Healing from trauma is a profound journey of recovery, resilience, and renewal. It involves confronting and addressing the emotional scars left by distressing experiences, ultimately leading to a path of emotional well-being and strength.
What Is Trauma?
Trauma is a complex and deeply distressing psychological experience that can have profound and lasting effects on an individual’s mental and emotional well-being. It can result from a wide range of events or situations that overwhelm a person’s ability to cope, leaving them with a sense of helplessness, fear, and powerlessness.
Trauma can have both immediate and long-term consequences on a person’s mental health, often leading to a range of emotional and psychological challenges 1 Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. (2014). Understanding the impact of trauma. National Library of Medicine; Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (US). Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK207191/ . Research shows that over 70% of the global population 2 Benjet, C., Bromet, E., Karam, E. G., Kessler, R. C., McLaughlin, K. A., Ruscio, A. M., Shahly, V., Stein, D. J., Petukhova, M., Hill, E., Alonso, J., Atwoli, L., Bunting, B., Bruffaerts, R., Caldas-de-Almeida, J. M., de Girolamo, G., Florescu, S., Gureje, O., Huang, Y., Lepine, J. P., … Koenen, K. C. (2016). The epidemiology of traumatic event exposure worldwide: results from the World Mental Health Survey Consortium. Psychological medicine, 46(2), 327–343. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291715001981 experience trauma in some form throughout their lives.
Signs Of Emotional Trauma In Adults And Children
Recognizing 3 Gersons, B. P., & Olff, M. (2005). Coping with the aftermath of trauma. BMJ (Clinical research ed.), 330(7499), 1038–1039. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.330.7499.1038 the signs of emotional trauma in adults and children is essential for early intervention and healing. In adults, these signs may include flashbacks, anxiety, mood swings, and social withdrawal. Children may exhibit behavioral changes, regression, nightmares, or aggression.
Trauma And Mental Health
Trauma and mental health are intricately related, bringing forth a wide range of physiological and psychological symptoms 4 Kleber R. J. (2019). Trauma and Public Mental Health: A Focused Review. Frontiers in psychiatry, 10, 451. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00451 :
- Physical or sexual abuse can result in PTSD symptoms 5 Chivers-Wilson K. A. (2006). Sexual assault and posttraumatic stress disorder: a review of the biological, psychological and sociological factors and treatments. McGill journal of medicine : MJM : an international forum for the advancement of medical sciences by students, 9(2), 111–118. like flashbacks, nightmares, and anxiety, alongside difficulties in forming trust-based relationships.
- Natural disasters can trigger acute stress reactions, anxiety, and specific phobias.
- Combat and war leads to combat-related PTSD symptoms, difficulties in anger management, and a sense of alienation from civilian life.
- Accidents or injury cause acute stress symptoms, anxiety, depression, and physical pain.
- Loss and grief can result in major depression symptoms 6 Campbell, D. G., Felker, B. L., Liu, C. F., Yano, E. M., Kirchner, J. E., Chan, D., Rubenstein, L. V., & Chaney, E. F. (2007). Prevalence of depression-PTSD comorbidity: implications for clinical practice guidelines and primary care-based interventions. Journal of general internal medicine, 22(6), 711–718. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11606-006-0101-4 , and feelings of guilt or regret.
- Childhood trauma leads to attachment difficulties, self-esteem problems, and mood disorders.
- Community violence can lead to PTSD symptoms, hypervigilance, and a heightened sense of danger.
- Terrorism or mass trauma can cause acute stress reactions, heightened anxiety, social withdrawal, and a sense of vulnerability within affected communities.
Read More About Anxiety Here
Mental Illness Triggered By Trauma
Trauma can significantly increase the risk of developing various mental illnesses 7 Mann, S. K., & Marwaha, R. (2022). Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). PubMed; StatPearls Publishing. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559129/ , including:
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
- Depression
- Anxiety Disorders
- Dissociative Disorders
- Substance Use Disorders
- Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD)
- Eating Disorders
- Self-Harm and Suicidal Behavior
- Personality Disorders
Read More About Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) Here
Addressing Childhood Trauma And Mental Health Issues
Addressing childhood trauma and mental health issues 8 Roche, A. I., Kroska, E. B., Miller, M. L., Kroska, S. K., & O’Hara, M. W. (2019). Childhood trauma and problem behavior: Examining the mediating roles of experiential avoidance and mindfulness processes. Journal of American college health : J of ACH, 67(1), 17–26. https://doi.org/10.1080/07448481.2018.1455689 is paramount for long-term well-being. Early intervention, through therapy, support, and a nurturing environment, can help individuals process their traumatic experiences and develop coping strategies. This, in turn, makes us aware of how trauma affects mental health, fosters psychological resilience, and eases signs of emotional trauma in adults in later years.
Read More About Therapy Here
Tips On How To Heal From Trauma
Consider 9 Koutra, K., Burns, C., Sinko, L., Kita, S., Bilgin, H., & Arnault, D. S. (2022). Trauma Recovery Rubric: A Mixed-Method Analysis of Trauma Recovery Pathways in Four Countries. International journal of environmental research and public health, 19(16), 10310. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191610310 the following measures on how to heal from trauma:
- Seek Professional Help: Reach out to a therapist or counselor experienced in trauma treatment.
- Establish A Support System: Surround yourself with understanding and supportive friends and family.
- Practice Self-Care: Prioritize sleep, nutrition, and exercise for physical and emotional well-being.
- Mindfulness And Meditation: Incorporate relaxation techniques to manage stress and anxiety.
- Express Emotions: Share your feelings through writing, art, or talking to a trusted person.
- EMDR Therapy: Consider Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing therapy for trauma processing.
- Grounding Techniques: Learn grounding exercises to stay connected to the present moment.
- Limit Triggers: Minimize exposure to reminders of the trauma when possible.
- Gradual Exposure: Work with a therapist on controlled exposure to reduce fear and anxiety.
- Set Realistic Goals: Break down recovery into achievable steps to regain a sense of control and progress.
Read More About Meditation Here
How To Help Your Loved One Heal From Trauma
If you appear to notice the tale-tell 10 Rehabilitation after traumatic injury. (2022). In PubMed. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK579697/ signs of emotional trauma in adults and children alike, you can help them. Consider the following measures to help your loved one to heal from trauma:
- Listen actively and non-judgmentally.
- Encourage them to seek professional help.
- Be patient and understanding of their pace.
- Create a safe and supportive environment.
- Learn about trauma and its effects.
- Offer consistent emotional support.
- Avoid pushing them to talk about it if they’re not ready.
- Respect their coping mechanisms and boundaries.
- Encourage self-care and healthy routines.
- Be there for them, but don’t try to “fix” everything.
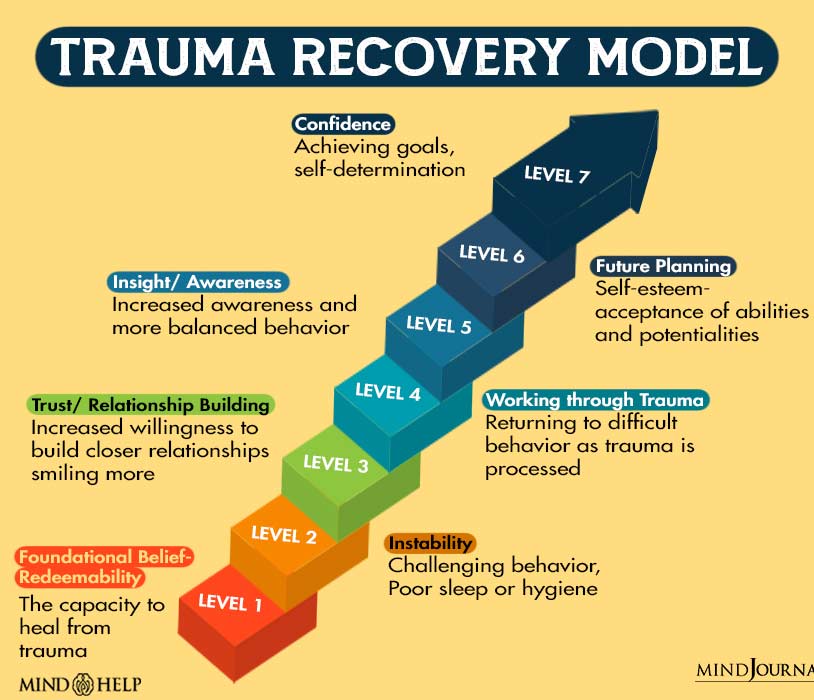
Signs You Are Healing From Trauma
Healing from trauma, both physically and mentally, is a gradual journey. It’s normal to have doubts about your progress. But by accurately recognizing 11 Center for Substance Abuse Treatment (US. (2014). Trauma Awareness. Nih.gov; Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (US). Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK207203/ how trauma affects mental health and decoding the signs you are healing from trauma, you can tailor your interventions and recovery plans effectively.
- Increased sense of safety and stability.
- Improved emotional regulation.
- Reduced intensity and frequency of flashbacks or nightmares.
- Greater ability to trust and connect with others.
- Enhanced self-esteem and self-worth.
- Improved sleep patterns and overall well-being.
- Decreased hypervigilance or anxiety.
- More healthy adaptive or coping strategies.
- A growing sense of empowerment and resilience.
- Increased engagement in daily life and future-oriented goals.
Read More About Self-Esteem Here

Takeaway
Trauma, if untreated, can result in a wide bevy of cognitive and behavioral disorders. Acknowledging its indicators and how trauma affects mental health can pave the way to providing appropriate support, such as therapy. Additionally, a safe, understanding environment can be instrumental in helping individuals of all ages recover from emotional trauma and build resilience.
At A Glance
- Trauma is a distressing experience with lasting effects on mental health.
- Signs of emotional trauma in adults and children include behavioral changes, anxiety, and mood swings.
- Trauma can lead to various mental health issues like PTSD, depression, and anxiety disorders.
- Addressing childhood trauma and mental health issues is crucial for long-term well-being.
- Tips on how to heal from trauma include seeking professional help, building a support system, and practicing self-care.
- Signs of healing from trauma include improved emotional regulation and increased sense of safety.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What Is Trauma Bonding?
Trauma bonding refers to the strong emotional connection that can form between a person and their abuser, often as a result of cycles of abuse and intermittent reinforcement.
2. What Is Trauma Therapy?
Trauma therapy is a specialized form of therapy aimed at helping individuals cope with and heal from the psychological and emotional effects of trauma.
3. What Is Generational Trauma?
Generational trauma, also known as intergenerational trauma, is the concept that trauma experienced by one generation can be passed down to subsequent generations, affecting their mental and emotional well-being.











