Cognition involves complex processes that shape our perceptions, thoughts, and interactions, defining our experiences and influencing emotional well-being. Its exploration reveals how cognitive functioning impacts emotions and psychological resilience.
What Is Cognition?
Cognition, in the realm of psychology, refers to the mental processes and activities 1 Weizenbaum, E., Torous, J., & Fulford, D. (2020). Cognition in Context: Understanding the Everyday Predictors of Cognitive Performance in a New Era of Measurement. JMIR mHealth and uHealth, 8(7), e14328. https://doi.org/10.2196/14328 related to acquiring, processing, storing, and using information. It encompasses a wide range of mental functions, including perception, attention, memory, reasoning, problem-solving, decision-making, language comprehension, and more.
Essentially, cognition is the set of processes that enable individuals to perceive the world, make sense of it, and interact with it effectively. These processes involve complex interactions between sensory inputs, past experiences, and internal mental representations.
The field of cognitive psychology, which emerged in the mid-20th century, focuses on understanding the intricacies of these cognitive processes. It seeks to uncover how humans think, learn, remember, and solve problems.
Pioneered by influential figures such as Ulric Neisser, Jean Piaget, and Noam Chomsky, cognitive psychology brought about a paradigm shift from behaviorism to a focus on mental processes. This shift led to the development of various theories and models that delve into the workings of the human mind.
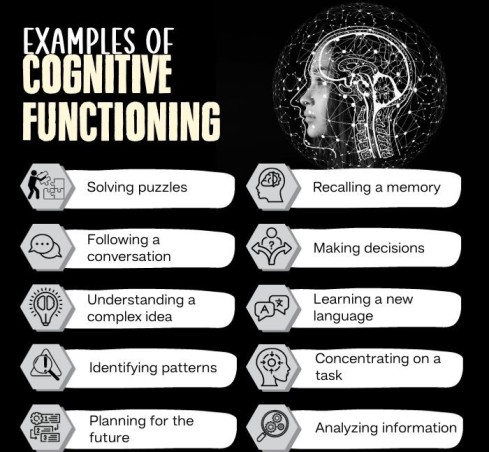
Types Of Cognitive Processes
Research 2 Jensen, M. P., Thorn, B. E., Carmody, J., Keefe, F. J., & Burns, J. W. (2018). The Role of Cognitive Content and Cognitive Processes in Chronic Pain: An Important Distinction?. The Clinical journal of pain, 34(5), 391–401. https://doi.org/10.1097/AJP.0000000000000559 shows there are 7 types of cognitive processes:
1. Perception:
Perception involves interpreting sensory input to comprehend our environment. Distorted perceptions in conditions like schizophrenia impact mental well-being. Combining therapy and medication is vital for managing these distortions and promoting a healthier mental state.
2. Attention:
Attention is the ability to focus on relevant stimuli while filtering out distractions. Techniques like mindfulness meditation improve attention control, aiding conditions like ADHD and contributing to overall mental well-being.
Read More About Attention Here
3. Memory:
Memory entails encoding, storing, and retrieving information. Memory biases, seen in depression, worsen negative moods. Therapies address these biases, helping individuals view past experiences more objectively and fostering balanced mental states.
Read More About Memory Here
4. Language and Communication:
Language processing enables effective communication. Conditions like aphasia and social anxiety hinder communication, affecting mental well-being. Targeted therapies help individuals overcome these barriers, enhancing interactions and promoting better mental health.
Read More About Communication Disorders Here
5. Reasoning and Problem-Solving:
Reasoning derives logical conclusions, and problem-solving finds solutions. Impaired skills, as in schizophrenia, disrupt decision-making. Cognitive remediation therapies restore these abilities, empowering individuals to make informed choices and regain control.
6. Emotion Regulation:
Emotion regulation manages emotional responses. Disorders often feature poor regulation. Emotion-focused therapies teach strategies to identify, understand, and regulate emotions, improving emotional well-being.
7. Decision-Making:
Decision-making assesses options for suitable choices. Impaired in conditions like addiction, interventions enhance decision-making, helping manage impulses and promote better mental health.
Read More About Decision-Making Here
Mental Health And Cognition
Everyday good cognition in mental health functioning offers several advantages 3 Clark, I. A., Hotchin, V., Monk, A., Pizzamiglio, G., Liefgreen, A., & Maguire, E. A. (2019). Identifying the cognitive processes underpinning hippocampal-dependent tasks. Journal of experimental psychology. General, 148(11), 1861–1881. https://doi.org/10.1037/xge0000582 , including:
- Effective problem-solving
- Good emotional regulation
- Greater adaptability and learning
- Enhanced coping mechanisms
- Positive self-perceptions
- Healthy relationships
- Reduced risks of mental health conditions like anxiety, depression, etc.
Cognition And Mental Health Disorders
Processes of cognition and mental health disorders are intricately related 4 Trivedi J. K. (2006). Cognitive deficits in psychiatric disorders: Current status. Indian journal of psychiatry, 48(1), 10–20. https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5545.31613 . Distorted perceptions intensify anxiety, impaired attention heightens frustration in depression, and memory distortions trigger trauma responses. Communication barriers due to language limitations amplify isolation, and compromised reasoning fuels helplessness in anxiety and mood disorders.
Poor emotion regulation deepens mood disorders, impaired decision-making drives impulsivity in substance use disorders, and limited cognitive flexibility strains adaptability.
Overthinking worsens anxiety, biased self-perception fuels conditions like eating disorders, and emotional suppression contributes to various mental strains. The symptoms of cognitive decline, if left untreated, can escalate into severe cognitive mental illness like:
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Schizophrenia
- Bipolar disorder
- Major depressive disorder
- Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
- Autism spectrum disorder (ASD)
- Huntington’s disease
- Traumatic brain injury (TBI)
Read More About Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) Here
Living With Cognitive Mental Illness
Living with cognitive mental illness entails grappling with daily challenges 5 Dhakal, A., & Bobrin, B. D. (2020). Cognitive Deficits. PubMed; StatPearls Publishing. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559052/ that intricately affect thoughts, perceptions, and abilities. The struggle encompasses difficulties in maintaining focus, coping with memory inconsistencies, and maneuvering through distorted cognitive patterns. This intricate journey reveals a disconnect between one’s inner experiences and the external world.
Beyond the immediate hurdles, cognitive illnesses have far-reaching consequences that disrupt daily activities, strain relationships, and diminish the overall quality of life. These consequences manifest in the form of memory impairment, compromised decision-making, distorted perceptions of reality, emotional turbulence, and hindered concentration.
Limitations Of Cognition In Mental Health
The limitations 6 Koliatsos V. E. (2016). A Clinical Approach to Cognitive Impairment. Focus (American Psychiatric Publishing), 14(4), 437–447. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.focus.20160026 of cognition in mental health include:
- Perceptual biases distort reality, worsening anxiety.
- Limited attention hampers engagement and worsens depression.
- Memory distortions trigger strong emotions, contributing to PTSD.
- Language limits hinder emotional expression and support seeking.
- Cognitive rigidity hinders problem-solving, fuels OCD behaviors.
- Emotional reasoning promotes avoidance, stunting growth.
- Overthinking in anxiety magnifies worries, clouds clarity.
- Decision paralysis in depression stalls progress due to rumination.
- Biased self-assessment affects self-image in eating disorders.
- Emotional suppression causes distress, leading to conditions like depression.
Read More About Depression Here
How To Improve Cognitive Skills
Consider the following measures 7 Piccirilli, M., Pigliautile, M., Arcelli, P., Baratta, I., & Ferretti, S. (2019). Improvement in cognitive performance and mood in healthy older adults: a multimodal approach. European journal of ageing, 16(3), 327–336. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10433-019-00503-3 on how to improve cognitive skills:
- Engage in mental exercises like puzzles and brain-training apps.
- Consume a balanced diet with antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Prioritize quality sleep for cognitive restoration.
- Exercise regularly to boost brain blood flow.
- Practice mindfulness and meditation to enhance focus and reduce stress.
- Stay socially active and commit to lifelong learning.
- Use memory aids, set goals, and organize tasks for effective cognitive management.
Read More About Mindfulness Here
Takeaway
Cognition stands as the bedrock of human mental functioning, encompassing an intricate web of processes that define how we perceive, understand, and interact with the world around us. From shaping our thoughts and memories to guiding our behaviors and decisions, cognition forms the core of our identity and experiences.
Its profound influence on every aspect of our lives underscores the significance of understanding and nurturing cognitive health. As we continue to explore the complexities of cognition, we pave the way for advancements in mental health care, education, and personal growth, ultimately unlocking the potential of the human mind.
At A Glance
- Cognition includes the mental processes and activities related to acquiring, processing, storing, and using information.
- It encompasses a range of functions such as perception, memory, attention, reasoning, language comprehension, and emotion regulation.
- The 7 types of cognitive processes include perception, attention, memory, language, reasoning, emotion regulation, and decision-making.
- Cognition and mental health are related, as cognitive distortions or impairments can intensify conditions like anxiety, depression, PTSD, etc.
- Severe cognitive mental illness like Alzheimer’s disease, schizophrenia, and bipolar disorder can impact a person’s quality of life.
- By grasping the intricacies of mental health and cognition, individuals and professionals can strive to enhance cognitive skills.
- Measures on how to improve cognitive skills include mental exercises, balanced nutrition, quality sleep, regular exercise, mindfulness, etc.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What does cognition have the most to do with?
Cognition has the most to do with mental processes such as thinking, understanding, and remembering.
2. How does cognition influence behavior?
Mental health and cognition are linked, because of which the former can influence behavior by shaping how individuals perceive, process, and respond to information from their environment.
3. How is cognition related to mental health disorders?
Cognition and mental health disorders are linked as these disorders often involve disruptions in cognitive functions, including thinking patterns, memory, and decision-making.