Impulse buying is the unplanned and spontaneous purchase of goods or services, typically driven by emotions rather than rational decision-making. It’s when a consumer buys something on the spot, without prior intention or planning.
Common Features of Impulse Buying:
- Emotion-driven: Often triggered by feelings like excitement, stress, boredom, or even sadness.
- Lack of planning: The purchase wasn’t on a shopping list or in the buyer’s original intention.
- Instant gratification: The buyer seeks immediate satisfaction or a mood boost.
- Little thought about consequences: There may be little consideration for the item’s usefulness, cost, or long-term value.
What Is Impulse Buying?
Impulse buying is a behavior in which a person makes a whimsical purchase without a financial plan or pre-shopping intention. It is characterized 1 Tran V. D. (2022). Consumer impulse buying behavior: the role of confidence as moderating effect. Heliyon, 8(6), e09672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09672 by the sudden urge to purchase something, and may sometimes have adverse consequences such as financial stress and debt.
Impulse Buying vs Compulsive Buying Disorder
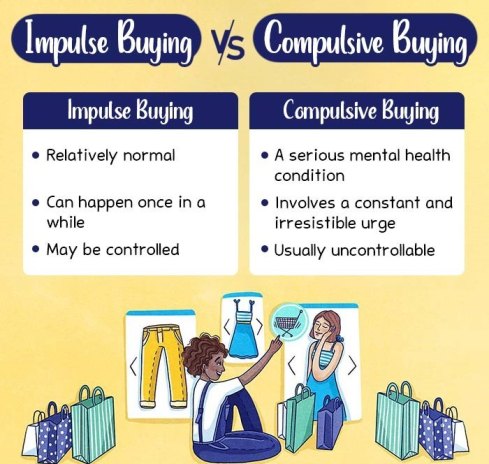
Impulse buying may sometimes be confused with compulsive buying disorder (CBD) 2 Müller, A., Mitchell, J. E., & de Zwaan, M. (2015). Compulsive buying. The American journal on addictions, 24(2), 132–137. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajad.12111 . Both terms, though related to buying 3 Granero, R., Fernández-Aranda, F., Mestre-Bach, G., Steward, T., Baño, M., Del Pino-Gutiérrez, A., Moragas, L., Mallorquí-Bagué, N., Aymamí, N., Gómez-Peña, M., Tárrega, S., Menchón, J. M., & Jiménez-Murcia, S. (2016). Compulsive Buying Behavior: Clinical Comparison with Other Behavioral Addictions. Frontiers in psychology, 7, 914. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2016.00914 , are quite different.
Impulse buying is largely unplanned and happens as the result of a sudden trigger. It’s quite common for most people to make an impulsive purchase once in a while. Compulsive buying disorder, on the other hand, is a condition where a person has the constant irresistible urge to buy something.
CBD, in contrast to impulse buying, is more of an addiction. People with CBD often experience excessive and frequent urges to shop uncontrollably. Their buying behavior may lead to extreme distress or social impairment.
Psychology Of Impulse Buying
Impulse buying activates the reward system 4 Gao, P., Zeng, Y., & Cheng, Y. (2022). The Formation Mechanism of Impulse Buying in Short Video Scenario: Perspectives From Presence and Customer Inspiration. Frontiers in psychology, 13, 870635. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.870635 in the brain, releasing bouts of dopamine when we buy something we desire, in other words, providing us with instant gratification. However, it can later lead to regret or self-reproach when we realize that the expenditure was probably unnecessary and avoidable.
Habitually engaging in impulse buying can make us dependent on the dopamine boost it provides and lead to negative consequences in the long term.
Psychological Triggers:
- Sales and discounts
- Attractive displays or packaging
- Limited-time offers
- Social media promotions
- Emotional state (e.g., shopping to relieve stress)
Signs Of Impulse Buying
The common signs of impulse buying behavior include:
- Spending money without prior planning
- Visiting stores that trigger impulse purchases
- Feelings of quick satisfaction following unplanned purchases
- Frequently returning unplanned buying due to regret
- Experiencing money problems frequently
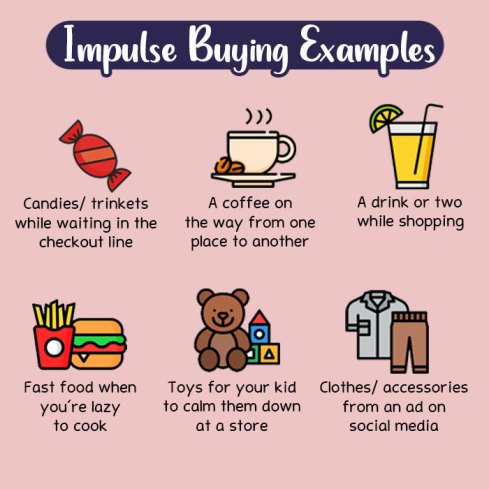
Impulse Buying Examples
- Grabbing a candy bar at the checkout counter
- Buying clothes just because they’re on sale
- Purchasing a gadget after seeing an ad, even if it’s not needed
What Motivates Impulse Buying?
The common 5 Rodrigues, R. I., Lopes, P., & Varela, M. (2021). Factors Affecting Impulse Buying Behavior of Consumers. Frontiers in psychology, 12, 697080. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.697080 causes of impulse buying include:
1. Individual Factors
Impulse buyers may be characterized by one or more of the following
- Low self-esteem
- High levels of anxiety
- Depressive symptoms
- High body-image dissatisfaction 6 Cai, Z., Gui, Y., Wang, D., Yang, H., Mao, P., & Wang, Z. (2021). Body Image Dissatisfaction and Impulse Buying: A Moderated Mediation Model. Frontiers in psychology, 12, 653559. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.653559
- Negative moods (like sadness)
- Inability to cope with stress
- Strong tendencies to develop obsessive-compulsive disorders
Read More About Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Here
2. Environmental/External Factors
The trigger for impulse buying is not solely internal. Several environmental factors can also play a significant role in impulse spending, such as
- Advertising 7 Wang, P., & Chapa, S. (2022). Online impulse buying behavior and marketing optimization guided by entrepreneurial psychology under COVID-19. Frontiers in psychology, 13, 939786. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.939786 —especially advertisements on social media,
- Influencer culture 8 Lina, Y., Hou, D., & Ali, S. (2022). Impact of online convenience on generation Z online impulsive buying behavior: The moderating role of social media celebrity. Frontiers in psychology, 13, 951249. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.951249 promoting certain brands and products,
- The glamorization of “retail therapy”
- The store environment
- Price reductions and discounts
- Product packaging and placement, etc.
Effects of Impulse Buying
The disadvantages of impulse buying involve
- Financial difficulties and stress (like debt)
- Disruptions in normal decision-making processes
- Emotional distress or disappointment in impulsively purchased products
- Developing irrational tendencies that favor instant self-gratification
- Accumulation of unnecessary items in living spaces
- Risks of developing mental disorders like hoarding disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, etc
Read More About Hoarding Disorder Here
How To Stop Impulse Buying
Understanding the psychology behind impulse buying can help individuals develop more mindful shopping habits and better financial self-control.
Consider the following ways to stop impulse buying:
- Make a monthly budget and stick to it.
- Make a fun money fund and permit yourself to make small splurges.
- Take a limited amount of cash when you go shopping.
- Rethink and wait for a few days before purchasing an item.
- Shop with a plan in mind. For instance, when you are shopping for clothes, look for versatile wardrobe staples that last longer and serve as long-term investments.
- Uninstall online shopping apps on your phone to prevent impulse buying on social media. Refrain from subscribing to email/message notifications for sales.
- Understand what triggers your impulse buying decisions. Refrain from shopping when you are sad or stressed.
- Lean into accountability when shopping. Consider bringing a friend when shopping, so that he/she can stall your buying sprees.
- Avoid using credit cards and online payment methods to prevent instant spending.
- Chalk out a long-term financial goal. Side-step Buying on impulse and overspending and embrace retirement funds, emergency savings, etc.
- Consider seeking help from a counselor if you’re finding it hard to stop impulse buying.
Takeaway
We all experience impulse buying at some point in our lives. However, chronic impulse buying plunges us into financial and social difficulties. Therefore, timely awareness and control over such purchasing tendencies are essential to avoid harmful consequences.
At A Glance
- Impulse buying is the sudden and immediate purchase of a product without any pre-shopping intention.
- Such behaviors are triggered by negative emotions related to sadness and stress.
- Impulsive shopping has its roots in the patient’s personality and hoarding tendencies, consumer culture, love for shopping, etc.
- Such a tendency can result in financial difficulties, stress, and poverty.
- The mental health effects of impulse buying include depression, anxiety, hoarding disorder, etc.
- Chronic impulse buying can be easily addressed with therapy and counseling.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is impulse buying?
Impulse buying is the unplanned and spontaneous purchase of goods or services, typically driven by emotions rather than rational decision-making. It’s when a consumer buys something on the spot, without prior intention or planning.
How to stop impulse shopping?
To stop impulse shopping, try pausing 24–48 hours before buying, stick to a list and budget, and track your spending to stay mindful. Avoid temptation by unsubscribing from promo emails, deleting shopping apps, and not shopping when stressed. Using cash instead of cards can also help limit unnecessary purchases.
What are the effects of impulse buying?
Impulse buying can lead to financial stress, overspending, and accumulating debt. It may cause regret, clutter, and emotional consequences like guilt or anxiety. Over time, it can affect savings goals and create unhealthy spending habits.