Geographical psychology is the study of how geographical factors, such as location, climate, and cultural influences, impact human behavior and psychological processes. It seeks to understand how the environment interacts with individual and collective psychological well-being, shaping various aspects of cognition, emotions, and social behavior.
What is Geographical Psychology
Geographical psychology is a specialized branch 1 Rentfrow P. J. (2020). Geographical psychology. Current opinion in psychology, 32, 165–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copsyc.2019.09.009 of psychology that focuses on exploring the connections between geographical locations and mental health phenomena. Its primary aim is to investigate why personality traits, life satisfaction, and social behavior exhibit variations or tend to cluster in specific areas, shedding light on the intricate interplay between location and human psychology.
Moreover, geographical location can have lasting effects on mental health 2 Jones, J. (2001). The geography of mental health. Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences, 10(4), 219–224. https://doi.org/10.1017/s1121189x00005388 by shaping critical factors such as social support networks, economic opportunities, exposure to natural disasters, and cultural norms.
For example, regions with limited social support networks may experience higher rates of loneliness and isolation, increasing the risk of depression and anxiety. Economic opportunities, or the lack thereof, can impact financial stress and job satisfaction, potentially leading to conditions like chronic stress and burnout.
Read More About Burnout Here
How Geographical Locations Impact Behavior
Geographical locations exert a 3 Götz, F. M., Stieger, S., Gosling, S. D., Potter, J., & Rentfrow, P. J. (2020). Physical topography is associated with human personality. Nature human behaviour, 4(11), 1135–1144. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-020-0930-x profound influence on human behavior through a complex interplay of environmental, cultural, and socio-economic factors. The physical characteristics of a location, such as climate, terrain, and natural resources, shape activities and lifestyle choices.
Cultural norms and social practices prevalent in specific regions dictate behavior, influencing social interactions, communication styles, and value systems. Ultimately, geographical locations serve as a backdrop that molds and guides human behavior, reflecting the intricate relationship between individuals and their surroundings.
Different Geographical Locations and Mental Health Issues
Different geography affects mental health care 4 Gärling, T. (2009). Environmental psychology: The contribution of geography to psychology. Journal of Environmental Psychology, 29(4), 538–539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvp.2009.10.005 with varying mental health issues, such as:
- Urban areas, characterized by pollution and noise, contribute to elevated stress levels and attention issues, potentially affecting mental well-being.
- Rural and remote regions face challenges of social isolation and limited communication opportunities.
- Natural disasters, such as hurricanes, earthquakes, or floods, can lead to post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) 5 Golitaleb, M., Mazaheri, E., Bonyadi, M., & Sahebi, A. (2022). Prevalence of Post-traumatic Stress Disorder After Flood: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Frontiers in psychiatry, 13, 890671. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2022.890671 , nightmares, and persistent worry.
- High temperatures and heatwaves have been linked to increased aggressive behavior and domestic violence.
- Air pollution has been associated with an increased risk of autism 6 Weisskopf, M. G., Kioumourtzoglou, M. A., & Roberts, A. L. (2015). Air Pollution and Autism Spectrum Disorders: Causal or Confounded?. Current environmental health reports, 2(4), 430–439. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40572-015-0073-9 , reduced cognitive abilities, and heightened attention, particularly in children.
Read More About Post-traumatic Stress Disorder (ptsd) Here
Factors Affecting Geographical Psychology and Mental Health
Several factors related 7 Kitchin, R. M., Blades, M., & Golledge, R. G. (1997). Relations Between Psychology and Geography. Environment and Behavior, 29(4), 554–573. https://doi.org/10.1177/001391659702900406 to geography affect mental health care, which include:
1. Selective Migration
The process of selective migration refers to the movement of individuals or groups to specific geographical locations based on their personal characteristics, preferences, or circumstances. This self-selection process can shape the composition of populations within certain areas and influence psychological patterns and well-being.
2. Ecological Influence
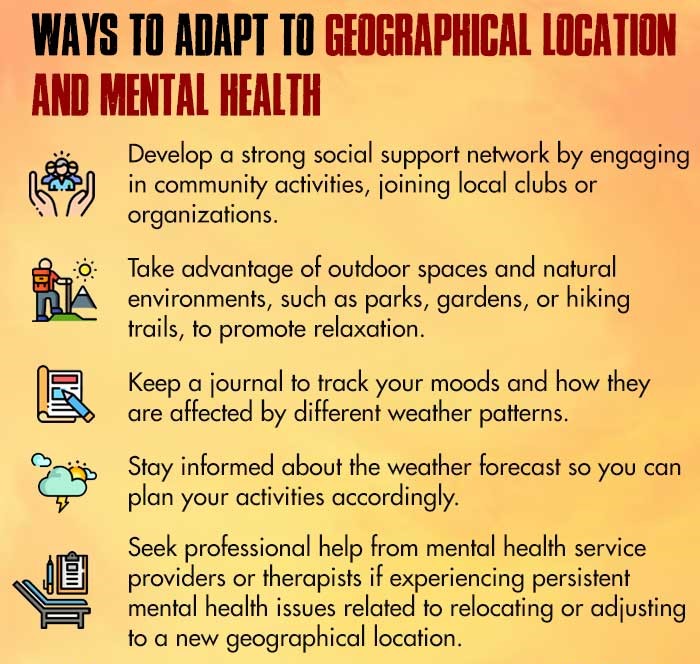
The ecological features of a particular geographic location, such as climate, natural resources, and physical terrain, can impact mental health outcomes. For example, living in areas with abundant green spaces and natural environments has been associated with positive mental health benefits.
3. Social Influence
The social context of a geographical location, including social norms, cultural values, and community dynamics, plays a crucial role in shaping mental health outcomes. Social support networks, community cohesion, and access to social resources can significantly impact psychological well-being.
4. Climate Condition
Extreme weather, limited sunlight exposure, or prolonged periods of snowfall can disrupt circadian rhythms and impact serotonin levels, resulting in various symptoms including low mood, fatigue, and alterations in appetite.
5. Homesickness
Being away from familiar surroundings and loved ones can contribute to feelings of homesickness, which can negatively impact an individual’s mood. This is especially relevant for individuals who have migrated or relocated to a new geographic location for various reasons, such as pursuing education, seeking better job opportunities, etc.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Does climate affect personality?
While climate can influence certain aspects of behavior and well-being, the direct impact of climate on personality traits is still a subject of ongoing research and debate within the field of psychology.
2. How does place related attachment relate to geographical psychology?
Place-related attachment is a central concept in geographical psychology as it explores how individuals form emotional connections to their geographical location, influencing their psychological experiences and behaviors within that specific place.
3. Can geographical psychology help in urban planning and design?
Geographical psychology can provide valuable insights for urban planning and design, enabling the creation of spaces that promote well-being, social cohesion, and a better quality of life for residents.