Binge drinking is characterized by the consumption of excessive amounts of alcohol or other beverages, such as cocktails, spirits, or mixed drinks, in a short timeframe. This form of heavy drinking poses significant health hazards, including impaired cognitive abilities, heightened vulnerability to accidents and injuries, and long-lasting detrimental effects on both physical and mental well-being.
What is Binge Drinking?
Binge drinking refers to episodes of 1 White, A. M., Tapert, S., & Shukla, S. D. (2018). Binge Drinking. Alcohol research : current reviews, 39(1), 1–3. excessive consumption of alcohol or other drinks, typically resulting in a state of intoxication. It is characterized by consuming four or more drinks for women and five or more drinks for men within a two-hour timeframe, surpassing the limits of moderate drinking.
The effects of binge drinking occur in social settings like parties or bars and carry an elevated risk of negative outcomes, including impaired judgment, accidents, injuries, and long-term health issues.
Beyond the immediate risks, binge drinking and mental health can have lasting effects 2 Mason-Jones, A. J., & Cabieses, B. (2015). Alcohol, binge drinking and associated mental health problems in young urban Chileans. PloS one, 10(4), e0121116. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0121116 on cognitive functioning. Moreover, it can contribute to the development or exacerbation of conditions like depression, anxiety, and cognitive decline. Recognizing nature, its potential consequences, and binge drinking treatment is crucial in promoting overall well-being and making informed choices for recovery.
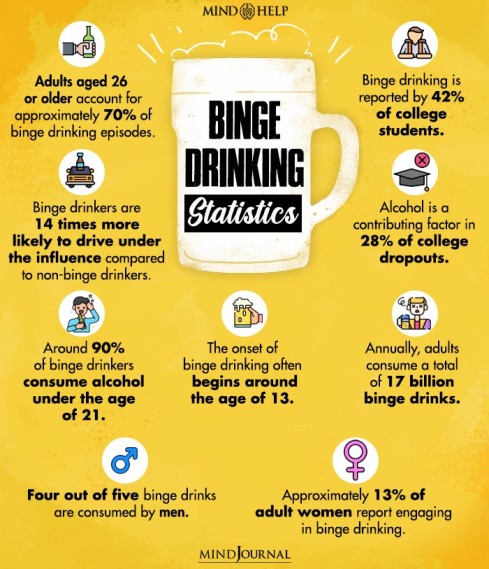
Signs of Binge Drinking
Here are some common 3 Flegel, K., MacDonald, N., & Hébert, P. C. (2011). Binge drinking: all too prevalent and hazardous. CMAJ : Canadian Medical Association journal = journal de l’Association medicale canadienne, 183(4), 411. https://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.110029 signs of binge drinking:
- Consistently consuming more alcohol than initially planned or intended.
- Struggling to stop or cut off once start drinking, experiencing a lack of control over the amount consumed.
- Mixing different types of alcohol (e.g., beer, wine, spirits) in larger amounts during a single drinking session.
- Becoming defensive when someone questions about drinking habits.
- Regularly experiencing periods of memory loss or gaps in memory after drinking episodes.
- Noticing that specific mental health issues, such as anxiety or depression, intensify or worsen after consuming alcohol.
- Engaging in risky or reckless actions after drinking, such as unsafe driving, engaging in sexual activities, or gambling.
Read More About Depression Here

Effects of Binge Drinking on Mental Health
The association between binge drinking and mental health can have significant impacts 4 Stephens, D. N., & Duka, T. (2008). Review. Cognitive and emotional consequences of binge drinking: role of amygdala and prefrontal cortex. Philosophical transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological sciences, 363(1507), 3169–3179. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2008.0097 , including:
- Impaired judgment and increased impulsive behavior can lead to emotional or aggressive outbursts, verbal abuse, or even physical abuse.
- Bipolar disorder by episodes of mania with associated signs of heightened energy, racing thoughts, and depressive episodes with associated signs of low self-esteem or lack of motivation.
- Psychotic episodes or signs of delusions leading an inability to distinguish reality from fiction.
- Alcohol use disorder by excessive consumption of alcohol through binge drinking for a longer time.
- Memory impairments and gaps in memory due to the effects of alcohol on the brain
- Symptoms of depressive disorder such as feelings of sadness and hopelessness due to disruption in neurotransmitter levels.
- Inability in emotional regulation, mood swings, and irritability can also intensify together the level of anxiety within an individual.
Read More About Self-esteem Here
Why do People Engage in Binge Drinking?
People engage in binge drinking for a variety of reasons 5 Krieger, H., Young, C. M., Anthenien, A. M., & Neighbors, C. (2018). The Epidemiology of Binge Drinking Among College-Age Individuals in the United States. Alcohol research : current reviews, 39(1), 23–30. , including:
- Stress related to the job or everyday stressors like personal relationships or financial difficulties.
- To cope with feelings of boredom or loneliness, seeking excitement or social interaction.
- Limited knowledge or awareness about the risks and consequences of excessive drinking.
- Coping with social anxiety or feeling more at ease in social situations.
- The influence of friends or social groups that engage in binge drinking can drive toward a desire to fit in or conform to social expectations.
Read More About Loneliness Here
How to Diagnose Binge Drinking?
Diagnosing typically involves 6 Rolland, B., & Naassila, M. (2017). Binge Drinking: Current Diagnostic and Therapeutic Issues. CNS drugs, 31(3), 181–186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40263-017-0413-4 comprehensive techniques for binge drinking recovery, such as:
- Assessing medical history and physical examination related to binge drinking symptoms.
- Screening tools such as 7 Dwyer-Clonts, M., Frates, E., & Suzuki, J. (2016). Managing Problem Drinking: Screening Tools and Brief Interventions for Primary Care Physicians. American journal of lifestyle medicine, 11(6), 424–429. https://doi.org/10.1177/1559827616629929 the Alcohol use disorders identification test (AUDIT) or the CAGE substance abuse screening tool.
- The healthcare professional may take interviews to gather adequate information about the frequency and context of drinking episodes.
How to Stop Binge Drinking
To initiate the process of binge drinking recovery, it is important to recognize the issue 8 Hanewinkel, R., Tomczyk, S., Goecke, M., & Isensee, B. (2017). Preventing Binge Drinking in Adolescents. Deutsches Arzteblatt international, 114(16), 280–287. https://doi.org/10.3238/arztebl.2017.0280 , set specific goals to reduce the amount the drinking, develop healthy coping mechanisms, such as physical exercise or meditation, and seek support from mental health professionals or addiction recovery centers for additional guidance and accountability.
Read More About Meditation Here

Takeaway
Binge drinking can have significant negative impacts on physical health, mental well-being, and overall quality of life. It is important to be aware of the signs of binge drinking and to seek help if needed.
Addressing binge drinking behaviors and seeking support from healthcare professionals or addiction recovery centers can lead to improved health conditions, reduced risk of associated harms, and make better the overall well-being of an individual.
Read More About Addiction Here
At A Glance
- Binge drinking is characterized by the consumption of excessive amounts of alcohol or other beverages.
- Common signs of binge drinking include excessive consumption, inability to stop, memory loss, mental health problems, etc.
- Binge drinking causes mental health issues, such as depression, anxiety, and substance use disorder.
- People can engage in binge drinking due to their overwhelming stress, loneliness, or due to lack of awareness.
- Diagnosing binge drinking typically involves physical examinations, screening tools, and interviews with mental health professionals.
- It is important to recognize the issue, set specific goals to reduce the amount of drinking, and develop healthy coping mechanisms.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Why is binge drinking dangerous?
It can have long-term health consequences, including liver damage, cardiovascular problems, and mental health conditions such as depression and anxiety disorder.
2. Does binge drinking affect women differently than men?
Binge drinking can affect women differently than men due to various factors, including physiological differences and the way alcohol is processed in the body.
3. How is binge drinking different from moderate drinking?
Binge drinking involves consuming a large amount of alcohol in a short period, leading to intoxication, whereas moderate drinking refers to consuming alcohol in moderation within recommended limits, without reaching a state of significant impairment.















