Mental health disability is popularly referred to as the disability and difficulties posed by mental illness. If untreated, the impact of mental health disability hamper a person’s personal and professional lives.
What Is Mental Health Disability?
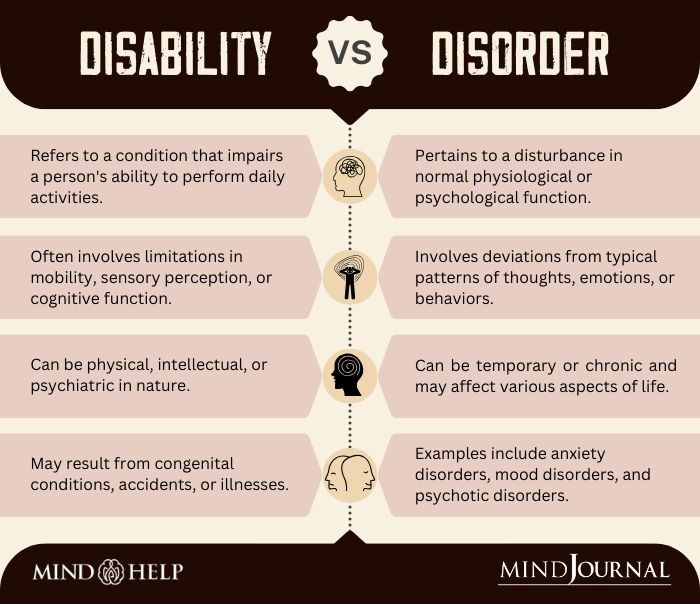
Mental health disability involves various mental heath disorders 1 Chaudhury, P. K., Deka, K., & Chetia, D. (2006). Disability associated with mental disorders. Indian journal of psychiatry, 48(2), 95–101. https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5545.31597 that severely interfere with one’s perceptions of himself or herself, thought processes, emotions, and behaviors—resulting into restrictions in performing routine tasks and duties. These mental health disabilities may be due to mental disorders (like depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, etc.) and can manifest as hindered IQ development and difficulty in successfully achieving developmental milestones.
These mental health disabilities include disturbances of cognitive processes such as remembering, focusing, processing information, etc. These emotional challenges include mood swings, extreme sadness, anxiety, and irrational fear. These may be seen as observable changes in behavior, such as social withdrawal, irregular sleeping pattern disrupted daily routine. However, such disabilities could make it difficult for a person to maintain well-being or relationships, fulfill daily activities, or hold on to jobs, etc.
Mental Health Disability In Films

Films often serve as a powerful medium to address the stigma surrounding mental health disabilities. Popular/acclaimed films over the years like “Silver Linings Playbook” (2012), “A Beautiful Mind” (2001), “Donnie Darko” (2001), “Psycho” (1960), “Joker” (2019), and “One Flew Over The Cuckoo’s Nest” (1975) have been lauded for fostering conversations about mental health disability and raising awareness and understanding.

Signs Of Mental Health Disability
Common 2 Ringland, K. E., Nicholas, J., Kornfield, R., Lattie, E. G., Mohr, D. C., & Reddy, M. (2019). Understanding Mental Ill-health as Psychosocial Disability: Implications for Assistive Technology. ASSETS. Annual ACM Conference on Assistive Technologies, 2019, 156–170. https://doi.org/10.1145/3308561.3353785 signs of mental health disability include:
- Memory loss
- Lack of concentration and irritability
- Poor decision-making skills
- Anger issues and open display of aggression
- Unexplained bouts of depression and anxiety
- Social withdrawal
- Sleep issues like Insomnia
- Issues in completing intellectual tasks like academic or school work
- Difficulty in handling normal daily tasks like bathing, cooking, or dressing, etc.
- Inability to maintain social relationships
Read More About Insomnia Here
Types Of Mental Health Disability
The common 3 Hogan A. J. (2019). Social and medical models of disability and mental health: evolution and renewal. CMAJ : Canadian Medical Association journal = journal de l’Association medicale canadienne, 191(1), E16–E18. https://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.181008 types of mental health disability include:
- Intellectual Disability: The affected individuals are characterized by restrictions of intellectual functioning and daily living skills.
- Learning Disability: The affected individuals have difficulties in obtaining and applying academic skills, leading to problems in reading, writing, math, etc.
- Developmental Disabilities: These encompass different physical problems as well as neurological, psychosocial, and emotional issues.
- Cognitive Disabilities: Sufferers experience cognitive impairment in various domains such as memory, attention, problem-solving, and language skills.
What Causes Mental Health Disability?
The common causes 4 Czeisler, M. É., Board, A., Thierry, J. M., Czeisler, C. A., Rajaratnam, S. M. W., Howard, M. E., & Clarke, K. E. N. (2021). Mental Health and Substance Use Among Adults with Disabilities During the COVID-19 Pandemic – United States, February-March 2021. MMWR. Morbidity and mortality weekly report, 70(34), 1142–1149. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7034a3 behind the development of mental health disabilities include:
- Genetic vulnerabilities and the inheritability of mental health disorders
- Brain chemistry imbalances, like an aberration of neurotransmitters
- Structural brain abnormalities
- Traumatic life events
- Prenatal exposure to substances, stress, toxins, etc.
- An adverse happening or a lack of care during childhood
- Pressures of societal expectations, discrimination, or other cultural factors
Read More About Genetics Here
Impact Of Mental Health Disability On Daily Life
The impact of mental health disability on an individual’s day-to-day activities varies, but mostly these create difficulties for cognitive, emotional, and daily functioning 5 Defar, S., Abraham, Y., Reta, Y., Deribe, B., Jisso, M., Yeheyis, T., Kebede, K. M., Beyene, B., & Ayalew, M. (2023). Health related quality of life among people with mental illness: The role of socio-clinical characteristics and level of functional disability. Frontiers in public health, 11, 1134032. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2023.1134032 (such as remembering appointments and completing routine tasks). This inability to forge and sustain social relationships leads to loneliness and emotional withdrawal. Moreover, it spills over into the professional dimensions wherein an individual suffers loss of livelihood or fails to pursue higher education.
These shortcomings associated with the signs of mental health disability often trigger issues of self-esteem, depression, anxiety, addiction, stress, etc. Eventually, this compounded effect drastically brings down physical health and the general quality of life, thereby reducing one’s ability to enjoy pleasant activities and decreasing the total satisfaction felt with life. Furthermore, widespread prejudice and bias towards people with mental health disabilities aggravate emotional distress, further isolating impaired individuals and discouraging them from seeking help.
Mental Health Disability In Children And Adolescents
The impact of mental health disabilities in children and adolescents involves considerably impaired growth and development, 6 García-Carrión, R., Villarejo-Carballido, B., & Villardón-Gallego, L. (2019). Children and Adolescents Mental Health: A Systematic Review of Interaction-Based Interventions in Schools and Communities. Frontiers in psychology, 10, 918. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00918 leading to academic challenges, social, and emotional difficulties as well as possible interruption in developmental stages. Bullying and other forms of prejudiced and discriminatory behavior exert greater vulnerability on young persons already faced with mental health difficulties. If left untreated, these mental health disabilities cause long-term damage to one’s future in education or occupation.
Mental Health Disability In Adults
The impact of mental health disability in adults has long-term implications for their general well-being and various areas of daily lives 7 Pouls, K. P., Koks-Leensen, M. C., Mastebroek, M., Leusink, G. L., & Assendelft, W. J. (2022). Adults with intellectual disabilities and mental health disorders in primary care: a scoping review. The British journal of general practice : the journal of the Royal College of General Practitioners, 72(716), e168–e178. https://doi.org/10.3399/BJGP.2021.0164 . Difficulties with work, relationships, and societal rejection due to stigma can trigger stress and emotional tension in affected individuals. These circumstances can further push disabled people into social isolation and loneliness, thereby reducing the quality of life and relationships.
Mental Health Disability In The Elderly
As the elderly get older, signs of mental health disability may impose significant obstacles to their psychological well-being 8 de Mendonça Lima, C. A., & Ivbijaro, G. (2013). Mental health and wellbeing of older people: opportunities and challenges. Mental health in family medicine, 10(3), 125–127. . Forgetting things easily, feeling sad, or being nervous can be some of the signs that elderly people are experiencing mental health problems related to old age. Such situations make them feel more segregated and isolated from others, especially if they have physical health conditions. Moreover, emotional stress could result in loss of self-control, identity, autonomy, etc.
How To Diagnose People With Mental Health Disability
Mental health disability can be effectively diagnosed through clinical interviews with mental health professionals 9 Pouls, K. P., Koks-Leensen, M. C., Mastebroek, M., Leusink, G. L., & Assendelft, W. J. (2022). Adults with intellectual disabilities and mental health disorders in primary care: a scoping review. The British journal of general practice : the journal of the Royal College of General Practitioners, 72(716), e168–e178. https://doi.org/10.3399/BJGP.2021.0164 that covers personal history, symptoms, and how one is able to conduct his or her activities on a day-to-day basis. Some standardized questionnaires such as the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) and Generalized Anxiety Disorder 7 (GAD-7) can measure the severity of symptoms, while others such as neuro-psychological testing [through the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS)] reflect cognitive performance.
Holistic assessments involve observational evaluations, psychological tests [such as Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI)], and referring to the criteria outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5). Structural and biochemical factors may be spotted by neuroimaging techniques like Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) or blood tests. This approach offers a complete diagnosis that enables targeted mental health disability treatment planning for sufferers.
Mental Health Disability Treatment
Mental health disability treatment 10 Antunes, A., Frasquilho, D., Azeredo-Lopes, S., Neto, D., Silva, M., Cardoso, G., & Caldas-de-Almeida, J. M. (2018). Disability and common mental disorders: Results from the World Mental Health Survey Initiative Portugal. European psychiatry : the journal of the Association of European Psychiatrists, 49, 56–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpsy.2017.12.004 often includes a combination of:
1. Pharmacotherapy:
Medications like antidepressants and antipsychotics are often prescribed to manage neurotransmitter imbalances and other neurobiological shortcomings in people with mental health disabilities.
2. Psychotherapy:
A large number of psychotherapies like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), interpersonal therapy (IPT), and family therapy is often availed to help the affected manage their behavioral and cognitive impairment.
Read More About Psychotherapy Here
3. Group Therapy:
Group therapies are often assigned to sufferers so that they can talk about and bond through shared experiences in a supportive environment.
Read More About Group Therapy Here
Self-strategies To Overcome Mental Health Disability
Consider the following self-strategies 11 Ormel, J., VonKorff, M., Ustun, T. B., Pini, S., Korten, A., & Oldehinkel, T. (1994). Common mental disorders and disability across cultures. Results from the WHO Collaborative Study on Psychological Problems in General Health Care. JAMA, 272(22), 1741–1748. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.272.22.1741 to overcome mental health disability:
- Understand your physical and mental shortcomings and formulate a plan to overcome mental health disabilities.
- Incorporate mindfulness and stress relief activities like meditation, yoga, etc. to reduce stress.
- Adopt a positive attitude and use daily affirmations to boost well-being.
- Follow a healthy lifestyle with a proper diet and adequate sleep.
- Develop a support system and communicate openly with them about your difficulties.
- Set realistic goals and plan achievable targets.
- Prioritize self-care practices like hobbies, support group activities, etc.
- Seek professional help and stick to a mental health disability treatment plan.
Read More About Meditation Here
Helping Someone To Overcome Mental Health Disability
Helping a person overcome mental health disability takes sympathy and support 12 Surjus, L. T., & Campos, R. T. (2014). Interface between intellectual disability and mental health: hermeneutic review. Revista de saude publica, 48(3), 532–540. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0034-8910.2014048004711 . In these cases, to listen without judging, to encourage, and to understand their challenges is crucial. Other ways to help the affected person is to guide him/her to seek professional assistance (like therapy and counseling) and link them with available mental health resources.
Takeaway
Approaching and addressing mental health disabilities necessitates sensitivity and empathy. Promoting awareness and understanding, while challenging stigma, contributes to a more inclusive and compassionate community. Recognizing the uniqueness of each person’s journey and offering genuine support can significantly impact their path to mental well-being.
At A Glance
- Mental health disability involves various mental disorders that severely interfere with one’s perceptions of himself or herself, thought processes, emotions, and behaviors.
- Common signs of mental health disability include memory loss, irritability, distorted cognition.
- The impact of mental health disability hamper a person’s personal and professional lives.
- Mental health disability can be of several types: intellectual, learning, developmental, and cognitive disabilities.
- Measures to overcome mental health disability include psychotherapies, medication, and social support.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can you have both mental and physical disabilities?
Yes, individuals can experience both mental and physical disabilities simultaneously.
2. Is mental disability permanent?
Mental health disabilities vary in permanence; some may be lifelong, while others can be managed or improved with appropriate mental health disability treatment.
3. Can a person with mental health disability get married?
Absolutely, individuals with mental health disabilities can and do get married, as mental health does not inherently preclude the ability to have fulfilling relationships.
4. Can mental retardation be detected at birth?
Mental retardation, now referred to as intellectual disability, can sometimes be detected at birth through assessments of developmental milestones and genetic testing, but a definitive diagnosis often occurs over time as the child grows.















