Table of Contents
What Is Dysgraphia?
Dysgraphia is a neurological disorder that affects a person’s ability to write coherently and efficiently. The term comes from the Greek words “dys” (meaning difficulty) and “graphia” (meaning writing). Individuals with dysgraphia may struggle with handwriting, spelling, and organizing written thoughts.
This condition can affect both children and adults and often leads to challenges in academic, social, and professional settings. Over time, these difficulties may also impact self-esteem and mental health, making early recognition and supportive interventions crucial. There are five different types of dysgraphia.
Dysgraphia Symptoms
Here are the common symptoms of dysgraphia:
- Illegible or inconsistent handwriting
- Trouble spacing letters and words properly
- Unusual grip or posture while writing
- Writing slowly and with visible effort
- Difficulty organizing thoughts on paper
- Problems with spelling, even common words
- Omitting or mixing up words and letters
- Trouble with grammar and sentence structure
- Avoidance of writing tasks
- Fatigue or frustration when writing
- Poor performance in written assignments despite strong verbal skills
- Low self-esteem related to writing ability
What Are The 5 Types of Dysgraphia?
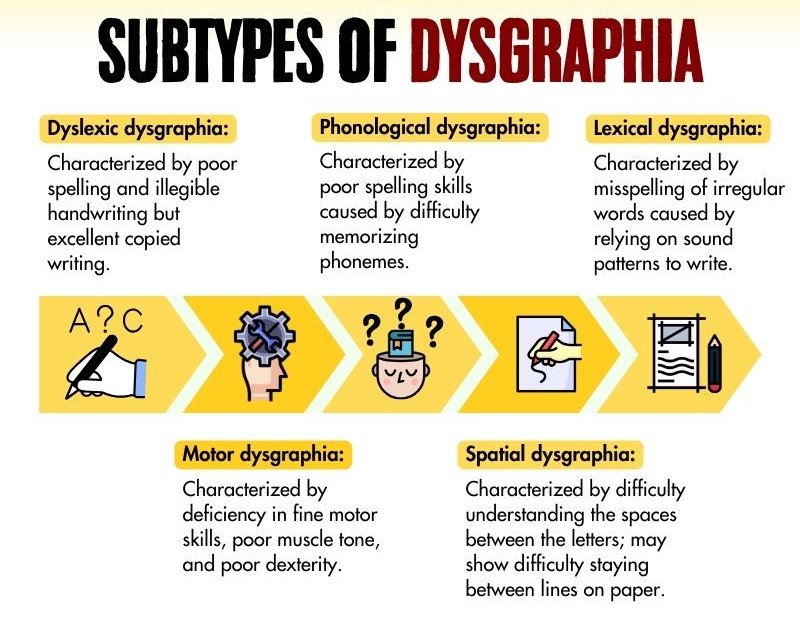
There are 5 types of dysgraphia:
Current research 1 Rocha Cabrero, F., & De Jesus, O. (2023). Dysgraphia. PubMed; StatPearls Publishing. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559301/ categorizes the different types of dysgraphia into 5 categories. The symptoms of these types of dysgraphia appear as early as 2-4 years of age and heavily impact childhood learning and development. The intensity of the symptoms differ depending on the nature of the following types of conditions:
1. Dyslexia Dysgraphia
Dyslexic dysgraphia is characterized by illegible handwriting 2 Chung, P. J., Patel, D. R., & Nizami, I. (2020). Disorder of written expression and dysgraphia: definition, diagnosis, and management. Translational pediatrics, 9(Suppl 1), S46–S54. https://doi.org/10.21037/tp.2019.11.01 , spelling errors, and excellent copied work. Individuals with this condition struggle to produce legible writing that is not copied from another source, despite having normal fine motor skills.
In this type of dyslexia, copied writings or drawings are typically clearer. It’s important to note that having dyslexic dysgraphia doesn’t necessarily mean the person has dyslexia. For instance, a student with dyslexic dysgraphia might write a messy, barely readable essay by hand but produce a neatly copied version when given a typed text to transcribe.
Read More About Dyslexia Here
2. Motor Dysgraphia
Motor dysgraphia is characterized by deficient fine motor skills, poor dexterity, poor muscle tone, and overall motor clumsiness. Individuals with this type may have acceptable letter formation in short samples of writing, but their overall handwriting and drawings are illegible, even when copied. However, their spelling abilities remain intact.
For example, a person with motor dysgraphia might struggle to write legibly due to poor muscle control, making their handwriting messy and difficult to read.
3. Spatial Dysgraphia
Spatial dysgraphia stems from issues with spatial awareness, causing difficulty in understanding the spaces between letters and staying within the lines on paper. Handwriting and drawings are consistently illegible, but spelling skills are not affected.
For instance, a student with spatial dysgraphia might struggle to keep their letters aligned on the page, resulting in uneven and poorly spaced writing.
4. Phonological Dysgraphia
Phonological dysgraphia is characterized by difficulties in writing and spelling unfamiliar words, non-words, and phonetically irregular words. Individuals with this type may struggle to memorize phonemes and blend them in the correct sequence to write a targeted word.
Someone with phonological dysgraphia, for example, might have trouble spelling words like “knight” or “yacht” because they have difficulty remembering the sounds and letter combinations.
5. Lexical Dysgraphia
Lexical dysgraphia occurs when a person can spell but relies heavily on sound-to-letter patterns when writing, leading to misspellings of irregular words. This type is rarer in children and more common in languages like English and French, which are less phonetic.
A person with lexical dysgraphia might consistently misspell words like “enough” or “Wednesday” because they rely on phonetic rules rather than memorizing the correct spellings.
Recovery From Dysgraphia
Recovery from the different types of dysgraphia is a continuous journey 3 Biotteau, M., Danna, J., Baudou, É., Puyjarinet, F., Velay, J. L., Albaret, J. M., & Chaix, Y. (2019). Developmental coordination disorder and dysgraphia: signs and symptoms, diagnosis, and rehabilitation. Neuropsychiatric disease and treatment, 15, 1873–1885. https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S120514 that involves ongoing support, practice, and adaptation to individual needs. While dysgraphia may not be “cured” in the traditional sense, individuals can make significant progress in managing their writing difficulties and improving overall functional abilities.
Management of dysgraphia treatment involves a collaborative approach involving educators, therapists, and caregivers to provide ongoing support and reinforcement of skills. Regular monitoring of progress, adjustments to interventions based on individual needs, and fostering a positive learning environment are essential components for successful management. With patience, perseverance, and the right support system in place, individuals with dysgraphia can thrive academically, socially, and personally, achieving their full potential despite the challenges posed by the condition.
Takeaway
Experts contend that it is crucial to address the mental health impacts of different types of dysgraphia. By acknowledging these effects, we can develop tailored dysgraphia treatment that promotes self-esteem and resilience. This holistic approach ensures individuals with dysgraphia can navigate challenges and thrive in inclusive environments.
At A Glance
- Dysgraphia is a neurological condition affecting writing abilities.
- There are 5 types of dyslexia: Dyslexic, Motor, Spatial, Phonological, and Lexical dysgraphia.
- Dyslexic dysgraphia results in illegible handwriting but clear copied work.
- Motor dysgraphia stems from poor fine motor skills.
- Spatial dysgraphia causes issues with letter spacing and alignment.
- Phonological dysgraphia affects spelling unfamiliar words.
- Lexical dysgraphia leads to misspelling irregular words due to reliance on sound-to-letter patterns.
- Dysgraphia treatment requires tailored dysgraphia therapy and a positive learning environment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the main types of dysgraphia?
The main types of dysgraphia are Dyslexic Dysgraphia, Motor Dysgraphia, Spatial Dysgraphia, Phonological Dysgraphia, and Lexical (Surface) Dysgraphia.
What are the symptoms of dysgraphia?
Common symptoms of dysgraphia include illegible handwriting, poor spelling, inconsistent spacing, difficulty organizing thoughts on paper, slow writing speed, unusual pencil grip, and avoidance of writing tasks.
What is treatment for Dysgraphia ?
Dysgraphia treatment typically includes occupational therapy, educational interventions, specialized writing programs, assistive technology (like speech-to-text tools), and classroom accommodations such as extra time or alternative assignments.