Table of Contents
Narcissism refers to an exaggerated sense of self-worth that distorts how a person sees themselves and limits their ability to empathize with others.
While occasional self-centered behavior is normal for most of us, consistently disregarding others’ needs and exhibiting an inflated sense of self-importance may point towards narcissistic personality disorder (NPD).
What Is Narcissism?
Narcissism is characterized by an exaggerated sense of self-importance, self-absorption, and an excessive focus on one’s own image.
It often comes with a constant need for admiration and attention, a lack of empathy, a tendency to disregard others’ feelings, and patterns of toxic, unhealthy relationships.
A narcissistic individual seeks gratification from egotistic admiration of his/her own idealized traits and self-image. A 2018 study 1 Hyatt, C. S., Sleep, C. E., Lamkin, J., Maples-Keller, J. L., Sedikides, C., Campbell, W. K., & Miller, J. D. (2018). Narcissism and self-esteem: A nomological network analysis. PloS one, 13(8), e0201088. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0201088 states “Narcissism is a personality construct typically characterized by grandiosity, vanity, entitlement, and exploitativeness.”
Narcissism is a fundamental personality trait. However, sometimes, an individual with narcissism traits may suffer from its chronic and clinical counterpart: Narcissistic personality disorder (NPD). It is a mental condition characterized by an elevated sense of self-fixation, entitlement, and grandiosity 2 Jonason, P.K., & Middleton, J.P. (2015). Dark Triad: The “Dark Side” of Human Personality. International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences. 10.1016/B978-0-08-097086-8.25051-4. .
However, despite being self-absorbed, narcissists tend to be highly insecure. They have low self-esteem because they constantly worry about how they are seen and perceived by others.
“Narcissistic patients are desperately attempting to manage their vulnerability,” explains a 2016 study 3 Gabbard, G. O., & Crisp-Han, H. (2016). The many faces of narcissism. World psychiatry : official journal of the World Psychiatric Association (WPA), 15(2), 115–116. https://doi.org/10.1002/wps.20323 . This can adversely affect how the individual thinks, behaves, reacts, and relates to his/her loved ones and others.
A person with NPD may tend to manipulate and exploit others and take their loved ones for granted. Narcissists tend to consider themselves superior and behave mostly in a “self-centered” manner. They may also possess exploitative traits used predominantly for achieving goals.
A recent study 4 Ellis, Lee & Farrington, David & Hoskin, Anthony. (2019). Handbook of Crime Correlates, 2nd Edition. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/333842967 elaborates that “genuine concern for the feelings and needs of others is almost completely absent. Instead, narcissistic individuals seem to view other persons as little more than objects for manipulation.”
History Of Narcissism
The term “narcissism” is derived from the name of Narcissus, a young hunter and god in Greek mythology, who falls in love with his own reflection and beauty in a pool of water.
The legend goes that he gazes at his reflection for the rest of his life. The pathological form of narcissism was initially identified by the English physician and writer Havelock Ellis in 1898—who also declared it a disorder.
Austrian neurologist and founding father of psychoanalysis, Sigmund Freud, believed 5 Palmowski B. (1989). Uber Narzissmuskonzepte bei S. Freud [Freud’s narcissism concept]. Zeitschrift fur Psychosomatische Medizin und Psychoanalyse, 35(2), 101–116. that it is primarily a common stage in child development. However, when such traits are exhibited after puberty, it can be considered a personality disorder 6 Kris A. O. (1994). Freud’s treatment of a narcissistic patient. The International journal of psycho-analysis, 75 ( Pt 4), 649–664. .
Narcissistic Personality Disorder (NPD)
NPD is one of the ten personality disorders 7 Fariba, K. A., Gupta, V., & Kass, E. (2022). Personality Disorder. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK556058/ identified in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5). “Narcissistic Personality Disorder (NPD) is characterized by a persistent pattern of grandiosity, fantasies of unlimited power or importance, and the need for admiration or special treatment,” explains one 2018 study 8 Kacel, E. L., Ennis, N., & Pereira, D. B. (2017). Narcissistic Personality Disorder in Clinical Health Psychology Practice: Case Studies of Comorbid Psychological Distress and Life-Limiting Illness. Behavioral medicine (Washington, D.C.), 43(3), 156–164. https://doi.org/10.1080/08964289.2017.1301875 .
People with this psychological condition possess and display traits of narcissism, such as an intense sense of self-importance and entitlement, and a lack of empathy 9 Baskin-Sommers, A., Krusemark, E., & Ronningstam, E. (2014). Empathy in narcissistic personality disorder: from clinical and empirical perspectives. Personality disorders, 5(3), 323–333. https://doi.org/10.1037/per0000061 , and an extreme need for attention and admiration.
Narcissistic personality disorder is characterized by self-centered thinking and arrogant behavior. However, beneath this facade, narcissists often have fragile self-esteem, making them highly sensitive to criticism. Their outward confidence is usually a mask for deep-rooted feelings of insecurity.
Research 10 Ronningstam E. (2011). Narcissistic personality disorder: a clinical perspective. Journal of psychiatric practice, 17(2), 89–99. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.pra.0000396060.67150.40 shows that people with NPD are hypersensitive, shy, and insecure. Moreover, they experience a sense of inadequacy, anxiety, pain, fear, interpersonal vulnerability, internal emotional distress, and even depression.
Still, they may appear demanding, extremely over-confident, selfish, patronizing, and highly manipulative to others.
However, such patterns of thought and behavior can cause significant psychological distress and harmfully affect different aspects of their lives, including personal relationships, social life, professional life, and even health in some cases.
Understanding Narcissism
Narcissistic personality disorder or narcissism is a cluster B personality disorder.
As narcissistic people harbor extremely positive self-concepts, they may become very disappointed and even depressed when they are unable to get the desired admiration and attention which they think they deserve.
As a result, they may often feel unsatisfied in relationships ,making them toxic partners, spouses, friends, coworkers, or bosses.
People with NPD often fail to realize that they have a personality disorder and hence do not typically seek help or treatment. As they refuse to acknowledge or change their toxic behavioral patterns, they look for others to blame 11 Lambe, S., Hamilton-Giachritsis, C., Garner, E., & Walker, J. (2018). The Role of Narcissism in Aggression and Violence: A Systematic Review. Trauma, violence & abuse, 19(2), 209–230. https://doi.org/10.1177/1524838016650190 for their unfulfilled and unrealistic needs.
They can often be hostile and react aggressively to others when faced with criticisms or negative feedback. “Narcissistic individuals are sensitive to insults and prone to react to such criticism with anger and hostility,” says a 2002 study 12 Witte, T. H., Callahan, K. L., & Perez-Lopez, M. (2002). Narcissism and anger: an exploration of underlying correlates. Psychological reports, 90(3 Pt 1), 871–875. https://doi.org/10.2466/pr0.2002.90.3.871 .
In fact, researchers 13 McCann, J. T., & Biaggio, M. K. (1989). Narcissistic personality features and self-reported anger. Psychological reports, 64(1), 55–58. https://doi.org/10.2466/pr0.1989.64.1.55 have observed that males with NPD are more likely to express anger in a physically violent manner than females. Narcissists often experience fluctuating and intense emotions 14 Svrakić D. M. (1985).
Emotional features of narcissistic personality disorder. The American journal of psychiatry, 142(6), 720–724. https://doi.org/10.1176/ajp.142.6.720 that are colored by their anxiety related to personal adequacy, control, and personal image and status 15 Grapsas, S., Brummelman, E., Back, M. D., & Denissen, J. J. A. (2020). The “Why” and “How” of Narcissism: A Process Model of Narcissistic Status Pursuit. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 15(1), 150–172. https://doi.org/10.1177/1745691619873350 .
Studies 16 Stinson, F. S., Dawson, D. A., Goldstein, R. B., Chou, S. P., Huang, B., Smith, S. M., Ruan, W. J., Pulay, A. J., Saha, T. D., Pickering, R. P., & Grant, B. F. (2008). Prevalence, correlates, disability, and comorbidity of DSM-IV narcissistic personality disorder: results from the wave 2 national epidemiologic survey on alcohol and related conditions. The Journal of clinical psychiatry, 69(7), 1033–1045. https://doi.org/10.4088/jcp.v69n0701 show that, in the United States, around 6.2% of the population have a lifetime prevalence of NPD—with about 7.7% being men and almost 4.8% being women. With treatment and therapy, one can learn to manage their narcissistic traits.
Read More About Cluster B Personality Disorder Here
Symptoms Of Narcissism

The signs of narcissism are as follows:
- An exaggerated sense of self-importance and excessive self-absorption
- A constant sense of entitlement and grandiosity
- A strong craving for constant attention, admiration, and validation
- Feeling superior to others, even without noteworthy achievements
- Preferring to associate only with people seen as high-status or influential
- Willingness to manipulate or exploit others for personal gain
- A noticeable lack of empathy or concern for others’ feelings
- Fantasies about unlimited success, power, beauty, love, or brilliance
- Viewing others as inferior and dominating social situations
- Arrogant, boastful, and pretentious behavior
- Frequently feeling victimized or misunderstood
- Reacting aggressively to feeling ignored, criticized, or mistreated
- Engaging in exploitative, toxic, and superficial relationships
- Beneath the arrogance, struggling with fragile self-esteem and low confidence
- Constantly exaggerating talents, achievements, or success
- Persistent feelings of jealousy toward others
- Believing that others are envious of them
- Displaying charm and charisma, but only when it serves their interests
- Undermining or downplaying other people’s accomplishments
- Reacting poorly to any form of criticism, often with hostility
- Emotional detachment or lack of genuine connection with others
- Struggling with intimacy or meaningful attachment in relationships
- Withdrawing socially, especially when admiration is lacking
- Emotional dysfunction 17 Weinberg E. (2006). Mentalization, affect regulation, and development of the self. Panel report. Journal of the American Psychoanalytic Association, 54(1), 251–270. https://doi.org/10.1177/00030651060540012501
- Internalized feelings of insecurity, shame, humiliation, emptiness, and vulnerability
- Extreme suspiciousness
- Mental disorders like anxiety, depression, mood disorders, etc.
Read More About Generalized Anxiety Disorder Here
Types Of Narcissism
Narcissism is widely regarded as a trait that exists as a spectrum. There is no specific or established number of subtypes of NPD.
However, certain types have been identified by researchers 18 Mitra, P., & Fluyau, D. (2022). Narcissistic Personality Disorder. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Available From: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK556001/ while others have become informally popular. Some of the most common narcissistic subtypes include:
1. Grandiose narcissism
The grandiose or overt type of NPD typically refers to what most people understand as a narcissistic personality. According to a 2018 study 19 Zajenkowski, M., Maciantowicz, O., Szymaniak, K., & Urban, P. (2018). Vulnerable and Grandiose Narcissism Are Differentially Associated With Ability and Trait Emotional Intelligence. Frontiers in psychology, 9, 1606. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2018.01606 , “grandiose narcissism is characterized by high self–esteem, interpersonal dominance, and a tendency to overestimate one’s capabilities.”
The major traits of Grandiose Narcissists are the following:
- An unrealistic and inflated sense of superiority
- An excessive overestimation of their own abilities
- Exhibitionistic behavioral tendencies
- Constantly seeking attention from everyone
- Displaying other traits that border on entitled, exploitative, authoritarian, unempathetic, aggressive, abusive and self-absorbed tendencies
2. Vulnerable narcissism
Also known as the covert subtype, vulnerable narcissism is characterized by shyness, inhibition, and distress. It “is also associated with lower levels of self-esteem, extraversion and agreeableness, [and] higher neuroticism,” elaborates a 2018 study. Vulnerable narcissists are also associated with a “more realistic self-perception of emotional abilities.”
The signs of Vulnerable Narcissism are as follows:
- They tend to downplay their own achievements
- Feeling jealous of others all the time
- Highly sensitive to criticism
- Becomes extremely defensive when criticized, even if it’s constructive criticism
- Continuously seeks approval and validation from other people
- Often appears insecure, angry, avoidant and overly cautious
3. Malignant narcissism
The malignant narcissism subtype is believed to be at the extreme end of the NPD continuum. “Malignant Narcissism is described as a core narcissistic personality disorder, antisocial behavior, ego-syntonic sadism, and a paranoid orientation,” explains a 2010 study 20 Goldner-Vukov, M., & Moore, L. J. (2010). Malignant Narcissism: from fairy tales to harsh reality. Psychiatria Danubina, 22(3), 392–405. .
The signs of Malignant Narcissism are as follows:
- Exhibits psychopathic tendencies
- Absence of a moral compass
- Having malicious and negative intentions
- Showing signs of being a masterful manipulator
- Exhibits mild neurotic or grandiose traits
- Shows paranoid, sadistic, cruel, and aggressive behavior
4. Other types
The other types of narcissistic personality are:
- Primordial narcissist
- Sexual narcissist
- Healthy narcissist
- Somatic narcissist
- High-Functioning or exhibitionist narcissist
- Spiritual narcissist
- Communal narcissist
- Conversational narcissist
- Cerebral or intellectual narcissist
Read More About Psychopath Here
What Causes Narcissism?
Although no specific causes of narcissism have been identified yet, certain risk factors influence the development of narcissistic personality disorder.
Some of the major causes or factors that contribute to Narcissistic Personality Disorder are the following:
1. Genetics
It has been observed that biology and genetics may play a role in the etiology of NPD. Although the causes are multifaceted, there may be a genetic predisposition at the onset, according to a study 21 Jang, K. L., Livesley, W. J., Vernon, P. A., & Jackson, D. N. (1996). Heritability of personality disorder traits: a twin study. Acta psychiatrica Scandinavica, 94(6), 438–444. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0447.1996.tb09887.x .
There may be some neurobiological factors 22 Jankowiak-Siuda, K., & Zajkowski, W. (2013). A neural model of mechanisms of empathy deficits in narcissism. Medical science monitor : international medical journal of experimental and clinical research, 19, 934–941. https://doi.org/10.12659/MSM.889593 at play as well. For instance, studies 23 Jauk, E., & Kanske, P. (2021). Can neuroscience help to understand narcissism? A systematic review of an emerging field. Personality neuroscience, 4, e3. https://doi.org/10.1017/pen.2021.1 show that subclinical narcissism is associated with variations in regional brain volumes in insular and prefrontal areas.
2. Trauma
Studies 24 Zvelc G. (2010). Object and subject relations in adulthood–towards an integrative model of interpersonal relationships. Psychiatria Danubina, 22(4), 498–508. have found that abuse and traumatic experiences—particularly in childhood or developing years—can contribute to the development of narcissistic personality disorder.
Adverse childhood experiences like abuse, abandonment, rejection, maltreatment 25 van Schie, C. C., Jarman, H. L., Huxley, E., & Grenyer, B. (2020). Narcissistic traits in young people: understanding the role of parenting and maltreatment. Borderline personality disorder and emotion dysregulation, 7, 10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40479-020-00125-7 , and other negative developmental experiences and having fragile egos during childhood can be risk factors.
A 2006 study 26 Otway, L. J., & Vignoles, V. L. (2006). Narcissism and childhood recollections: a quantitative test of psychoanalytic predictions. Personality & social psychology bulletin, 32(1), 104–116. https://doi.org/10.1177/0146167205279907 elaborates “childhood experiences may help to explain the paradoxical combination of grandiosity and fragility in adult narcissism.”
3. Excessive praise
Research 27 Mitra, P., & Fluyau, D. (2022). Narcissistic Personality Disorder. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK556001/ also shows that “excessive praise, including the belief that a child may have extraordinary abilities, may also lead to NPD.”
According to a 2015 study 28 Brummelman, E., Thomaes, S., Nelemans, S. A., Orobio de Castro, B., Overbeek, G., & Bushman, B. J. (2015). Origins of narcissism in children. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 112(12), 3659–3662. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1420870112 , parents often give special attention and exceptional treatment to children to boost their self-esteem.
However, overvaluing a child can lead to the development of narcissism in children. Contrarily, overly criticizing parents can also result in the onset of narcissism.
4. Other causes
Other environmental causes and risk factors contributing to the development of NPD may include the following:
- Unstable or inconsistent parenting
- Lack of validation during childhood and adolescence 29 Bleiberg E. (1994). Normal and pathological narcissism in adolescence. American journal of psychotherapy, 48(1), 30–51. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.psychotherapy.1994.48.1.30
- Extremely high and unrealistic parental expectations
- Neglect or lack of care
- Parental overindulgence 30 Wetzel, E., & Robins, R. W. (2016). Are Parenting Practices Associated with the Development of Narcissism? Findings from a Longitudinal Study of Mexican-origin Youth. Journal of research in personality, 63, 84–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrp.2016.05.005
- Oversensitive temperament
- Growing up with narcissistic, manipulative, or toxic parents
- Cultural and social influences
What Are The Comorbidities Associated With Narcissism?
A 2017 study 31 Eaton, N. R., Rodriguez-Seijas, C., Krueger, R. F., Campbell, W. K., Grant, B. F., & Hasin, D. S. (2017). Narcissistic Personality Disorder and the Structure of Common Mental Disorders. Journal of personality disorders, 31(4), 449–461. https://doi.org/10.1521/pedi_2016_30_260 states that NPD “shows high rates of comorbidity with mood, anxiety, substance use, and other personality disorders.” A person with narcissistic personality disorder often develops several other comorbid 32 Kacel, E. L., Ennis, N., & Pereira, D. B. (2017). Narcissistic Personality Disorder in Clinical Health Psychology Practice: Case Studies of Comorbid Psychological Distress and Life-Limiting Illness. Behavioral medicine (Washington, D.C.), 43(3), 156–164. https://doi.org/10.1080/08964289.2017.1301875 mental health conditions, such as:
- Bulimia nervosa
- Anorexia nervosa
- Social anxiety disorder
- Depression
- Panic disorder
- Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD)
- Antisocial personality disorder
- Borderline personality disorder (BPD 33 Hörz-Sagstetter, S., Diamond, D., Clarkin, J. F., Levy, K. N., Rentrop, M., Fischer-Kern, M., Cain, N. M., & Doering, S. (2018). Clinical Characteristics of Comorbid Narcissistic Personality Disorder in Patients With Borderline Personality Disorder. Journal of personality disorders, 32(4), 562–575. https://doi.org/10.1521/pedi_2017_31_306 )
- Physical health issues like cardiovascular problems 34 Reinhard, D. A., Konrath, S. H., Lopez, W. D., & Cameron, H. G. (2012). Expensive egos: narcissistic males have higher cortisol. PloS one, 7(1), e30858. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0030858 , coronary disorders, etc.
- Substance abuse 35 Parmar, A., & Kaloiya, G. (2018). Comorbidity of Personality Disorder among Substance Use Disorder Patients: A Narrative Review. Indian journal of psychological medicine, 40(6), 517–527. https://doi.org/10.4103/IJPSYM.IJPSYM_164_18 (like alcoholism or drug addiction)
- Self-harm and suicidal tendencies
According to a 2009 study 36 Ritter, K., Roepke, S., Merkl, A., Heuser, I., Fydrich, T., & Lammers, C. H. (2010). Komorbiditäten bei Patienten mit einer Narzisstischen Persönlichkeitsstörung im Vergleich zu Patienten mit einer Borderline-Persönlichkeitsstörung [Comorbidity in patients with narcissistic personality disorder in comparison to patients with borderline personality disorder]. Psychotherapie, Psychosomatik, medizinische Psychologie, 60(1), 14–24. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0028-1102943 , “in general, patients with NPD showed similar co-occurring disorders as patients with BPD, or with the co-diagnosis NPD and BPD.” Further studies 37 Schoenleber, M., Sadeh, N., & Verona, E. (2011). Parallel syndromes: two dimensions of narcissism and the facets of psychopathic personality in criminally involved individuals. Personality disorders, 2(2), 113–127. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0021870 show that a person with narcissism can also develop a psychopathic personality.
“Although antisocial personality disorder is associated with psychopathy, it also seems common in individuals with narcissistic personality traits,” explain researchers 38 Martínez-López, J., Medina-Mora, M. E., Robles-García, R., Madrigal, E., Juárez, F., Tovilla-Zarate, C. A., Reyes, C., Monroy, N., & Fresán, A. (2019). Psychopathic Disorder Subtypes Based on Temperament and Character Differences. International journal of environmental research and public health, 16(23), 4761. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16234761 . Moreover, narcissism is found 39 Coleman, D., Lawrence, R., Parekh, A., Galfalvy, H., Blasco-Fontecilla, H., Brent, D. A., Mann, J. J., Baca-Garcia, E., & Oquendo, M. A. (2017). Narcissistic Personality Disorder and suicidal behavior in mood disorders. Journal of psychiatric research, 85, 24–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2016.10.020 to be closely associated with a greater risk of suicidal death than any other personality disorder.
Read More About Panic Disorder Here
How To Diagnose Narcissistic Personality Disorder?
Narcissists rarely seek treatment on their own, as they typically don’t believe they have a personality disorder or mental health condition. However, they might approach a professional for help with related issues depression, anxiety, or even substance abuse.
This often makes diagnosing narcissistic personality disorder (NPD) a challenge for mental health professionals. Even so, a qualified healthcare provider can diagnose NPD through careful assessment.
Some key narcissistic traits, such as grandiosity, an inflated self-importance, and a lack of empathy or emotional connection – can interfere with relationships and daily life.
For an NPD diagnosis, these traits and their impact must be consistent across different situations and persist over time.
It’s also important to rule out whether these patterns are part of normal development, culturally acceptable behaviors, substance use, or other mental or medical conditions.
Narcissism can be diagnosed medically 40 Ronningstam E. (2010). Narcissistic personality disorder: a current review. Current psychiatry reports, 12(1), 68–75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11920-009-0084-z when the symptoms lead to subjective distress and functional impairment in the patient’s occupational, social, and personal life. So even if they may not admit to having a condition or personality disorder, they are aware that their thoughts and behaviors cause them severe distress.
A psychiatrist, psychologist, or therapist can ask the patient to fill out certain questionnaires or undergo specific personality tests to determine if they have NPD. Common screening tools used in narcissism diagnosis include:
- International personality disorder examination (IPDE 41 Loranger, A. W., Sartorius, N., Andreoli, A., Berger, P., Buchheim, P., Channabasavanna, S. M., Coid, B., Dahl, A., Diekstra, R. F., & Ferguson, B. (1994). The International Personality Disorder Examination. The World Health Organization/Alcohol, Drug Abuse, and Mental Health Administration international pilot study of personality disorders. Archives of general psychiatry, 51(3), 215–224. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.1994.03950030051005 )
- Millon clinical multiaxial inventory III (MCMI-III 42 Caparrós, B. C., & Hoz, E. V. (2013). Millon clinical multiaxial inventory III (MCMI-III) and communication styles in a sample of university students. The Spanish journal of psychology, 16, E85. https://doi.org/10.1017/sjp.2013.85 )
- Personality diagnostic questionnaire-4 (PDQ-4 43 Fossati, A., Maffei, C., Bagnato, M., Donati, D., Donini, M., Fiorilli, M., Novella, L., & Ansoldi, M. (1998). Brief communication: criterion validity of the Personality Diagnostic Questionnaire-4+ (PDQ-4+) in a mixed psychiatric sample. Journal of personality disorders, 12(2), 172–178. https://doi.org/10.1521/pedi.1998.12.2.172 )
Mental health professionals (MHPs) may also conduct lab tests, physical exams, and psychological evaluations for differential diagnosis of NPD.
How To Treat Narcissism?
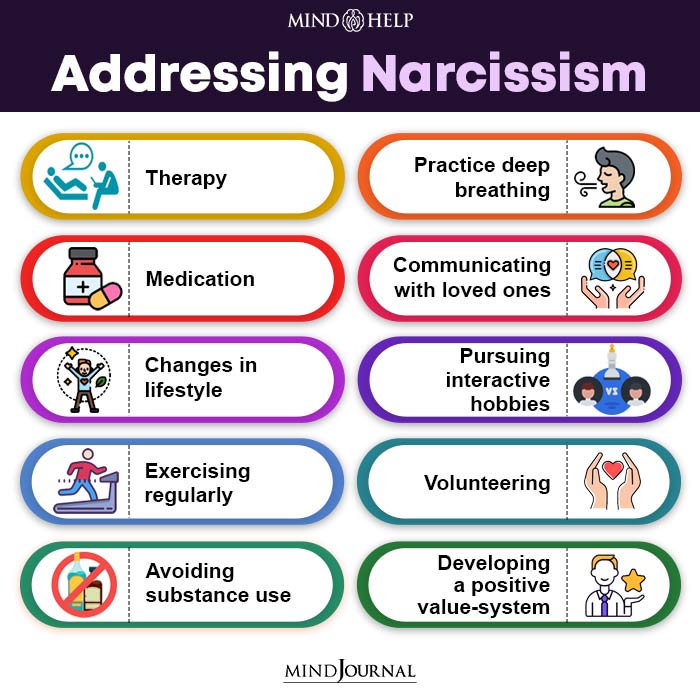
Narcissism, as a personality trait, isn’t something that can be completely “cured.” However, when it comes to narcissistic personality disorder (NPD), treatment is possible through a combination of therapy and, in some cases, medication.
While there’s no specific medication designed to treat NPD itself, certain medications can help manage related symptoms like anxiety, depression, or mood instability.
Therapy, particularly talk therapy, plays a key role in helping individuals with NPD understand their behaviors, challenge negative thought patterns, and work toward healthier relationships.
Though NPD is considered a long-term condition, treatment can reduce its impact and help improve overall quality of life.
Some of the commonly available options in treatment for narcissism include:
1. Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy or talk therapy is considered the most effective treatment 44 Maillard, P., Berthoud, L., Kolly, S., Sachse, R., & Kramer, U. (2020). Processes of Change in Psychotherapy for Narcissistic Personality Disorder. Journal of personality disorders, 34(Suppl), 63–79. https://doi.org/10.1521/pedi.2020.34.supp.63 for NPD. Such therapy is targeted at addressing the thoughts, beliefs, emotions, and behaviors related to narcissism.
Therapists work with the patients to make them realize how their behaviors are driven by their emotions and help them set goals associated with behavioral change. Psychotherapy can enable 45 Kiliç, N., & Eryilmaz, A. (2019). Investigating Narcissistic Personality Traits in the Context of Positive Psychotherapy. Noro psikiyatri arsivi, 56(1), 40–46. https://doi.org/10.29399/npa.22794 a narcissist to:
- Understanding the root causes and emotions that cause a person to exhibit narcissistic behavior
- Developing healthier strategies to regulate and handle emotions
- Learning to accept criticism by recognizing genuine strengths and abilities
- Identifying and working on underlying self-esteem and self-worth issues
- Improving the ability to connect with others on a deeper level and build more meaningful, intimate relationships
Some of the most helpful and widely recommended forms of therapy for the treatment of narcissism typically include:
- Schema-focused therapy 46 Dieckmann, E., & Behary, W. (2015). Schematherapie: Ein Ansatz zur Behandlung narzisstischer Persönlichkeitsstörungen [Schema Therapy: An Approach for Treating Narcissistic Personality Disorder]. Fortschritte der Neurologie-Psychiatrie, 83(8), 463–478. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0035-1553484
- Group psychotherapy 47 Macaskill N. D. (1980). The narcissistic core as a focus in the group therapy of the borderline patient. The British journal of medical psychology, 53(2), 137–143. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2044-8341.1980.tb01428.x
- Psychodynamic psychotherapy 48 Wilczek, A., Weinryb, R. M., Gustavsson, P. J., Barber, J. P., Schubert, J., & Asberg, M. (1997). Symptoms and character traits in patients selected for long-term psychodynamic psychotherapy. The Journal of psychotherapy practice and research, 7(1), 23–34.
- Psychoanalytic psychotherapy 49 Kernberg O. F. (2014). An overview of the treatment of severe narcissistic pathology. The International journal of psycho-analysis, 95(5), 865–888. https://doi.org/10.1111/1745-8315.12204
- Family therapy 50 Jones S. A. (1987). Family therapy with borderline and narcissistic patients. Bulletin of the Menninger Clinic, 51(3), 285–295.
- Psychoanalysis 51 Higgitt, A., & Fonagy, P. (1992). Psychotherapy in borderline and narcissistic personality disorder. The British journal of psychiatry : the journal of mental science, 161, 23–43. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.161.1.23
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT 52 Matusiewicz, A. K., Hopwood, C. J., Banducci, A. N., & Lejuez, C. W. (2010). The effectiveness of cognitive behavioral therapy for personality disorders. The Psychiatric clinics of North America, 33(3), 657–685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psc.2010.04.007 )
- Couple therapy 53 Links, P. S., & Stockwell, M. (2002). The role of couple therapy in the treatment of narcissistic personality disorder. American journal of psychotherapy, 56(4), 522–538. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.psychotherapy.2002.56.4.522
- Supportive psychotherapy 54 Zalman, H., Doorn, K. A., & Eubanks, C. F. (2019). Alliance challenges in the treatment of a narcissistic patient: the case of Alex. Research in psychotherapy (Milano), 22(2), 351. https://doi.org/10.4081/ripppo.2019.351
- In-patient treatment 55 Hinrichs J. (2016). Inpatient Therapeutic Assessment With Narcissistic Personality Disorder. Journal of personality assessment, 98(2), 111–123. https://doi.org/10.1080/00223891.2015.1075997
- Mentalization therapy 56 Drozek, R. P., & Unruh, B. T. (2020). Mentalization-Based Treatment for Pathological Narcissism. Journal of personality disorders, 34(Suppl), 177–203. https://doi.org/10.1521/pedi.2020.34.supp.177
- Transference-focused therapy 57 Diamond, D., & Hersh, R. G. (2020). Transference-Focused Psychotherapy for Narcissistic Personality Disorder: An Object Relations Approach. Journal of personality disorders, 34(Suppl), 159–176. https://doi.org/10.1521/pedi.2020.34.supp.159
- Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT 58 Neacsiu, A. D., & Tkachuck, M. A. (2016). Dialectical behavior therapy skills use and emotion dysregulation in personality disorders and psychopathy: a community self-report study. Borderline personality disorder and emotion dysregulation, 3, 6. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40479-016-0041-5 )
A 2000 study 59 Gabbard G. O. (2000). Psychotherapy of personality disorders. The Journal of psychotherapy practice and research, 9(1), 1–6. states “Psychoanalysis and psychoanalytic therapy have long been used in the treatment of patients with personality disorders (PDs).” Therapy helps to replace harmful beliefs and negative behaviors with positive ones by helping the patient identify them in the first place.
It can help them develop a more realistic and healthier self-image. In fact, studies 60 Baskin-Sommers, A., Krusemark, E., & Ronningstam, E. (2014). Empathy in narcissistic personality disorder: from clinical and empirical perspectives. Personality disorders, 5(3), 323–333. https://doi.org/10.1037/per0000061 have found that therapy can enable narcissists to develop empathy.
2. Medications
A mental health professional may prescribe certain medications to address symptoms of narcissism and other comorbid conditions (such as bipolar disorder, substance use disorder or addiction, anxiety, depression 61 Saito, S., Kobayashi, T., & Kato, S. (2013). Seishin shinkeigaku zasshi = Psychiatria et neurologia Japonica, 115(4), 363–371. , eating disorders, etc.).
For instance, antidepressants 62 Dunlop, B. W., DeFife, J. A., Marx, L., Garlow, S. J., Nemeroff, C. B., & Lilienfeld, S. O. (2011). The effects of sertraline on psychopathic traits. International clinical psychopharmacology, 26(6), 329–337. https://doi.org/10.1097/YIC.0b013e32834b80df (like selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), mood stabilizers, antipsychotics, or anti-anxiety drugs) are commonly prescribed to NPD patients.
3. Lifestyle changes
Apart from psychotherapy and medication, experts also recommend lifestyle changes and healthy coping strategies to help manage clinical narcissism.
These additional steps are especially important, as individuals with narcissism often struggle to see the value in treatment and may be more likely to give up on the process.
These strategies can help a narcissist recover successfully:
- Stay physically active and exercise regularly as it boosts your mood and self-esteem 63 Sharma, A., Madaan, V., & Petty, F. D. (2006). Exercise for mental health. Primary care companion to the Journal of clinical psychiatry, 8(2), 106. https://doi.org/10.4088/pcc.v08n0208a
- Practice deep breathing 64 Ma, X., Yue, Z. Q., Gong, Z. Q., Zhang, H., Duan, N. Y., Shi, Y. T., Wei, G. X., & Li, Y. F. (2017). The Effect of Diaphragmatic Breathing on Attention, Negative Affect and Stress in Healthy Adults. Frontiers in psychology, 8, 874. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00874 and other relaxation exercises, like mindfulness meditation 65 Goyal, M., Singh, S., Sibinga, E. M., Gould, N. F., Rowland-Seymour, A., Sharma, R., Berger, Z., Sleicher, D., Maron, D. D., Shihab, H. M., Ranasinghe, P. D., Linn, S., Saha, S., Bass, E. B., & Haythornthwaite, J. A. (2014). Meditation programs for psychological stress and well-being: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA internal medicine, 174(3), 357–368. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.13018 , yoga 66 Shohani, M., Badfar, G., Nasirkandy, M. P., Kaikhavani, S., Rahmati, S., Modmeli, Y., Soleymani, A., & Azami, M. (2018). The Effect of Yoga on Stress, Anxiety, and Depression in Women. International journal of preventive medicine, 9, 21. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_242_16 , massage 67 Nazari, F., Mirzamohamadi, M., & Yousefi, H. (2015). The effect of massage therapy on occupational stress of Intensive Care Unit nurses. Iranian journal of nursing and midwifery research, 20(4), 508–515. https://doi.org/10.4103/1735-9066.161001 , and aromatherapy 68 Toda, M., & Matsuse, R. (2020). Endocrinological effect of lavender aromatherapy on stressful visual stimuli. Contemporary clinical trials communications, 17, 100547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conctc.2020.100547 , to reduce stress anxiety and depressive symptoms
- Don’t hesitate to ask for help and support from your family and friends
- Try volunteering 69 Han, S. H., Kim, K., & Burr, J. A. (2020). Stress-Buffering Effects of Volunteering on Daily Well-Being: Evidence From the National Study of Daily Experiences. The journals of gerontology. Series B, Psychological sciences and social sciences, 75(8), 1731–1740. https://doi.org/10.1093/geronb/gbz052 and pursuing interests and hobbies to counter self-absorbing negative thoughts
- Join online support groups or local support groups in your community
- Avoid alcohol and other substances to better manage your thoughts, emotions, and behavior
- Follow the doctor’s instructions, stick to the treatment plan, and attend therapy sessions regularly
- Learn and practice positive conflict resolution strategies
Read More About Psychotherapy Here
Coping Strategies For Loved Ones
Living with a narcissist can be challenging, especially when they are your family member or friend. If you have a loved one with narcissistic personality disorder, here are a few tips that can help you cope better:
- Identify the signs and symptoms of narcissism
- Encourage them to seek treatment for NPD
- Set strong and healthy personal boundaries
- Don’t take their behavior personally
- Practice self-care and do things that you enjoy
- Be compassionate and respond to them calmly
- Seek support from others and talk to friends and family
- Consult a therapist, if needed
Takeaway
While someone with narcissism may come across as manipulative, mean or selfish, it’s important to remember that narcissistic personality disorder is a mental health condition that requires understanding, treatment, and support.
With the right treatment, individuals can work toward reducing NPD symptoms, developing greater empathy, improving self-esteem, addressing underlying insecurities, and building healthier, more meaningful relationships.
Narcissism At A Glance
- Narcissism is excessive self-overvaluation that causes a distorted sense of self-worth and reduces a person’s empathic receptivity.
- Its pathological form, narcissistic personality disorder (NPD), is a mental disorder.
- A narcissistic individual seeks gratification from egotistic admiration of his/her own idealized traits and self-image.
- People with NPD often fail to realize that they have a personality disorder and hence do not typically seek help or treatment.
- Around 6.2% of the global population has a lifetime prevalence of NPD.
- The symptoms of NPD include a sense of self-importance, grandiosity, or lack of intimacy or empathy that impair the narcissist’s everyday functioning.
- NPD can be easily addressed with therapy and/or medication.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is narcissism genetic?
Genetics and neurobiology might play a role in the development of narcissistic personality disorder. However, research contends that environmental factors are primarily associated with narcissism.
2. Is narcissism a mental illness?
Narcissism is a fundamental personality trait. However, when a person develops a clinical condition in which he/she harbors an inflated sense of self, a lack of empathy, and an obsession for attention—the person is said to suffer from a narcissistic personality disorder (NPD).
3. Can narcissism be cured?
There is no cure for narcissism because it is a fundamental personality trait. However, narcissistic personality disorder (NPD) can be addressed with psychotherapy, medication, and self-help strategies.