Human trafficking and mental health lead to significant challenges for survivors and long-lasting consequences, including trauma, anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). It is crucial to provide targeted mental health support and interventions as the solutions to human trafficking that cater to survivors’ unique needs, fostering their healing, and recovery, and empowering them to rebuild their lives and attain a renewed sense of well-being.
What is Human Trafficking?
Human trafficking is a criminal activity 1 Toney-Butler, T. J., Ladd, M., & Mittel, O. (2023). Human Trafficking. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430910/ that involves the recruitment, transportation, transfer, harboring, or receipt of individuals through the use of force, fraud, or coercion for the purpose of exploitation, encompassing various forms such as forced labor, sexual exploitation, child exploitation, forced marriage, and organ trafficking.
It is deeply tragic that children make up a significant portion of human trafficking victims, with an alarming average age of just 12 2 Baird, K., & Connolly, J. (2023). Recruitment and Entrapment Pathways of Minors into Sex Trafficking in Canada and the United States: A Systematic Review. Trauma, violence & abuse, 24(1), 189–202. https://doi.org/10.1177/15248380211025241 years old for involvement in sex trafficking.
Furthermore, human traffickers exploit individuals of all ages, backgrounds, and nationalities for their own financial gain, with an estimated 27.6 million 3 Ladd, M., & Jones, E. B. (2022). Texas Human Trafficking. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK573077/#:~:text=Human%20trafficking%20is%20a%20%24150,thousand%20people%20in%20the%20world. victims worldwide at any given time.
The impact on survivors’ mental health and well-being 4 Cary, M., Oram, S., Howard, L. M., Trevillion, K., & Byford, S. (2016). Human trafficking and severe mental illness: an economic analysis of survivors’ use of psychiatric services. BMC health services research, 16, 284. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-016-1541-0 is profound, as human trafficking subjects them to extreme and prolonged trauma, resulting in a range of psychological, emotional, and social challenges. Survivors may experience symptoms like suicidal ideation, dissociation, distrust, and difficulties in forming relationships and reintegrating into society.

Women, Mental Health and Human Trafficking
Globally, women and girls 5 Deshpande, N. A., & Nour, N. M. (2013). Sex trafficking of women and girls. Reviews in obstetrics & gynecology, 6(1), e22–e27. comprise 65 percent of all trafficking victims, with over 90 percent of identified female victims trafficked for sexual exploitation. Research indicates that women subjected to sex trafficking experience heightened fear, isolation, and greater trauma and mental health requirements compared to victims of other crimes.
Moreover, trafficked women and girls face increased rates of physical and sexual violence, memory impairment, sexually transmitted diseases, and traumatic brain injuries.
It is crucial to prioritize protection and safety 6 Ray, Nilanjana. (2017). Human Trafficking: A Form of Violence against Women. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/320685184_Human_Trafficking_A_Form_of_Violence_against_Women/citation/download of trafficked women. This entails providing secure shelters, safe houses, and tailored healthcare services to address their specific needs. Additionally, comprehensive legal and social support systems are essential in assisting survivors in seeking justice and rebuilding their lives.
Mental Illness and Human Trafficking
Here are some ways in which mental health 7 Altun, S., Abas, M., Zimmerman, C., Howard, L. M., & Oram, S. (2017). Mental health and human trafficking: responding to survivors’ needs. BJPsych international, 14(1), 21–23. https://doi.org/10.1192/s205647400000163x can be affected by human trafficking:
- Survivors of human trafficking may experience Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) characterized by intrusive memories, and flashbacks related to the experiences.
- Survivors of trafficking often experience symptoms of depression, such as feelings of sadness, hopelessness, guilt, and worthlessness which are common among survivors.
- To cope with the trauma and distressing memories, some survivors may turn to substance abuse as a means of self-medication.
- Human trafficking can cause symptoms of anxiety, such as excessive worry due to traumatic experiences ongoing fear, and threat endured by survivors.
- The extreme trauma and distress experienced by survivors of trafficking can increase the risk of suicidal ideation and self-harming behaviors.
Read More About PTSD Here
Types of Human Trafficking
There are different forms 8 Muraszkiewicz, Julia & Constantinou, Angelo. (2015). Review of the media framing of human trafficking. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Types-of-human-trafficking-mentioned-in-UK-press_fig1_327107447 of human trafficking, such as:
1. Sex Trafficking
This involves the recruitment, transportation, or harboring of individuals for the purpose of sexual exploitation 9 Marcinkowski, B., Caggiula, A., Tran, B. N., Tran, Q. K., & Pourmand, A. (2022). Sex trafficking screening and intervention in the emergency department: A scoping review. Journal of the American College of Emergency Physicians open, 3(1), e12638. https://doi.org/10.1002/emp2.12638 . Victims are forced into prostitution, pornography, or other forms of sexual services.
2. Labor Trafficking
This form of trafficking involves the exploitation of individuals through forced labor 10 Kiss, L., & Zimmerman, C. (2019). Human trafficking and labor exploitation: Toward identifying, implementing, and evaluating effective responses. PLoS medicine, 16(1), e1002740. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1002740 in various industries, such as agriculture, construction, domestic work, manufacturing, and mining. Victims may work excessively long hours, receive little or no pay, and endure hazardous conditions.
3. Child Trafficking
Children are particularly vulnerable to trafficking. They are forced into labor 11 Wood L. C. N. (2020). Child modern slavery, trafficking and health: a practical review of factors contributing to children’s vulnerability and the potential impacts of severe exploitation on health. BMJ paediatrics open, 4(1), e000327. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjpo-2018-000327 , used for begging, or subjected to sexual exploitation.
4. Organ Trafficking
Organ trafficking refers to the illicit trade 12 Gonzalez, J., Garijo, I., & Sanchez, A. (2020). Organ Trafficking and Migration: A Bibliometric Analysis of an Untold Story. International journal of environmental research and public health, 17(9), 3204. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17093204 of organs, where individuals are coerced, deceived, or exploited into providing their organs for transplantation. These victims may come from impoverished backgrounds, marginalized communities, or regions with limited access to healthcare, making them more susceptible to manipulation and exploitation.
How Does Human Trafficking Take Place?
Possible causes and risk factors 13 Fedina, L., Williamson, C., & Perdue, T. (2019). Risk Factors for Domestic Child Sex Trafficking in the United States. Journal of interpersonal violence, 34(13), 2653–2673. https://doi.org/10.1177/0886260516662306 associated with human trafficking include:
- Individuals living in poverty may be more susceptible to promises of better employment and financial stability, making them vulnerable to trafficking.
- Gender inequality, discrimination 14 Dahal, P., Joshi, S. K., & Swahnberg, K. (2022). A qualitative study on gender inequality and gender-based violence in Nepal. BMC public health, 22(1), 2005. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-022-14389-x , and limited access to education and employment opportunities can increase the risk of trafficking.
- The demand for cheap labor in various industries, such as agriculture, construction, and manufacturing, creates opportunities for labor trafficking.
- Many individuals lack education and awareness and fear of seeking help or reporting their situation enhances the prevalence of human trafficking.
- Migrants may become easy targets 15 Lumley-Sapanski, A., Schwarz, K., Cano, A. V., Babiker, M. A., Crowther, M., Death, E., Ditcham, K., Eltayeb, A. R., Jones, M. E. K., & Mir, M. P. (2023). Exacerbating Pre-Existing Vulnerabilities: an Analysis of the Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Human Trafficking in Sudan. Human Rights Review, 1–21. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12142-023-00683-7 for traffickers who exploit their lack of legal protection, language barriers, and limited support networks.
- The age group of children and adolescents are highly vulnerable to trafficking due to their inherent dependency and susceptibility to manipulation through false assurances.
Mental Health Impact Of Human Trafficking
The long-lasting 16 Dahal, P., Joshi, S. K., & Swahnberg, K. (2015). ‘We are looked down upon and rejected socially’: a qualitative study on the experiences of trafficking survivors in Nepal. Global health action, 8, 29267. https://doi.org/10.3402/gha.v8.29267 psychological effects of human trafficking include:
- Disruption in survivors’ ability to form secure attachments and trust others.
- A negative self-image and low self-esteem as the survivors often internalize the shame, guilt, and blame associated with the trafficking experience.
- Difficulty in seeking support, being subjected to victim-blaming, or fear disclosing their experiences due to societal judgment and lack of understanding.
- The impairment of cognitive functioning, including attention, concentration, and memory due to the chronic stress and trauma experienced during trafficking.
- A profound identity crisis, as survivors struggle with the loss of autonomy, self-worth, and a disrupted sense of self.
Read More About Depression Here
Therapeutic Care For Human Trafficking Victims
Here are some therapeutic approaches 17 Salami, T., Gordon, M., Coverdale, J., & Nguyen, P. T. (2018). What Therapies are Favored in the Treatment of the Psychological Sequelae of Trauma in Human Trafficking Victims?. Journal of psychiatric practice, 24(2), 87–96. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRA.0000000000000288 for the victims of human trafficking:
1. Trauma-Informed Therapy
Trauma-focused therapies, such as 18 Purkey, E., Patel, R., & Phillips, S. P. (2018). Trauma-informed care: Better care for everyone. Canadian family physician Medecin de famille canadien, 64(3), 170–172. Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR), Trauma-Focused Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (TF-CBT), and Narrative Exposure Therapy (NET), can help survivors process their traumatic experiences, manage distressing symptoms, and regain a sense of control.
2. Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT techniques can be useful in helping survivors 19 Chand, S. P., Kuckel, D. P., & Huecker, M. R. (2022). Cognitive Behavior Therapy. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470241/ identify and challenge negative thought patterns, manage symptoms of anxiety and depression, and develop healthy coping skills. It can also assist in addressing any distorted beliefs or self-blame that may have resulted from the trafficking experience.
Read More About CBT Here
3. Family Therapy
Human trafficking affects not only the survivor but also the entire family system 20 Varghese, M., Kirpekar, V., & Loganathan, S. (2020). Family Interventions: Basic Principles and Techniques. Indian journal of psychiatry, 62(Suppl 2), S192–S200. https://doi.org/10.4103/psychiatry.IndianJPsychiatry_770_19 . Family therapy can address the collective trauma experienced by the family and help each member understand their role in the recovery process.
It allows for the exploration of shared trauma symptoms, triggers, and coping strategies, as well as the development of effective ways to support each other’s healing.
4. Art Therapy and Expressive Therapies
Creative and expressive therapies, such as art therapy 21 Shukla, A., Choudhari, S. G., Gaidhane, A. M., & Quazi Syed, Z. (2022). Role of Art Therapy in the Promotion of Mental Health: A Critical Review. Cureus, 14(8), e28026. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.28026 , music therapy, dance/movement therapy, or drama therapy, can help survivors process their emotions, express themselves non-verbally, and promote healing and self-discovery.
5. Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
Mindfulness practices such as deep breathing exercises and yoga 22 Rao, R. M., Nagendra, H. R., Raghuram, N., Vinay, C., Chandrashekara, S., Gopinath, K. S., & Srinath, B. S. (2008). Influence of yoga on mood states, distress, quality of life and immune outcomes in early stage breast cancer patients undergoing surgery. International journal of yoga, 1(1), 11–20. https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-6131.36789 can assist in managing the psychological effects of human trafficking on victims that is, anxiety, reducing stress, and cultivating a sense of calm and self-awareness.
Read More About Mindfulness Here
6. Psychosocial Intervention
Psychosocial interventions assist survivors 23 Garg, A., Panda, P., Malay, S., & Rose, J. A. (2021). A Human Trafficking Educational Program and Point-of-Care Reference Tool for Pediatric Residents. MedEdPORTAL : the journal of teaching and learning resources, 17, 11179. https://doi.org/10.15766/mep_2374-8265.11179 in developing or re-establishing essential life skills and social connections. This can include training in areas such as communication, problem-solving, social interaction, financial management, and self-care, empowering survivors to regain independence and reintegrate into society.
Takeaway
Mental health and human trafficking have severe implications, often resulting in conditions such as anxiety disorders, depression, PTSD, and substance abuse among survivors. Addressing the mental health needs of trafficking victims is crucial for their recovery and well-being, requiring comprehensive and trauma-informed interventions that prioritize their safety, support, and empowerment.
At A Glance
- Human trafficking refers to the illegal and exploitative trade of human beings for various purposes, such as labor, sexual exploitation, etc.
- Trafficked women and girls face increased rates of physical and sexual violence and sexually transmitted diseases.
- To cope with mental illness and human trafficking, some survivors may turn to substance abuse as a means of self-medication.
- The types of human trafficking include sex trafficking, labor trafficking, child trafficking, and organ trafficking.
- Gender inequality, poverty, etc. play a significant role in human trafficking.
- Survivors of human trafficking may experience Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
- Therapeutic approaches such as cognitive behavioral therapy, and family therapy can be applied to dealing with the mental effects of human trafficking.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Who are the most vulnerable to human trafficking?
Children, women, migrants, refugees, and other individuals with limited education and economic opportunities are among the most vulnerable groups susceptible to human trafficking.
2. How can human trafficking survivors receive help and support?
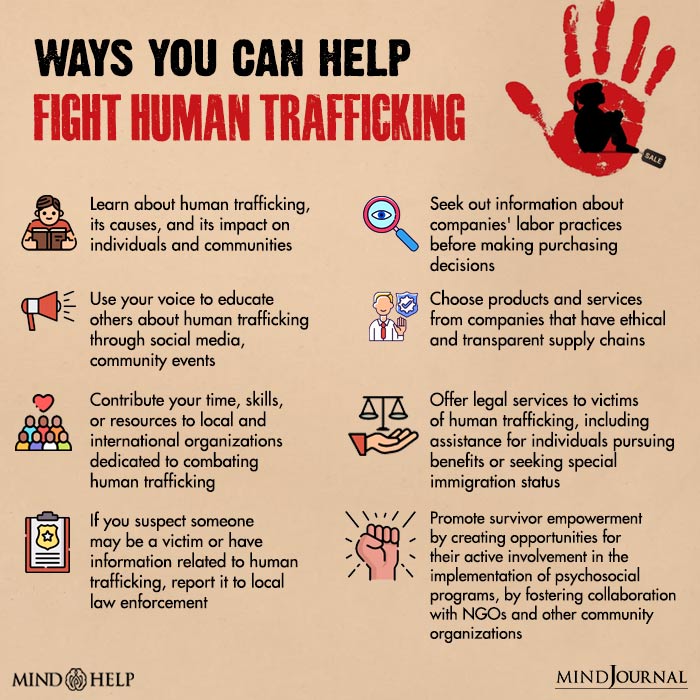
Human trafficking survivors can receive help and support through various channels, including specialized NGOs and organizations that provide shelter, healthcare, counseling, legal aid, and vocational training. Additionally, collaboration with law enforcement agencies and community support networks is crucial in providing comprehensive assistance.
3. How to stop human trafficking?
Human trafficking can be prevented by implementing comprehensive measures that include rigorous law enforcement, promoting socioeconomic development, raising public awareness, providing victim support, and strengthening international cooperation.
4. How to recognize the effects of human trafficking on victims?
The key steps for recognizing the mental effects of human trafficking include conducting structured interviews, utilizing trauma-specific assessments, and developing individualized treatment plans based on assessment findings and diagnoses to address the survivor’s specific mental health needs.