Heuristics are mental shortcut techniques used to solve problems and make decisions efficiently. These techniques are used to reduce the decision making time and allow the individual to function without interrupting their next course of action.
What Is Heuristics?
Heuristics are a time-saving approach to solving problems and making decisions efficiently. Heuristics processes are usually used to find quick answers and solutions to problems. However, decisions based on this mindset are not always accurate. They serve as quick mental references that are used for everyday problems and experiences.
Humans and animals resort to this mindset because processing every information that comes into the brain takes time and effort. With the help of these shortcut techniques, the brain can make faster and efficient decisions despite the consequences. This is known as the accuracy effort trade-off theory. This theory works because not every decision requires the same amount of time and energy.
Hence, people use it as a means to save time. Another reason why people resort to heuristics is that the brain simply doesn’t have the capacity to process everything and so they must resort to these mental shortcuts to make quick decisions. A 2014 study 1 Mousavi, S., & Gigerenzer, G. (2014). Risk, uncertainty, and heuristics. Journal of Business Research, 67(8), 1671-1678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2014.02.013 demonstrated that in case of uncertainty and a lack of information, heuristics allows a “less is more effect” wherein less information leads to more accuracy. It is worth mentioning that the applicability and usefulness of heuristics depend on the situation.
A 2011 study 2 Gigerenzer G, Gaissmaier W. Heuristic decision making. Annu Rev Psychol. 2011;62:451-82. doi: 10.1146/annurev-psych-120709-145346. PMID: 21126183. pointed out that there may be two reasons for relying on heuristics. They are:
- Individuals and organizations often rely on simple heuristics in an adaptive way
- Ignoring part of the information can lead to more accurate judgments than weighing and adding all information
Although heuristics are useful, sometimes they can be inaccurate. In case an individual relies on it too heavily, it may result in incorrect judgments or cognitive biases. Understanding commonly unfavorable heuristics and identifying situations that may affect behavior can help individuals avoid mental pitfalls. It is important to assess major problems by making a list of pros and cons. In order to avoid inaccurate decisions, you can consult trusted individuals, take time to think through things where quick decisions may cause significant problems such as catching an important flight. Hence, it is important to be mindful of the information that is being processed in the brain to make accurate decisions.
History Of Heuristics
Nobel prize-winning psychologist, Herbert Simon suggested that although people attempt to make rational decisions, humans are subject to cognitive limitations. A 2013 study 3 Rachlin, H. (2003). Rational thought and rational behavior: A review of bounded rationality: The adaptive toolbox. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 79(3), 409-412. https://doi.org/10.1901/jeab.2003.79-409 pointed out that rational decisions involve weighing different factors such as potential costs against potential benefits. People are often limited by time to make choices as well as the amount of information we have at our disposal. Other factors that influence our thinking are overall intelligence and accuracy of perceptions.
Psychologists Amos Tversky and Daniel Kahneman proposed that cognitive biases influence how people think and the judgements people make about events. Due to these limitations, we are often forced to rely on our instinctive shortcuts i.e heuristics to make sense of the world. Simon’s research indicated that humans have a limited ability to make rational decisions. On the other hand, Tversky and Kahneman’s research 4 Kahneman, D., & Tversky, A. (1977). Prospect theory. An analysis of decision making under risk. https://doi.org/10.21236/ada045771 represented how people have specific ways to simplify the decision-making process.
Read More About Decision-Making Here
Types Of Heuristics
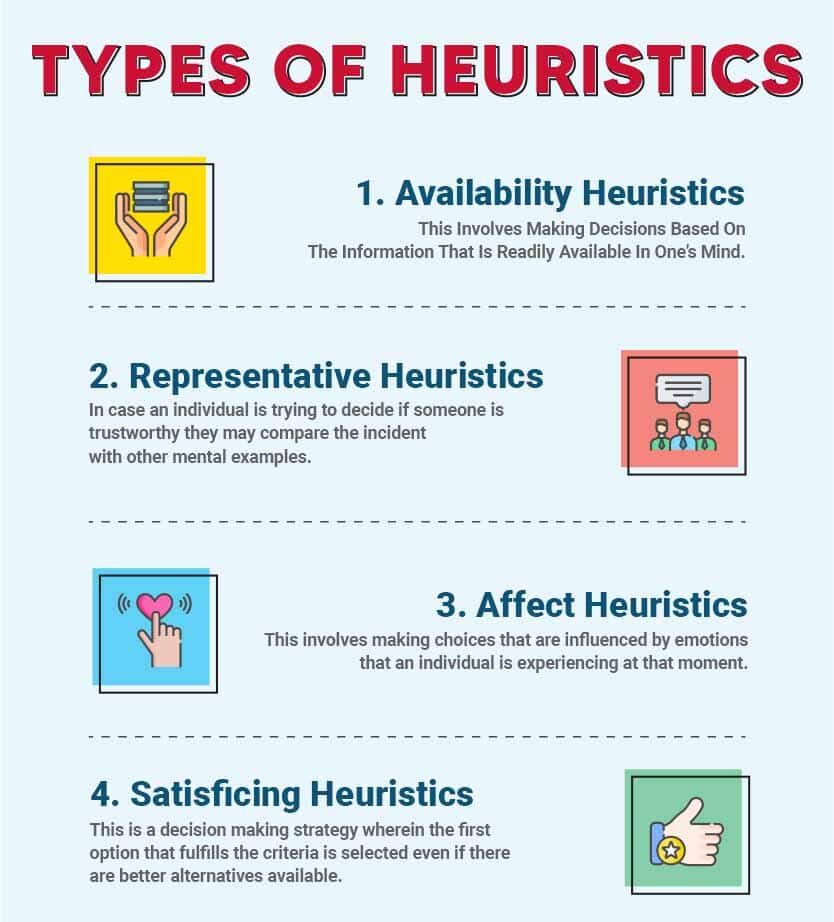
Some of the common heuristics may include the following:
1. Availability Heuristics
This involves making decisions based on the information that is readily available in one’s mind. When an individual makes a decision, they immediately refer to a number of relevant examples. Since the relevant information is readily available in their memory, they are more likely to conclude that these outcomes are common. For example, dramatic, violent deaths are usually more highly publicized and hence have higher availability.
Another instance where availability heuristics may work is if an individual is thinking about taking a trip and thinks of a number of recent airline accidents. This may lead them to think that air travel is dangerous. This may also enable them to resort to traveling by car instead. Since airline disasters came to their mind easily, the availability heuristics lead them to think that plane crashes are more common even though it may not be entirely true.
2. Representative Heuristics
This involves making a decision based on the comparison of the present situation and the most relevant mental prototype. In case an individual is trying to decide if someone is trustworthy they may compare the incident with other mental examples. For instance, an older woman sitting beside you at a train station may remind you of your grandmother. You may immediately assume that she may be kind, gentle, and trustworthy. People tend to believe in the existing mental information since the traits match up to the individual’s mental prototype.
3. Affect Heuristics
This involves making choices that are influenced by emotions that an individual is experiencing at that moment. Research 5 Finucane, M. L., Alhakami, A., Slovic, P., & Johnson, S. M. (2000). The affect heuristic in judgments of risks and benefits. Journal of Behavioral Decision Making, 13(1), 1-17. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1099-0771(200001/03)13:1<1::aid-bdm333>3.0.co;2-s has demonstrated that people are more likely to view decisions as having benefits and lower risks when their mood is positive. However, negative emotions lead people to focus on the potential downfall of a decision rather than the possible benefits.
4. Satisficing Heuristics
This is a decision making strategy wherein the first option that fulfills the criteria is selected even if there are better alternatives available. Hebert Simon formulated the concept of satisficing. This theory 6 Simon, H. A. (1955). A behavioral model of rational choice. The Quarterly Journal of Economics, 69(1), 99. https://doi.org/10.2307/1884852 is used to choose one alternative from a set of alternatives in situations of uncertainty. In this case, uncertainty refers to the total set of alternatives and their consequences that cannot be known or foreseen. For instance, professional real estate entrepreneurs rely on this theory to decide where they should invest to develop new commercial areas. Although there may be better alternatives available, they resort to the first option that fulfills their criteria.
Advantages Of Heuristics
Some of the most common advantages of using this cognitive approach are:
- Facilitates timely decisions
- Makes decision making simpler
- Less information, more accuracy
- Quick answers to problems
- Reduces complex information into simple and manageable set of choices
- Frees up cognitive resources for more complex planning
Heuristics & Cognitive Bias
Although heuristics can advance our problems and decision-making process, it can even cause errors. It can often lead to inaccurate judgments based on how common things can occur and how certain events influence our decisions. It is important to realize that even though something worked in the past, it doesn’t necessarily mean that it will work again. Relying on existing heuristics can make it difficult to see alternatives or brainstorm new ideas. A 2014 study pointed out that heuristics can also contribute to other things such as stereotypes and prejudice. Due to this people often overlook more relevant information and create stereotypical categorization that is not entirely true.
Read More About Cognitive Bias Here
Making Quick Decisions With Heuristics
Heuristics allow us to make quick decisions and make our life easier. It is often accurate. However, it is important to be aware of what is influencing our decisions in order to avoid potential cognitive biases. This will allow us to make more accurate decisions.
Heuristics At A Glance
- Heuristics are mental shortcut techniques used to solve problems and make decisions efficiently.
- Heuristics processes are usually used to find quick answers and solutions to problems.
- They serve as quick mental references that are used for everyday problems and experiences.
- With the help of these shortcut techniques, the brain can make faster and efficient decisions despite the consequences.
- Sometimes it may result in incorrect judgments or cognitive biases.
- It is important to be aware of what is influencing our decisions in order to avoid potential cognitive biases.