Table of Contents
Body-Focused Repetitive Behaviors or BFRB is a serious mental health issue that often goes unchecked because of an obvious understanding of these obsessive intense behaviors such as biting, pulling, or nailing, as normal tendencies. However, these can culminate into something much more damaging over time.
What Are Body Focused Repetitive Behaviors?
Some urges can be extremely intense and obsessive at the same time while being repetitive. These sorts of behaviors are usually termed as usual obsessions or urges by most people, thus people suffering from the disorder often go through late diagnosis. These urges are called Body Focused Repetitive Behavior or BFRB. According to a 2012 study 1 Siddiqui, E. U., Naeem, S. S., Naqvi, H., & Ahmed, B. (2012). Prevalence of body-focused repetitive behaviors in three large medical colleges of Karachi: a cross-sectional study. BMC research notes, 5, 614. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-0500-5-614 , BFRB refers to “a group of behaviors that include skin picking (dermatillomania), hair pulling (trichotillomania) and nail biting (onychophagia), which result in physical and psychological difficulties.” These obsessions, tendencies and behaviors are often identified as nervous habits 2 Hansen DJ, Tishelman AC, Hawkins RP, Doepke KJ. Habits with potential as disorders. Prevalence, severity, and other characteristics among college students. Behav Modif. 1990 Jan;14(1):66-80. doi: 10.1177/01454455900141005. PMID: 2294902. .
But when these begin to impair a person’s ability to function normally in everyday life, then such habits can become devastating and are known as impulse control disorders 3 Fariba K, Gokarakonda SB. Impulse Control Disorders. [Updated 2020 Oct 6]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK562279/ . It is one of the most misdiagnosed and misunderstood disorders. Since most of the times the symptoms remain unchecked, it gradually leads to worsening the state of the patient. In most cases these habits get dismissed as mere ‘bad habits’. Many times the patients with this specific disorder are diagnosed with obsessive compulsive disorder or OCD, but in reality the illnesses are distinct in nature in spite of having a few core similarities. The distinction 4 Hodges, & Rosemary. (2019). The Relationship between Efficacious Treatments for Pediatric Obsessive-compulsive Disorder and Body-focused Repetitive Behaviors: A Review. https://search.proquest.com/openview/563e677945677605ba2000ffa4381598/1?pq-origsite=gscholar&cbl=18750&diss=y can be found in self-harming rituals, like cutting oneself or inflicting pain on oneself.
Typically, the condition starts to develop during childhood and adolescence. 13.7% 5 Teng, E. J., Woods, D. W., Twohig, M. P., & Marcks, B. A. (2002). Body-focused repetitive behavior problems. ResearchGate. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/11294101_Body-Focused_Repetitive_Behavior_Problems of the population is reported to get diagnosed with at least one BFRB in their lifetime. The search for the origin or causes of the disorder are still in progress but a few reasons can be identified as of now. One of the main causes has been found in terms of hereditary. Genes play a huge role as a reason behind the illness. There are other factors like the personality of the person, or the excessive amount of stress one person is taking in, or even childhood traumas. The age when a person gets diagnosed with the disorder is also very crucial to note as that can primarily speak for certain urges of the person. It is also found out that women are more likely to get the disorder than men 6 Siddiqui, E. U., Naeem, S. S., Naqvi, H., & Ahmed, B. (2012). Prevalence of body-focused repetitive behaviors in three large medical colleges of Karachi: a cross-sectional study. BMC research notes, 5, 614. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-0500-5-614 .
Symptoms Of Body Focused Repetitive Behavior
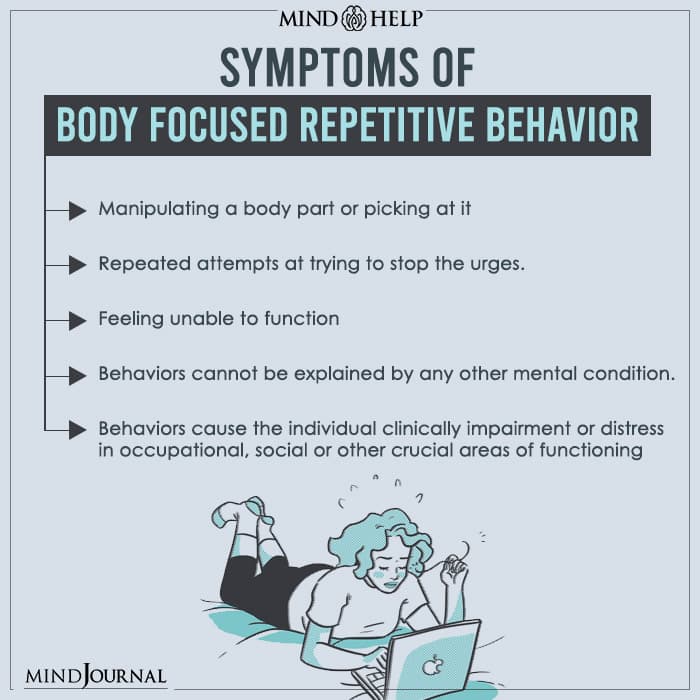
BFRB refers to any behavior related to self-grooming that damages the body. The behaviors can include picking or pulling at skin, biting, or scraping skin or hair. Some of the specific BFRB symptoms are the following:
- Manipulating a body part or picking at it, which results in damage usually.
- Repeated attempts at trying to stop or reducing the urges.
- Feeling unable to function or deeply distressed because of the BFRB.
- The hair-pulling, nail biting or teeth grinding behaviors that cannot be explained by any other mental condition.
- The skin picking, hair eating, or nail biting behaviors cause the individual clinically impairment or distress in occupational, social or other crucial areas of functioning.
Types Of BFRB

This disorder can show up in different ways, in the form of different obsessive recurring urges. Some of the commonly noticed types of Body Focused Repetitive Behaviors are as follows:
1. Dermatillomania
People with this type usually get the urge to pick on their skin. Mostly, these can be pimples, scabs or bumps on the skin, but when worsened people can get the urge to obsessively pick on their healthy skin. According to a study 7 Hawatmeh, A., & Al-Khateeb, A. (2017). An unusual complication of dermatillomania. Quantitative imaging in medicine and surgery, 7(1), 166–168. https://doi.org/10.21037/qims.2016.12.02 , dermatillomania is also known as excoriation disorder, psychogenic excoriation or neurotic picking.
It is a skin picking disorder which is “characterized by repetitive skin picking leading to tissue damage.” It can be noticed in people who might already have obsessive-compulsive disorder. Specialists might suggest wearing bandages on the fingers and bare skin that invites the patient’s urges to pick at. Sometimes, doctors also advise keeping the mind and hands busy with a fidget spinner or something similar.
Read More About Dermatillomania Here
2. Onychophagia
Nail Biting or onychophagia is “a common oral habit, observed in both children and adults,” according to research 8 Tanaka, O. M., FarinazzoVitral, R. W., Tanaka, G. Y., Guerrero, A. P., & Camargo, E. S. (2008, August). Nailbiting, or onychophagia: A special habit. ScienceDirect.com | Science, health and medical journals, full text articles and books. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0889540608000048 . It could be caused by heredity, stress, anxiety, loneliness, inactivity, learned from others or due to poor hygiene. As many as 30% of the demography 9 Baghchechi, M., Pelletier, J. L., & Jacob, S. E. (2020). Art of Prevention: The importance of tackling the nail biting habit. International journal of women’s dermatology, 10.1016/j.ijwd.2020.09.008. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijwd.2020.09.008 show symptoms of this specific illness and many of them are unaware of the condition. The downside to prolonged obsessive nail biting can bring damage to the nails as well as to the teeth at times. This can easily cause infections in those areas. Keeping the nails trimmed and using a nail product with a bitter taste are often advised by professionals to keep the urges in check.
3. Morsicatio Buccarum
Many patients of BFRB show this tendency of biting the inside of their mouths which leads to sores and swelling in the inner lining of the mouth as a consequence. This type is known as Morsicatio Buccarum or as oral frictional hyperkeratosis 10 Cam K, Santoro A, Lee JB. Oral frictional hyperkeratosis (morsicatio buccarum): an entity to be considered in the differential diagnosis of white oral mucosal lesions. Skinmed. 2012 Mar-Apr;10(2):114-5. PMID: 22545331. . In some cases, people suffering from this specific type of Body Focused Repetitive Behavior might find the inside of their mouth as bumpy which increases the urge to chew on it more. This can also cause infection over time. It is advised to use something like a chewing gum that provides the same feeling, in order to get rid of the disorder.
4. Morsicatio Labiorum
This type is very similar to the previous one as people with this disorder tend to bite, chew or suck on their inner lips. If Morsicatio Labiorum 11 노영석. (2012, October). Repository at Hanyang University: Three cases of ‘Morsicatio Labiorum’. Repository at Hanyang University. https://repository.hanyang.ac.kr/handle/20.500.11754/42974 is practised over a longer time period, it can make the skin cells of the inner lip slough off while creating a gray/white/yellow rough patch. A device called a “lip bumper” can be used to keep the lower teeth away from the lips, which can eventually break the cycle.
5. Morsicatio Linguarum
Similar to Buccarum and Labiorum, patients with Linguarum 12 Min, K. W., & Park, C. K. (2008, November 26). Morsicatio Labiorum/Linguarum – Three Cases Report and a Review of the Literature. Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine. https://www.jpatholtm.org/upload/pdf/kjp-43-2-174.pdf get the urge to chew on the sides of their tongue. The reason behind this certain type can be stress. It is also an extremely common type of BFRB. Dentists may advise wearing a special kind of mouth guard that helps shield the tongue by covering the teeth. However, stress management is the best way to cope with this.
6. Onychotillomania
This specific type also focuses on the urges to pick and pull at the nails of fingers and toes, and the skin surrounding the nail. One can even bite and/or chew on these areas. One 2016 study 13 Rieder, E. A., & Tosti, A. (2016). Onychotillomania: An underrecognized disorder. ScienceDirect.com | Science, health and medical journals, full text articles and books. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0190962216303176 reveals that onychotillomania makes sufferers constantly tamper with the different elements in their nails. The condition is also highly uncommon & underreported. “Onychotillomania is characterized by a range of nonspecific findings, including bizarre morphology of the nail plate and damage to the nail bed and periungual skin,” adds the study. Several adverse effects can show up over time, like hangnails, open sores/wounds, infection caused by passing germs to the wounds by saliva. The urges can be kept in somewhat control by using putty-like squeeze balls, or even gloves in extreme cases.
7. Dermatophagia
Patients suffering from this type 14 Hawsawi, K. A., Aboud, K. A., & Ramesh, V. (n.d.). Dermatophagia Simulating Callosities. CiteSeerX. https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.693.2616&rep=rep1&type=pdf of BFRB show urges of chewing on their skin and then eating the residue or the scabs. Usually an irregular amount of tension or worry can be a stressor. Many times something feeble like a hangnail or a bump on the skin can bring out the urges. Many patients with this disorder believe that they can get rid of these habits by starting off with the basics, like choosing to stop chewing a small area, i.e. any finger/finger nail. Also known as “wolf-biter”, it is “a habit or compulsion, consciously or subconsciously, to bite one’s own skin,” explains a research 15 Scott MJ Jr, Scott MJ 3rd. Dermatophagia: “wolf-biter”. Cutis. 1997 Jan;59(1):19-20. PMID: 9013066. .
8. Rhinotillexomania
Nose picking is a very common habit that most people exhibit. However, if one does it obsessively, they might just be suffering from Rhinotillexomania. People with this type of BFRB tend to spend hours on a quotidian basis, trying to clean their noses. In most cases patients with this disorder are more likely to have other similar repetitive focused behavior like skin picking/ biting their nails. Specialists suggest to pay attention when one gets the urge and ask them to write down what and how they feel at that moment.
9. Trichotillomania
Research 16 Grant, J. E., & Chamberlain, S. R. (2016). Trichotillomania. The American journal of psychiatry, 173(9), 868–874. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.2016.15111432 states that this disorder is “characterized by the repetitive pulling out of one’s own hair leading to hair loss and functional impairment.” Generally anxiety or boredom trigger this sort of behavior 17 Hautmann, G., Hercogova, J., & Lotti, T. (2002, June). Trichotillomania. ScienceDirect.com | Science, health and medical journals, full text articles and books. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0190962202000002 . People try to pluck hair off their eyelashes, eyebrows, or other body parts, most of the time they remain unaware of the action. The symptoms usually appear around the age of 10-13 18 Panza, K. E., Pittenger, C., & Bloch, M. H. (2013). Age and gender correlates of pulling in pediatric trichotillomania. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 52(3), 241–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaac.2012.12.019 , but it can stay with one for the rest of their life. It can only be replaced with a healthier habit like knitting, crocheting, cross-stitching etcetera. It is an episodic and chronic disorder that is challenging to treat.
Read More About Trichotillomania Here
10. Trichophagia
Approximately, 5%-10% 19 Grant, J. E., & Odlaug, B. L. (2008). Clinical characteristics of trichotillomania with trichophagia. Comprehensive psychiatry, 49(6), 579–584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comppsych.2008.05.002 of people having Trichotillomania have this specific BFRB of chewing on their hair, and in some cases, eating it. This is called Trichophagia 20 Grant, J. E., & Odlaug, B. L. (2008). Clinical characteristics of trichotillomania with trichophagia. Comprehensive psychiatry, 49(6), 579–584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comppsych.2008.05.002 . Rare cases claim that some people have the tendency to eat other people’s or animal’s hair even. This habit of swallowing hair can lead to forming a hairball in the stomach which can be life-threatening if not taken out in time.
11. Trichodaganomania
This type also concerns hair biting habits. As it is comparatively hard to chew on the hair on the scalp, people resort to chewing or nibbling on hair attached to other body parts 21 Jafferany, M., Feng, J., & Hornung, R. L. (2009). Trichodaganomania: The compulsive habit of biting one’s own hair. ScienceDirect.com | Science, health and medical journals, full text articles and books. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0190962208010116 . Similar to the other Body Focused Repetitive Behaviors, negative feelings can be the root cause of this as well.
12. Trichotemnomania
Individuals with Trichotemnomania 22 Mutluer, L., Ates, B., Nasiroglu, S., & Eray, S. (2018, January 11). Three adolescent cases of a very rare disorder: Trichotemnomania. Taylor & Francis. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/24750573.2017.1420377 feel a strong urge to remove hair from the body. Going beyond just the scalp, the ones exhibiting this type of behavior feel the urge to remove hair from all over their body, including eyebrows, pubic hair and hair from arms and feet. It is an obsessive-compulsive act like Trichodaganomania, that leads the patient into believing that ridding themselves from their hair will do away with their unwanted thoughts.
Causes Of BFRBs
Since, there are a limited number of research studies that have been conducted on BFRB, the causes 23 Teng, E. J., Woods, D. W., & Twohig, M. P. (2016, July 26). Body-focused repetitive behavior problems: Prevalence in a Nonreferred population and differences in perceived somatic activity – Ellen J. Teng, Douglas W. Woods, Michael P. Twohig, brook A. Marcks, 2002. SAGE Journals. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/0145445502026003003 of the illness are not well understood up until now. Although, amongst many other probable causes, predisposition toward BFRBs are found to be inherited. In a general population, a higher number of BFRBs are found in immediate family members of the patient suffering from the disorder.
However, there are other factors involved alongside BFRBs being an inherited predisposition. Other species than humans, like primates such as chimpanzees, monkeys show signs of overgrooming, hair pulling and picking at their own and other’s nits. Other animals like dogs, cats, mice also exhibit extreme self-grooming tendencies. In order to understand the complex neurobiology that causes the human experience of BFRBs, these extreme grooming and damaging behaviors in animals are being currently being researched.
Diagnosis Procedure
As body focused repetitive disorders are mostly not well-understood, it leads to misdiagnosis often. Most individuals tend to dismiss the symptoms as mere habits. In some cases, medical specialists diagnose BFRBs as symptoms of obsessive-compulsive disorder. Thus, it is very important for a mental health professional to have the knowledge of how BFRB symptoms are distinct from OCD.
All the BRFBs are categorised as obsessive compulsive or related disorders, but these actually need to be put in a broader category. OCD and BRFBs might occur together or separately in a person. Sometimes, one of the disorders increases the chances of getting the other, but in reality the symptoms and urges are distinctive in case of each mental condition. BFRBs are very much different from intentional self-harming behaviors as well. In case of body focused repetitive behaviors, the individual seeks pleasure or relief by acting on their urges and the damage caused to the body parts is rarely intentional.
Treatments For Body Focused Repetitive Behavior
As the success rate of the treatment of body-focused repetitive behaviors are inconsistent, it leads to misdiagnosis of the condition. Specialists mostly take help of various therapy methods to treat anxiety or compulsivity related illnesses. In many cases BFRBs are driven by co-occurring mental health disorders. Identifying these co-occurring conditions can help in treating BFRB successfully. Success in treatment is supposedly more likely to take place when a professional applies individualized treatment, as every person has different sensitivities and causes different reactions. Generally, there are two treatment procedures that are widely used by health professionals which have a steady success rate: Psychotherapy and Pharmacotherapy.
1. Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy method uses the following treatment procedures:
A. Cognitive Behavior Therapy (CBT)
CBT is considered as the golden standard of the possible treatment of Body Focused Repetitive Behaviors. One of the most empirical evidences of CBT treatment approach having a habit reversal training that specifically focuses on repetitive focused behaviors.
Read More about Cognitive Behavior Therapy Here
B. Habit Reversal Therapy (HRT)
HRT mainly focuses on identifying triggers and coping through them, but it also involves many other components. There are some activities like keeping oneself’s hands busy, leaning towards societal support, and logging helps the individual to keep the urges at bay. The reason behind this being that years of scientific studies 24 Skurya, J., Jafferany, M., & Everett, G. J. (2020, June 15). Habit reversal therapy in the management of body focused repetitive behavior disorders. Wiley Online Library. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/dth.13811 have presented reports and ways of optimizing skills in a controlled setting. But what is essential is that one does not require therapy to use these. Though the onus and accountability might feel debilitating to some, it is something that can never be avoided.
2. Medications
Pharmacotherapy or medication for BFRBs has a lower success rate than psychotherapy as only a few types of body focused repetitive behaviors have been recorded to be treated with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, Clomipramine, Naltrexone, Neuroleptics, Lithium etcetera.
3. Coping Strategies
Although many of the BFRB can be unconsciously operating in a person, and with proper medication and clinical therapy only the habits can be restricted or redirected. However, there are a few prominent self-help strategies that one can use to get the urges in somewhat control:
- Using a medium (application) to record and track the patient’s progress in remitting the BFRBs.
- Trying to be mindful of oneself’s thoughts helps in moments when they feel triggered.
- In case of skin picking habits, adapting a skincare routine helps in redirecting the feeling of stress.
- Practicing acupressure like calming technique.
- Reading up and knowing about the disorder so get the reaction. that you can do the best of your abilities to manage the reaction.
- Look for other people who are going through the same.
- Art can be a great form of redirection.
- Start using a gadget that helps you track your progress and keeps your hands and mind busy.
Understanding BFRB
Body Focused Repetitive Behavior is essentially a compulsive physical manifestation induced by a singular or multiple psychological stressors. These triggers or stressors appear due to excessive anxiety and stress. Although in most scenarios, the symptoms get overlooked for a prolonged period of time which results in late diagnosis. In many cases, the symptoms seem to arrive at a young age and manifest into actions that are more obsessive and destructive in nature.
Lack of knowledge and oblivion are the reasons behind it. The effects of using these behaviors over a long time can bring up many adversities, such as serious infection, or lifethreateting disease caused by the infection. Thus, paying attention to these minute early symptoms might just save one’s life and help them have a life of contentment and retain good health.
BFRB At A Glance
- Body-focused repetitive behaviors are intense urges like biting, picking, and pulling that can cause damage.
- Typically, the condition starts to develop during childhood and adolescence.
- It has been found that women are more likely to get the disorder than men.
- Genetics is believed to be one of the main causes.
- Generally, there are two treatment procedures that are widely used by health professionals and have a steady success rate: Psychotherapy and Pharmacotherapy.