A concussion is a brain injury caused by forceful head or body impact, yielding physical symptoms and potential neurological disruption. It underscores the link between brain health and emotional well-being, impacting short and long-term mental health.
What Is Concussion?
A concussion is a type of traumatic brain injury (TBI) that occurs when there is a sudden and forceful impact or blow to the head, causing the brain to move rapidly within the skull. This movement can result in temporary disruption of normal brain function 1 Ferry, B., & DeCastro, A. (2020). Concussion. PubMed; StatPearls Publishing. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537017/ .
When a concussion occurs, the brain undergoes a rapid acceleration and deceleration within the skull. This movement can stretch and damage brain cells, disrupt neurotransmitter function, and lead to temporary changes in brain activity.
The impact can cause a cascade of chemical changes and inflammation in the brain, affecting the normal functioning of neurons. This, in turn, can severely impact our brain structure and functioning as well as mental health.

Symptoms Of Concussion

Research 2 Ferry, B., & DeCastro, A. (2021). Concussion. PubMed; StatPearls Publishing. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30725702/ attributes the common symptoms of concussion to:
- Headache or pressure in the head
- Confusion, feeling dazed, or trouble concentrating
- Dizziness and problems with balance
- Nausea, vomiting, or sensitivity to light and noise
- Fatigue, drowsiness, or difficulty sleeping
- Irritability, mood changes, or increased fussiness
- Blurred vision, difficulty focusing, or slurred speech
- Changes in coordination, unsteady walking, or clumsiness
- Forgetfulness, memory problems, or changes in attention span
- Altered eating habits
- Mood swings, irritability, or lack of interest in activities
Causes Of Concussion
The common 3 Romeu-Mejia, R., Giza, C. C., & Goldman, J. T. (2019). Concussion Pathophysiology and Injury Biomechanics. Current reviews in musculoskeletal medicine, 12(2), 105–116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12178-019-09536-8 causes of concussion include:
- Sports: Contact sports like football, soccer, hockey, and boxing raise concussion risk through collisions, tackles, and falls.
- Falls: Trips, slips, and falls, especially from heights, can lead to head impacts and potential concussions.
- Vehicles: Car accidents, causing abrupt stops or jolts, can forcefully move the brain within the skull, resulting in a concussion.
- Altercations: Head-targeted violence like punches and kicks can lead to concussions.
- Bicycles and Motorcycles: Collisions, particularly without proper gear, can cause head impacts and potential concussions.
- Recreational Activities: Activities like skiing, skateboarding, and rollerblading come with fall and collision risks that may lead to concussions.
- Workplace: Industries such as construction can increase head injury risk due to falls, falling objects, or machinery accidents.
Concussion And Mental Health
The effects of concussions on mental health can be severe, due to the disruption they cause in normal brain activity. Following a concussion, individuals often experience a range of cognitive and emotional changes 4 Giza, C., Greco, T., & Prins, M. L. (2018). Concussion: pathophysiology and clinical translation. Handbook of clinical neurology, 158, 51–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-63954-7.00006-9 that can affect their overall mental well-being.
Cognitive functions such as memory, concentration, attention, and decision-making can be impaired, leading to difficulties in managing daily tasks and responsibilities. This cognitive “fogginess” or “brain fog” can contribute to frustration, decreased self-esteem, and increased stress as individuals struggle to perform as they did prior to the injury.
Concussion and mental health are related as, emotionally, concussions can lead to mood swings, irritability, anxiety, and even symptoms of depression. These emotional changes can stem from the physiological effects of the injury, as well as the challenges individuals face in adapting to the limitations imposed by their symptoms.
Read More About Anxiety Here
The frustration of not being able to perform at one’s usual level, coupled with the uncertainty of when symptoms will resolve, can contribute to heightened emotional distress. Additionally, disruptions in sleep patterns that often accompany concussions can further exacerbate emotional instability and hinder the brain’s healing process.

How Concussions Cause Mental Illness In Children
Concussion and mental health in children are related due to the vulnerability of their developing brains. Disruption of neural connections during a concussion can lead to cognitive and emotional changes 5 Ledoux, A. A., Webster, R. J., Clarke, A. E., Fell, D. B., Knight, B. D., Gardner, W., Cloutier, P., Gray, C., Tuna, M., & Zemek, R. (2022). Risk of Mental Health Problems in Children and Youths Following Concussion. JAMA network open, 5(3), e221235. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.1235 , potentially contributing to mental health issues.
Symptoms like mood swings, concentration difficulties, and irritability, often associated with certain mental health disorders, might appear in children after concussions.
Prolonged and untreated concussions cause mental illness symptoms like anxiety or depression. Coping with school, social life, and recovery stress could further strain a child’s mental well-being, underscoring the need for attentive care and support.
Read More About Depression Here
Diagnosis Of Concussion
The diagnosis of a concussion involves a multifaceted process 6 Tator C. H. (2013). Concussions and their consequences: current diagnosis, management and prevention. CMAJ : Canadian Medical Association journal = journal de l’Association medicale canadienne, 185(11), 975–979. https://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.120039 that encompasses medical history review, physical examination, cognitive and balance assessments, symptom checklists, and, when necessary, neuro-imaging. Clinicians gather information about the injury, symptoms, and medical background to diagnose concussions accurately.
Neuro-cognitive tests 7 Quatman-Yates, C., Hugentobler, J., Ammon, R., Mwase, N., Kurowski, B., & Myer, G. D. (2014). The utility of the balance error scoring system for mild brain injury assessments in children and adolescents. The Physician and sportsmedicine, 42(3), 32–38. https://doi.org/10.3810/psm.2014.09.2073 like ImPACT and balance evaluations like BESS gauge cognitive and coordination functions. A symptom checklist aids in assessing common concussion-related issues. Imaging might be employed to exclude severe head injuries.
Neuro-psychological testing and baseline assessments for those at risk further enhance diagnostic accuracy, ensuring proper care and management for concussion recovery.
Treatment For Concussion
The treatment for concussions involves a variety of therapies 8 Jones, J. C., & O’Brien, M. J. (2021). Medical Therapies for Concussion. Clinics in sports medicine, 40(1), 123–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csm.2020.08.005 , assisted by pharmacotherapy:
- Pain Management: Leverage over-the-counter pain relievers, like acetaminophen, to alleviate headaches. Initiate caution with NSAIDs like ibuprofen due to potential bleeding risk.
- Physical Therapy: Explore tailored exercises recommended by professionals to address balance and coordination difficulties.
- Vision And Vestibular Therapy: Employ specialized techniques to tackle visual and balance issues associated with the concussion.
- Medication: In certain cases, targeted medication might be prescribed to manage severe headaches or sleep disruptions.
- Concussion Supportive Therapy: Utilize therapies (like concussion supportive therapy) designed to provide comprehensive support during the recovery process.
Read More About Therapy Here
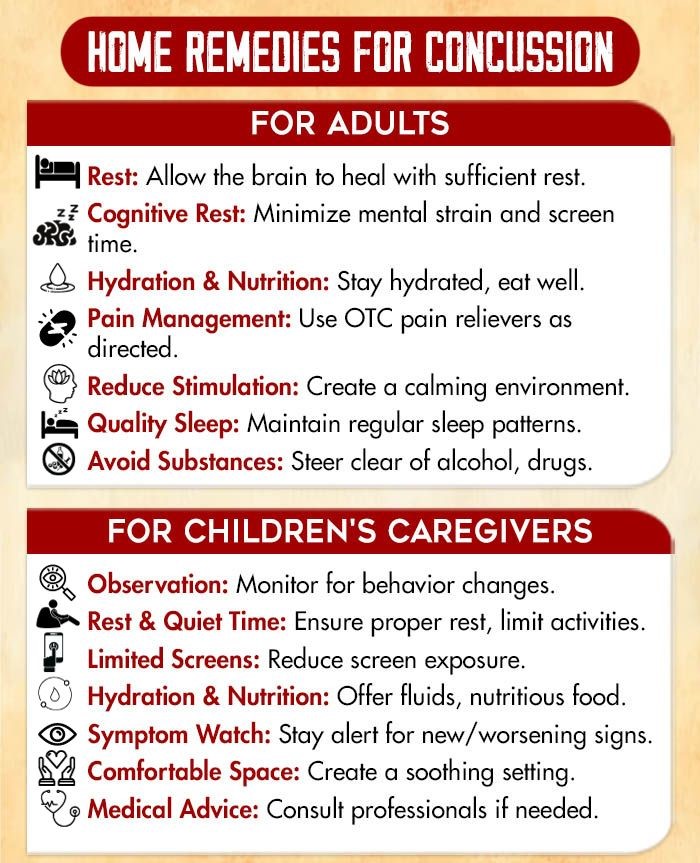
Self-help Strategies For Coping With Concussion
Consider the following self-help strategies 9 Heslot, C., Azouvi, P., Perdrieau, V., Granger, A., Lefèvre-Dognin, C., & Cogné, M. (2022). A Systematic Review of Treatments of Post-Concussion Symptoms. Journal of clinical medicine, 11(20), 6224. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11206224 to cope in concussion recovery:
- Rest: Allow the brain to heal; prioritize sleep.
- Hydration: Drink water to support brain function.
- Nutrient-rich Diet: Eat antioxidants, omega-3s, vitamins.
- Limit Screens: Reduce cognitive strain from screens.
- Manage Environment: Control light and noise sensitivity.
- Gradual Activity: Slowly reintroduce physical and mental tasks.
- Relaxation: Practice meditation, yoga, deep breathing.
- Herbal Supplements: Try ginkgo biloba, turmeric for inflammation.
- Acupuncture: Explore for potential symptom relief.
Read More About Meditation Here
Takeaway
The symptoms of concussions remain a critical area of concern in the realm of sports, healthcare, and overall well-being. The intricate interplay between the brain’s delicate structure and the potential for long-lasting cognitive and neurological effects underscores the importance of continued research, proper diagnosis, and effective management strategies.
As awareness grows, it is imperative that stakeholders across sports, medicine, and society collaborate to implement stringent protocols that prioritize player safety, ensuring that the impact of concussions is minimized and that individuals at all levels can engage in physical activities with reduced risk to their neurological health.
At A Glance
- A concussion is a traumatic brain injury resulting from a forceful head impact that temporarily disrupts brain function.
- Rapid brain movement within the skull during a concussion can damage cells, disrupt neurotransmitters, and alter brain activity.
- Symptoms of concussion include headaches, confusion, dizziness, nausea, fatigue, and mood changes.
- Common causes of concussion are sports, falls, accidents, altercations, and recreational activities.
- Concussions cause mental illness like depression, anxiety, etc.
- The effects of concussions on mental health are particularly severe in children.
- Treatment for concussion includes concussion supportive therapy, medication, and supportive care.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. If My Child Has A Concussion, Will S/he Be Ok?
If my child has a concussion, they will likely recover with proper care and medical guidance like concussion supportive therapy.
2. How Can I Tell If My Child Has Sustained A Concussion?
You can tell if your child has sustained a concussion by observing symptoms such as headache, confusion, dizziness, nausea, and mood changes.
3. Does My Child Need To Give Up Sports If S/he Has Suffered A Concussion?
Whether your child needs to give up sports after suffering a concussion depends on their situation, as medical evaluation will determine the appropriate course of action.















