [mfn] Ekor M. (2014). The growing use of herbal medicines: issues relating to adverse reactions and challenges in monitoring safety. Frontiers in pharmacology, 4, 177. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2013.00177 [/mfn] can be found in household kitchens like ginger, garlic, lemon, parsley, lavender, fenugreek, tea, oregano, black pepper, etc. among others.
B. Changes in nutrition/diet
The food we eat affects our well-being in a lot of ways. Holistic health and healing tries to make use of healthy nutritious food to enable the body to reach optimum levels of health. A 2014 [mfn] Sadighi, J., Montazeri, A., & Jahangiri, K. (2014). Towards a Holistic Approach to Healthy Diet: Evidence from Iranian Health Perception Study. Iranian journal of public health, 43(6), 828–834. [/mfn] study found that “healthy diet and other determinants of lifestyle are very integrated into each other.” This means healthy nutrition and diet can affect other factors of our well-being like our emotional and mental states. A holistic approach to nutrition makes individuals aware of healthy eating habits and also tries to manage their diet by creating customized meal plans.
4. External energy
Holistic healing believes that energy [mfn] Srinivasan T. (2010). Energy medicine. International journal of yoga, 3(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-6131.66770 [/mfn] around us flows through objects. It makes use of energies from healing sources and believes it to get transferred to the body of the patient. Practitioners of external energy are called healers and they try to channel this energy to other people who can benefit from it.
A. Electromagnetic therapy
This category of holistic health is concerned with the use of magnets or even electromagnets. Practitioners try to transfer the supposed healing energy from magnets to patients. The magnetic energy is believed to heal and cure diseases and ailments. A 2020 study [mfn] Paolucci, T., Pezzi, L., Centra, A. M., Giannandrea, N., Bellomo, R. G., & Saggini, R. (2020). Electromagnetic Field Therapy: A Rehabilitative Perspective in the Management of Musculoskeletal Pain – A Systematic Review. Journal of pain research, 13, 1385–1400. https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S231778 [/mfn] found that Electromagnetic therapy indeed provides “a non-invasive, safe, and easy method to treat pain with respect to musculoskeletal diseases.”
B. Reiki
Reiki is a type of energy healing which originated in Japan. It involves transfer of the energy from our universe which travels through the palm of the practitioner to the patient. It is based on the belief that whenever energy in our body gets stagnant at places, it creates an energy block. Practitioners try to remove these blocks and enable the flow of energy again. Some Reiki healers even make use of crystals and other earthly stones which they believe contain healing energies. Reiki may be beneficial for managing pain and anxiety, as backed by a 2015 study [mfn] Thrane, S., & Cohen, S. M. (2014). Effect of Reiki therapy on pain and anxiety in adults: an in-depth literature review of randomized trials with effect size calculations. Pain management nursing : official journal of the American Society of Pain Management Nurses, 15(4), 897–908. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmn.2013.07.008 [/mfn] .
C. Qigong
Qigong is a healing technique in holistic health which originated in China and is considered to be the foundation of all oriental or Chinese medicine. A 2011 study [mfn] Jahnke, R., Larkey, L., Rogers, C., Etnier, J., & Lin, F. (2010). A comprehensive review of health benefits of qigong and tai chi. American journal of health promotion : AJHP, 24(6), e1–e25. https://doi.org/10.4278/ajhp.081013-LIT-248 [/mfn] mentions that “earliest forms of Qigong make up one of the historic roots of contemporary Traditional Chinese Medicine.” It involves the use of controlled breathing, meditation and other exercises which focuses on body movement and is also associated with “physiological and psychological functionality.” It is used for maintaining optimum health in individuals, training for spirituality and even martial arts.
5. Mind
The mind is believed to be connected [mfn] Renoir, T., Hasebe, K., & Gray, L. (2013). Mind and body: how the health of the body impacts on neuropsychiatry. Frontiers in pharmacology, 4, 158. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2013.00158 [/mfn] to our body and can even assist in our mental and emotional health. Modern studies have proven that a healthy mind leads to better physical well-being. Our thoughts, beliefs and ideas can affect the way we feel and function.
A. Meditation
This is a holistic practice where a person uses his/her mind to focus on a specific object, activity or thought. A 2011 study [mfn] Sharma H. (2015). Meditation: Process and effects. Ayu, 36(3), 233–237. https://doi.org/10.4103/0974-8520.182756 [/mfn] found that “according to Vedic science, the true purpose of meditation is to connect oneself to one’s deep inner self.” Meditation [mfn] Behan C. (2020). The benefits of meditation and mindfulness practices during times of crisis such as COVID-19. Irish journal of psychological medicine, 37(4), 256–258. https://doi.org/10.1017/ipm.2020.38 [/mfn] is believed to increase our awareness and attention. It also helps us to become mentally clear and achieve a stable and calm state emotionally. Research [mfn] Goyal, M., Singh, S., Sibinga, E. M., Gould, N. F., Rowland-Seymour, A., Sharma, R., Berger, Z., Sleicher, D., Maron, D. D., Shihab, H. M., Ranasinghe, P. D., Linn, S., Saha, S., Bass, E. B., & Haythornthwaite, J. A. (2014). Meditation programs for psychological stress and well-being: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA internal medicine, 174(3), 357–368. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.13018 [/mfn] has shown that meditation may be effective in reducing stress, depression, anxiety and even pain.
B. Biofeedback
Biofeedback is a technique in holistic health which involves the use of auditory or visual feedback. According to a recent study [mfn] Malik K, Dua A. Biofeedback. [Updated 2021 Apr 19]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK553075/ [/mfn] “it is a technique to augment the normal sensory feedback and allow better control of body functions that are usually considered involuntary.” It helps individuals to recognize and understand the signs and symptoms of various ailments. It is based on the belief that harnessing our mind’s power can help us in becoming aware of what is going on inside our body. Aspects of health like body temperature, muscle tension and increased heart rate can be measured to identify any underlying symptoms. The procedure involves electrodes which are attached to the person’s fingers or skin. The signals are transmitted to a monitor which can display various body functions like breathing rate, heart rate, blood pressure, sweating, muscle tension among others.
C. Hypnosis
Hypnosis is a holistic health process which involves creating a trance or hypnotic state in individuals. A 2019 study [mfn] Williamson A. (2019). What is hypnosis and how might it work?. Palliative care, 12, 1178224219826581. https://doi.org/10.1177/1178224219826581 [/mfn] states that it is “a waking state of awareness.” In this state people are said to have increased concentration, focus and awareness. Individuals in hypnosis may seem like they are zoned out, but they are actually in a state of super-consciousness. The process is carried out by a therapist who assists the person in reaching a hypnotic state. Various studies have shown that hypnosis has various therapeutic benefits. It can help reduce pain, anxiety and even help with dementia.
6. Senses
It is believed that our senses like touch, hearing, sight, taste and smell have a huge role to play in our overall health. These beliefs are also backed by Ayurveda which states that these senses are our gateways of perception. Our senses influence the way we feel and determine our emotions and thoughts. Examples of healing therapies using senses are:
A. Music, dance and art
Practicing a creative skill like music, dance or even art [mfn] Pratt R. R. (2004). Art, dance, and music therapy. Physical medicine and rehabilitation clinics of North America, 15(4), 827–vii. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmr.2004.03.004 [/mfn] has been shown to greatly improve our overall well-being. It provides for a way for people to cope with emotional conflicts and also increase self-consciousness. It lets people express themselves through practicing these creative arts and allows for greater mental and emotional wellbeing. Engaging in any creative practice influences our brain wave patterns. It helps individuals express their hidden emotions, and can reduce anxiety, fear and even stress.
B. Visualization and imagery
This category of holistic health uses the power of our senses to make individuals think about a happy feeling or a peaceful setting. A practitioner guides the person into a relaxed state which may even involve the use of hypnosis. A 2003 study [mfn] Kingwatsiaq, N., & Pii, K. (2003). Healing the body and the soul through visualization: a technique used by the Community Healing Team of Cape Dorset, Nunavut. Arctic anthropology, 40(2), 90–92. https://doi.org/10.1353/arc.2011.0083 [/mfn] states that “during visualization one assumes a relaxed state with one’s eyes closed and imagines oneself in the context of a story told by the person guiding the imagery.”
The person is guided in a way that he/she tends to think in detail of a place or a setting, which further helps to calm and relax them. Guided visualization and imagery is thought to be beneficial because it helps to redirect a person’s attention from a stressful situation to a more relaxed state. This practice is believed to greatly reduce stress, anxiety, depression and provides for greater mental and emotional stability.
Holistic Healing – The Future Looks Promising
Holistic healing techniques and practices are just beginning to enter mainstream medicine and have been the subject of a lot of research and studies. Although some practices might be more effective than others, we are still at an early stage to successfully predict the outcomes of such holistic techniques.










Leave a Reply