Table of Contents
Smoking is a harmful habit that can seriously damage both mental and physical health. While some people turn to smoking for temporary relief or as a way to cope with stress, what often starts as an occasional habit can quickly turn into an addictive, life-threatening and dangerous habit.
What Is Smoking?
A 2021 research paper 1 Adams TN, Morris J. Smoking. [Updated 2021 Feb 21]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537066/ defines smoking as the practice of inhaling and exhaling the smoke of certain plant-based burning substances into the bloodstream. It is considered to be one of the most significant global public health issues.
Though there are numerous plant materials people use as a substance, such as marijuana 2 Lafaye, G., Karila, L., Blecha, L., & Benyamina, A. (2017). Cannabis, cannabinoids, and health. Dialogues in clinical neuroscience, 19(3), 309–316. https://doi.org/10.31887/DCNS.2017.19.3/glafaye , cocaine 3 Cocaine Research Report. (2016). Drugabuse.gov | National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA). https://www.drugabuse.gov/download/1141/cocaine-research-report.pdf?v=3f3fb3f0903dfa8879388c2a5d086cb9 , hashish, the dried leaves of tobacco plants are the most common ones. It contains a high amount of nicotine that causes extreme addiction.
“Nicotine addiction is a complex disorder, habitual use of tobacco and tobacco products continues to be a significant contributor to health problems worldwide, which in part may be related to the increasing affordability of tobacco and nicotine products,” explained the researchers 4 Widysanto A, Combest FE, Dhakal A, et al. Nicotine Addiction. [Updated 2021 May 22]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499915/ .
People smoke tobacco in a number of ways, like smoking a cigarette, a pipe or a cigar even. Nicotine refers to an alkaloid that can have harmful effects on a person’s psychological and physiological well-being.
A 2015 study 5 Mishra, A., Chaturvedi, P., Datta, S., Sinukumar, S., Joshi, P., & Garg, A. (2015). Harmful effects of nicotine. Indian journal of medical and paediatric oncology : official journal of Indian Society of Medical & Paediatric Oncology, 36(1), 24–31. https://doi.org/10.4103/0971-5851.151771 claims that it causes several premature diseases and deaths worldwide than any other human habit or behavior does.
Tobacco use is linked to a wide range of both psychological, physical and mental disorders and diseases, such as the following:
- Diabetes 6 Chang S. A. (2012). Smoking and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes & metabolism journal, 36(6), 399–403. https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2012.36.6.399
- Cancer 7 Jacob, L., Freyn, M., Kalder, M., Dinas, K., & Kostev, K. (2018). Impact of tobacco smoking on the risk of developing 25 different cancers in the UK: a retrospective study of 422,010 patients followed for up to 30 years. Oncotarget, 9(25), 17420–17429. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.24724
- Obstructive pulmonary diseases 8 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (US); National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion (US); Office on Smoking and Health (US). How Tobacco Smoke Causes Disease: The Biology and Behavioral Basis for Smoking-Attributable Disease: A Report of the Surgeon General. Atlanta (GA): Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (US); 2010. 7, Pulmonary Diseases. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK53021/
- Schizophrenia 9 Lucatch, A. M., Lowe, D., Clark, R. C., Kozak, K., & George, T. P. (2018). Neurobiological Determinants of Tobacco Smoking in Schizophrenia. Frontiers in psychiatry, 9, 672. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00672
- Panic disorder 10 Moylan, S., Jacka, F. N., Pasco, J. A., & Berk, M. (2012). Cigarette smoking, nicotine dependence and anxiety disorders: a systematic review of population-based, epidemiological studies. BMC medicine, 10, 123. https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7015-10-123
- Pneumonia 11 Baskaran, V., Murray, R. L., Hunter, A., Lim, W. S., & McKeever, T. M. (2019). Effect of tobacco smoking on the risk of developing community acquired pneumonia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PloS one, 14(7), e0220204. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0220204
- Dementia 12 Cataldo, J. K., Prochaska, J. J., & Glantz, S. A. (2010). Cigarette smoking is a risk factor for Alzheimer’s Disease: an analysis controlling for tobacco industry affiliation. Journal of Alzheimer’s disease : JAD, 19(2), 465–480. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-2010-1240
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder 13 Abramovitch, A., Pizzagalli, D. A., Geller, D. A., Reuman, L., & Wilhelm, S. (2015). Cigarette smoking in obsessive-compulsive disorder and unaffected parents of OCD patients. European psychiatry : the journal of the Association of European Psychiatrists, 30(1), 137–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpsy.2013.12.003
- Eating disorder 14 Anzengruber, D., Klump, K. L., Thornton, L., Brandt, H., Crawford, S., Fichter, M. M., Halmi, K. A., Johnson, C., Kaplan, A. S., LaVia, M., Mitchell, J., Strober, M., Woodside, D. B., Rotondo, A., Berrettini, W. H., Kaye, W. H., & Bulik, C. M. (2006). Smoking in eating disorders. Eating behaviors, 7(4), 291–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eatbeh.2006.06.005
- Miscarriages 15 Pineles, B. L., Park, E., & Samet, J. M. (2014). Systematic review and meta-analysis of miscarriage and maternal exposure to tobacco smoke during pregnancy. American journal of epidemiology, 179(7), 807–823. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwt334
- Bipolar disorder 16 Thomson, D., Berk, M., Dodd, S., Rapado-Castro, M., Quirk, S. E., Ellegaard, P. K., Berk, L., & Dean, O. M. (2015). Tobacco use in bipolar disorder. Clinical psychopharmacology and neuroscience : the official scientific journal of the Korean College of Neuropsychopharmacology, 13(1), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.9758/cpn.2015.13.1.1
- Anxiety and depression 17 Fluharty, M., Taylor, A. E., Grabski, M., & Munafò, M. R. (2017). The Association of Cigarette Smoking With Depression and Anxiety: A Systematic Review. Nicotine & tobacco research : official journal of the Society for Research on Nicotine and Tobacco, 19(1), 3–13. https://doi.org/10.1093/ntr/ntw140
- Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder 18 McClernon, F. J., & Kollins, S. H. (2008). ADHD and smoking: from genes to brain to behavior. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1141, 131–147. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1441.016
- Cardiovascular diseases and stroke 19 Lakier J. B. (1992). Smoking and cardiovascular disease. The American journal of medicine, 93(1A), 8S–12S. https://doi.org/10.1016/0002-9343(92)90620-q
The Psychological Mechanism Of Smoking
Several researchers 20 Anzengruber, D., Klump, K. L., Thornton, L., Brandt, H., Crawford, S., Fichter, M. M., Halmi, K. A., Johnson, C., Kaplan, A. S., LaVia, M., Mitchell, J., Strober, M., Woodside, D. B., Rotondo, A., Berrettini, W. H., Kaye, W. H., & Bulik, C. M. (2006). Smoking in eating disorders. Eating behaviors, 7(4), 291–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eatbeh.2006.06.005 and psychologists have examined certain psychological mechanisms that can pose risk factors for tobacco use.
They have found that low levels of self-esteem and self-confidence, depressive mood, negative thoughts 21 Weinstein, S. M., & Mermelstein, R. J. (2013). Dynamic associations of negative mood and smoking across the development of smoking in adolescence. Journal of clinical child and adolescent psychology : the official journal for the Society of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, American Psychological Association, Division 53, 42(5), 629–642. https://doi.org/10.1080/15374416.2013.794698 , and personal well-being are closely interlinked with tobacco addiction. Smoking is considered the most effective and easiest way of delivering nicotine to the brain.
Studies 22 Benowitz N. L. (2009). Pharmacology of nicotine: addiction, smoking-induced disease, and therapeutics. Annual review of pharmacology and toxicology, 49, 57–71. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.48.113006.094742 explain that nicotine exerts an influence on multiple brain systems that leads to affecting people’s behavior, personality, feeling, and thinking. There are a variety of reasons why people start using tobacco.
A 2004 research 23 Jarvis M. J. (2004). Why people smoke. BMJ (Clinical research ed.), 328(7434), 277–279. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.328.7434.277 found that most of the reasons are related to changing one’s self-image, portraying oneself as more attractive, and displaying one’s physical and emotional strength.
Some of the most common causes behind this behaviors are the following:
- To prove courage or fearlessness on a dare
- Impact of advertisements and media portrayals
- To come across as more stylist, sophisticated, or modern
- Influence from friends, family, or relatives
- As an act of rebellion or defiance against authority
- To cope anxiety, tension, or stress
- As a method to control or lose weight
Many people believe that smoking helps relieve stress and manage anxiety or depression. However, the reality is quite the opposite.
Smoking is a highly addictive habit that can seriously harm a person’s mental health. In fact, smokers are more likely to experience symptoms of depression, and anxiety compared to those who don’t smoke.
A 2017 research paper 24 West R. (2017). Tobacco smoking: Health impact, prevalence, correlates and interventions. Psychology & health, 32(8), 1018–1036. https://doi.org/10.1080/08870446.2017.1325890 says that the worldwide prevalence of tobacco smoking is around 1 billion, where males smoke at higher rates than females, with 30% and 7% prevalence respectively.
Studies 25 Jha P, MacLennan M, Chaloupka FJ, et al. Global Hazards of Tobacco and the Benefits of Smoking Cessation and Tobacco Taxes. In: Gelband H, Jha P, Sankaranarayanan R, et al., editors. Cancer: Disease Control Priorities, Third Edition (Volume 3). Washington (DC): The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development / The World Bank; 2015 Nov 1. Chapter 10. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK343639/ doi: 10.1596/978-1-4648-0349-9_ch10 have estimated that tobacco use kills approximately 5 million people annually worldwide, accounting for over 20% of all deaths of adult men and 5% of deaths of adult women.
Understanding Smoking Addiction
The smoke of burning tobacco contains thousands of harmful chemicals. Research 26 Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Preventing Nicotine Addiction in Children and Youths; Lynch BS, Bonnie RJ, editors. Growing up Tobacco Free: Preventing Nicotine Addiction in Children and Youths. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 1994. 2, THE NATURE OF NICOTINE ADDICTION. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK236759/ says that the significant one ‘nicotine’ develops a dangerous addiction in people.
Single nicotine inhalation becomes a permanent addiction by going through the following process that includes:
- The smoke gets rapidly absorbed through the lungs into the bloodstream that carries it directly to the heart. A 2010 study 27 Benowitz, N. L., Hukkanen, J., & Jacob, P., 3rd (2009). Nicotine chemistry, metabolism, kinetics and biomarkers. Handbook of experimental pharmacology, (192), 29–60. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-69248-5_2 suggests, when a person inhales the smoke, it reaches the brain within about 10-20 seconds.
- As the nicotine enters the heart directly, it does not get a chance to dissipate. A high concentration of nicotine remains in the lungs and the bloodstream until it reaches the brain.
- According to 2013 research 28 Tweed, J. O., Hsia, S. H., Lutfy, K., & Friedman, T. C. (2012). The endocrine effects of nicotine and cigarette smoke. Trends in endocrinology and metabolism: TEM, 23(7), 334–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2012.03.006 , nicotine stimulates the adrenal glands to release the adrenaline hormone in the brain which is solely responsible for developing pleasure and energy.
- A 1997 study 29 Haass, M., & Kübler, W. (1997). Nicotine and sympathetic neurotransmission. Cardiovascular drugs and therapy, 10(6), 657–665. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00053022 explains that nicotine affects the central nervous system and increases one’s blood pressure, breathing, and heart rate. But the feeling of pleasure and energy is temporary.
- Studies 30 Bruijnzeel A. W. (2012). Tobacco addiction and the dysregulation of brain stress systems. Neuroscience and biobehavioral reviews, 36(5), 1418–1441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2012.02.015 have found, once the nicotine reaches people’s brains, it helps to improve their mood as well as decrease their anger and stress. The nicotine relaxes one’s muscles and reduces appetite.
- Nicotine also activates the dopamine signal 31 Benowitz N. L. (2009). Pharmacology of nicotine: addiction, smoking-induced disease, and therapeutics. Annual review of pharmacology and toxicology, 49, 57–71. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.48.113006.094742 that leads to a kind of relaxing sensation in the brain. The dopamine release instantly produces a sense of pleasure and happiness in people.
Our body and brain quickly adapt to the regular intake of nicotine. Over time, this slowly develops into an addiction, that causes noticeable changes in brain function.
As the body builds a higher tolerance to nicotine, a person starts craving larger amounts to feel the same effect. This creates a repetitive cycle of nicotine entering the brain, providing temporary relief, and then wearing off, eventually trapping a person in a pattern of smoking addiction.
How Smoking Affects The Brain
When a person smokes, nicotine starts to act like the neurotransmitters that are already present in the human brain. A 2011 research 32 D’Souza, M. S., & Markou, A. (2011). Neuronal mechanisms underlying development of nicotine dependence: implications for novel smoking-cessation treatments. Addiction science & clinical practice, 6(1), 4–16. explains that the brain decreases the acetylcholine receptors to compensate for the increased signal activity caused by nicotine.
This gradually leads to nicotine tolerance in the brain. When an individual starts to smoke regularly and frequently, the nicotine begins to reduce their ability to feel pleasure.
It causes the smoker to need more nicotine inhalation to sustain the pleasure. It also activates the reward system 33 De Biasi, M., & Dani, J. A. (2011). Reward, addiction, withdrawal to nicotine. Annual review of neuroscience, 34, 105–130. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-neuro-061010-113734 of the human brain and increases the levels of dopamine, a chemical messenger that influences rewarding behaviors 34 Bromberg-Martin, E. S., Matsumoto, M., & Hikosaka, O. (2010). Dopamine in motivational control: rewarding, aversive, and alerting. Neuron, 68(5), 815–834. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2010.11.022 .
Research says that certain other chemicals in tobacco products, including acetaldehyde, increases the effects of nicotine in the brain.
It requires more research to detect the effects of smoking on a person’s cognitive abilities. But smoking damages certain areas by causing thinning in some crucial areas. According to a 2015 study 35 Karama, S., Ducharme, S., Corley, J., Chouinard-Decorte, F., Starr, J. M., Wardlaw, J. M., Bastin, M. E., & Deary, I. J. (2015). Cigarette smoking and thinning of the brain’s cortex. Molecular Psychiatry, 20(6), 778-785. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2014.187 , smokers tend to have a thinner cerebral cortex than others as nicotine destroys the brain’s grey matter.
“Smoking is significantly associated with gray matter volume loss in the prefrontal cortex, the anterior cingulate cortex, the insula, and the olfactory gyrus.”, explained by a 2014 research paper 36 Fritz, H. C., Wittfeld, K., Schmidt, C. O., Domin, M., Grabe, H. J., Hegenscheid, K., Hosten, N., & Lotze, M. (2014). Current smoking and reduced gray matter volume-a voxel-based morphometry study. Neuropsychopharmacology : official publication of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology, 39(11), 2594–2600. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2014.112 .
The cerebral cortex 37 Jawabri KH, Sharma S. Physiology, Cerebral Cortex Functions. [Updated 2021 May 4]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538496/ is considered extremely crucial for thinking abilities, memory, perception, and learning.
Smoking And Mental Health
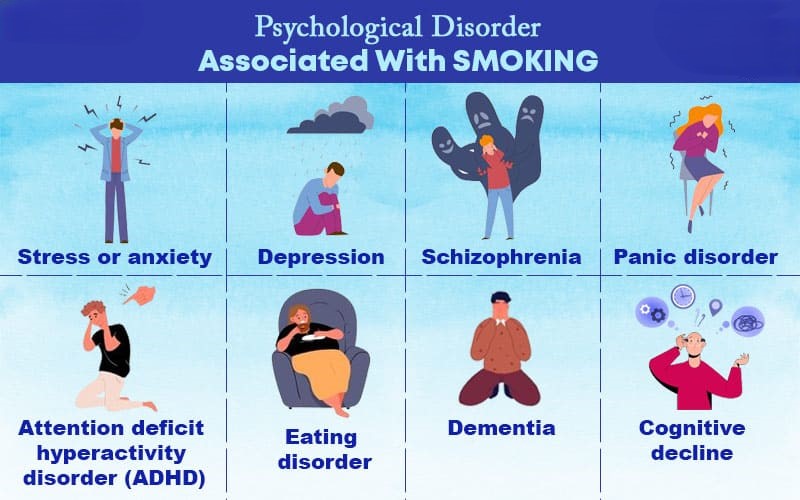
Many people believe that smoking helps them manage stress and anxiety. However, the reality is that nicotine addiction can cause serious harm to both physical and mental health.
A 2013 study 38 Minichino, A., Bersani, F. S., Calò, W. K., Spagnoli, F., Francesconi, M., Vicinanza, R., Delle Chiaie, R., & Biondi, M. (2013). Smoking behaviour and mental health disorders–mutual influences and implications for therapy. International journal of environmental research and public health, 10(10), 4790–4811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph10104790 states that smokers are more likely to suffer from various psychological disorders than non-smokers. Nicotine inhalation provides a boost in confidence and a great sense of achievement at first.
But it gradually reduces the feeling of pleasure once it becomes an addiction. Studies 39 Benowitz N. L. (2009). Pharmacology of nicotine: addiction, smoking-induced disease, and therapeutics. Annual review of pharmacology and toxicology, 49, 57–71. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.48.113006.094742 have found that nicotine interferes with the functioning of neurotransmitters and exerts several neuroendocrine effects that lead to developing several psychological complications.
Nicotine addiction is associated with a number of mental and psychological disorders and conditions, such as:
1. Stress or anxiety
Most people tend to smoke with the aim of reducing stress. Nicotine offers instant relaxation, and that’s why people partake in the habit because they believe that it will reduce their anxiety and stress. Once a person finishes smoking, the nicotine level begins to fall in their body.
A 2017 research 40 Benowitz, N. L., & Burbank, A. D. (2016). Cardiovascular toxicity of nicotine: Implications for electronic cigarette use. Trends in cardiovascular medicine, 26(6), 515–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcm.2016.03.001 claims that the nicotine level makes their hearts beat faster and increases their blood pressure. One might experience anxiety 41 Picciotto, M. R., Brunzell, D. H., & Caldarone, B. J. (2002). Effect of nicotine and nicotinic receptors on anxiety and depression. Neuroreport, 13(9), 1097–1106. https://doi.org/10.1097/00001756-200207020-00006 and intolerable craving for nicotine. It also decreases one’s capability to deal with stress.
Read More About Anxiety Here
2. Depression
Research 42 Fluharty, M., Taylor, A. E., Grabski, M., & Munafò, M. R. (2017). The Association of Cigarette Smoking With Depression and Anxiety: A Systematic Review. Nicotine & tobacco research : official journal of the Society for Research on Nicotine and Tobacco, 19(1), 3–13. https://doi.org/10.1093/ntr/ntw140 says that a person with depression tends to get addicted to smoking more than any other person. Many people get addicted to nicotine without showing any symptoms of depression.
A 2007 research paper 43 Lembke, A., Johnson, K., & DeBattista, C. (2007). Depression and smoking cessation: does the evidence support psychiatric practice?. Neuropsychiatric disease and treatment, 3(4), 487–493. claims that people with depression often struggle a lot and experience severe withdrawal symptoms while quitting smoking. Depression and nicotine addiction are closely associated as smoking often leads to depression, which in turn often encourages one to start smoking.
Nicotine stimulates dopamine release that develops a sense of happiness. As depressive people lack positive feelings, they end up relying on nicotine to temporarily increase their dopamine supply.
Read More About Major Depressive Disorder ( Depression ) Here
3. Schizophrenia
According to a 2018 study 44 Lucatch, A. M., Lowe, D., Clark, R. C., Kozak, K., & George, T. P. (2018). Neurobiological Determinants of Tobacco Smoking in Schizophrenia. Frontiers in psychiatry, 9, 672. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00672 , schizophrenia patients are more likely to get addicted to nicotine. As nicotine develops a temporary pleasurable feeling, research 45 Quigley, H., & MacCabe, J. H. (2019). The relationship between nicotine and psychosis. Therapeutic advances in psychopharmacology, 9, 2045125319859969. https://doi.org/10.1177/2045125319859969 says that it may seem to reduce some of the symptoms of schizophrenia or the side effects of medicines used for the treatment.
A 2013 research 46 Fotuhi, O., Fong, G. T., Zanna, M. P., Borland, R., Yong, H. H., & Cummings, K. M. (2013). Patterns of cognitive dissonance-reducing beliefs among smokers: a longitudinal analysis from the International Tobacco Control (ITC) Four Country Survey. Tobacco control, 22(1), 52–58. https://doi.org/10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2011-050139 explains that tobacco may improve concentration and decrease the unpleasant hyperstimulation experienced by schizophrenia patients.
But studies 47 Kendler, K. S., Lönn, S. L., Sundquist, J., & Sundquist, K. (2015). Smoking and schizophrenia in population cohorts of Swedish women and men: a prospective co-relative control study. The American journal of psychiatry, 172(11), 1092–1100. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.2015.15010126 have shown that regular use of nicotine may increase the chances of schizophrenia.
Read More About Schizophrenia Here
4. Panic disorder
A 2018 research paper 48 Farris, S. G., Brown, L. A., Goodwin, R. D., & Zvolensky, M. J. (2017). Panic attack history and smoking topography. Drug and alcohol dependence, 171, 84–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2016.11.023 suggests that regular smoking is considered to be a risk factor for the first occurrence of panic attacks and disorders. Nicotine addiction can increase the lifetime risk of panic disorder by three times.
Studies 49 Lakier J. B. (1992). Smoking and cardiovascular disease. The American journal of medicine, 93(1A), 8S–12S. https://doi.org/10.1016/0002-9343(92)90620-q have found that it plays a big role when it comes to increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease in patients suffering from panic disorder.
Read More About Panic Disorder Here
5. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
A 2009 research 50 McClernon, F. J., & Kollins, S. H. (2008). ADHD and smoking: from genes to brain to behavior. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1141, 131–147. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1441.016 explains that tobacco consumption in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder patients results from an attempt at self-medication. ADHD patients tend to use nicotine to relieve the symptoms of the disorder.
Studies 51 Wickström R. (2007). Effects of nicotine during pregnancy: human and experimental evidence. Current neuropharmacology, 5(3), 213–222. https://doi.org/10.2174/157015907781695955 show that women are more likely to get addicted to nicotine early and late in their pregnancy period.
6. Dementia
According to a 2014 study 52 Zhou, S., Zhou, R., Zhong, T., Li, R., Tan, J., & Zhou, H. (2014). Association of smoking and alcohol drinking with dementia risk among elderly men in China. Current Alzheimer research, 11(9), 899–907. https://doi.org/10.2174/1567205011666141001123356 , smoking is one of the significant risk factors for dementia. Inhaling the smoke of tobacco is associated with increased oxidative stress 53 Kamceva, G., Arsova-Sarafinovska, Z., Ruskovska, T., Zdravkovska, M., Kamceva-Panova, L., & Stikova, E. (2016). Cigarette Smoking and Oxidative Stress in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease. Open access Macedonian journal of medical sciences, 4(4), 636–640. https://doi.org/10.3889/oamjms.2016.117 . Oxidative stress refers to the imbalance between toxic molecules and antioxidants.
This imbalance damages the cells in the human body. Research 54 Luca, M., Luca, A., & Calandra, C. (2015). The Role of Oxidative Damage in the Pathogenesis and Progression of Alzheimer’s Disease and Vascular Dementia. Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity, 2015, 504678. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/504678 says that this imbalance is closely related to the onset of dementia. Nicotine inhalation increases the other risk factors of dementia, such as high blood pressure and stroke 55 Shah, R. S., & Cole, J. W. (2010). Smoking and stroke: the more you smoke the more you stroke. Expert review of cardiovascular therapy, 8(7), 917–932. https://doi.org/10.1586/erc.10.56 .
Read More About Dementia Here
7. Cognitive decline
People may experience cognitive decline as they get older. A 2012 study 56 Sabia, S., Elbaz, A., Dugravot, A., Head, J., Shipley, M., Hagger-Johnson, G., Kivimaki, M., & Singh-Manoux, A. (2012). Impact of smoking on cognitive decline in early old age: the Whitehall II cohort study. Archives of general psychiatry, 69(6), 627–635. https://doi.org/10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.2016 claims that smokers are more likely to experience the symptoms of cognitive decline much earlier than others.
Smokers may experience the following symptoms:
- Confusion regarding visual-spatial tasks 57 Fernandes, T., Almeida, N. L., & Santos, N. (2017). Effects of smoking and smoking abstinence on spatial vision in chronic heavy smokers. Scientific reports, 7(1), 1690. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-01877-z
- Personality changes 58 Littlefield, A. K., & Sher, K. J. (2012). Smoking desistance and personality change in emerging and young adulthood. Nicotine & tobacco research : official journal of the Society for Research on Nicotine and Tobacco, 14(3), 338–342. https://doi.org/10.1093/ntr/ntr219
- Hallucination 59 Quigley, H., & MacCabe, J. H. (2019). The relationship between nicotine and psychosis. Therapeutic advances in psychopharmacology, 9, 2045125319859969. https://doi.org/10.1177/2045125319859969
- Losing motivation 60 Blank, M. D., Ferris, K. A., Metzger, A., Gentzler, A., Duncan, C., Jarrett, T., & Dino, G. (2017). Physical Activity and Quit Motivation Moderators of Adolescent Smoking Reduction. American journal of health behavior, 41(4), 419–427. https://doi.org/10.5993/AJHB.41.4.6
- Anxiety and depression 61 Leventhal, A. M., & Zvolensky, M. J. (2015). Anxiety, depression, and cigarette smoking: a transdiagnostic vulnerability framework to understanding emotion-smoking comorbidity. Psychological bulletin, 141(1), 176–212. https://doi.org/10.1037/bul0000003
Read More About Cognitive decline Here
8. Eating disorders
A 2005 study 62 Jessen, A., Buemann, B., Toubro, S., Skovgaard, I. M., & Astrup, A. (2005). The appetite-suppressant effect of nicotine is enhanced by caffeine. Diabetes, obesity & metabolism, 7(4), 327–333. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1463-1326.2004.00389.x says that smoking can decrease appetite and increases satiety. Many people with eating disorders try to suppress their appetite by smoking cigarettes.
Research says that women suffering from eating disorders are at greater risk for smoking and higher dependence on nicotine, especially those who display impulsive behavior and binge eat.
Read More About Eating disorders Here
Smoking And Personality

Several significant studies 63Terracciano, A., & Costa, P. T., Jr (2004). Smoking and the Five-Factor Model of personality. Addiction (Abingdon, England), 99(4), 472–481. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1360-0443.2004.00687.x have examined the connection between smoking and people’s different personality characteristics.
These studies have identified the three most common personality traits linked to the psychological aspects of smoking, which include:
1. The extraversion dimension
Certain personality characteristics of extroverts are closely interlinked with nicotine addiction. Extrovert and introvert personalities differ according to the level of necessary stimulation for personal well-being.
A recent 2020 study 64 Pashapour, H., Musavi, S., Dadashzadeh, H., & Mohammadpoorasl, A. (2020). Relationship between Extraversion and Tobacco Smoking Among High School Students. International journal of preventive medicine, 11, 134. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_177_19 suggests that extroverts often try to change their external environment by increasing their activity and internal environment by ingesting substances.
The extraversion dimension includes several key factors, such as:
- Positive emotions
- Assertiveness
- Sociability
- Activity level
- Vivacity
2. The neuroticism dimension
A 2002 research 65 Goodwin, R., & Hamilton, S. P. (2002). Cigarette smoking and panic: the role of neuroticism. The American journal of psychiatry, 159(7), 1208–1213. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.159.7.1208 says that certain personality traits of neuroticism make an individual sensitive to nicotine properties. Such people often use smoke to cope with their stress and anxiety.
Research 66 Lahey B. B. (2009). Public health significance of neuroticism. The American psychologist, 64(4), 241–256. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0015309 shows that the neuroticism dimension is associated with some psychological disorders, including depression and anxiety. These personalities portray high frequency and intensity of negative affect.
The neuroticism dimension includes several key factors, such as:
- Jealousy
- Hostility
- Anger
- Depression
- Negative thoughts
- Psychological vulnerability
- Anxiety
3. The psychoticism dimension
According to a 1984 research paper 67 Parkes K. R. (1984). Smoking and the Eysenck personality dimensions: an interactive model. Psychological medicine, 14(4), 825–834. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0033291700019796 , the association between psychoticism and tobacco intake is the most consistent dimension.
The psychoticism dimension includes several key factors, such as:
- Impulsivity
- Cynicism
- Coldness
- Reduced inhibition
- Low conscientiousness
- Reduced conformity
- Antisocial actions and behaviors
- Attraction toward exciting sensations
Initiating Factors Of Smoking
The factors that trigger the habit of smoking among regular and adult smokers are quite different from those factors that are associated with smoking initiation.
A 2011 study 68 Peltzer K. (2011). Early smoking initiation and associated factors among in-school male and female adolescents in seven African countries. African health sciences, 11(3), 320–328. mentions that higher nicotine addiction among various population ranges is triggered or influenced by different psychological, social, economic, and cultural factors, including:
- Peer pressure and influence (the most common factor)
- Smoking habits of parents or siblings
- Low socioeconomic background
- Poor living conditions and long-term unemployment
- Exposure to substances during childhood
- Easy availability of tobacco products
- Personal beliefs about the perceived benefits of nicotine
- Financial stress and pressure
- History of anxiety or depression
- Impact of aggressive tobacco marketing
- Previous experimentation with tobacco products
- Lower chances of working in indoor, smoke-free environments
- Limited parental involvement or supervision
- Poor academic performance
- Inability to confidently refuse cigarettes
- Low self-esteem and self-worth
- Lack of awareness about the harmful effects of tobacco
Smoking Withdrawal
When people suddenly stop smoking and no tobacco is entering their body, they experience certain mild to severe unpleasant physical and psychological symptoms.
These symptoms are called nicotine withdrawal symptoms 69 Benowitz N. L. (2010). Nicotine addiction. The New England journal of medicine, 362(24), 2295–2303. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra0809890 . The severity of the symptoms largely depends on how much and how long the person has smoked.
Research 70 Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Preventing Nicotine Addiction in Children and Youths; Lynch BS, Bonnie RJ, editors. Growing up Tobacco Free: Preventing Nicotine Addiction in Children and Youths. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 1994. 2, THE NATURE OF NICOTINE ADDICTION. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK236759/ says that these withdrawal symptoms can be observed in a person within 24-48 hours after he/she last smoked. The symptoms are considered a sign of psychological and physical dependence on nicotine.
A 2015 research 71 McLaughlin, I., Dani, J. A., & De Biasi, M. (2015). Nicotine withdrawal. Current topics in behavioral neurosciences, 24, 99–123. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-13482-6_4 has mentioned some of the most common physical and psychological withdrawal symptoms of nicotine, such as:

- Intense craving for nicotine
- Weight gain
- Anxiety and depression
- Changes in appetite
- Headaches and dizziness
- Problems in concentrating
- Sleeping disorders
- Stress and restlessness
- Fatigue
- Constipation
- Mental fog
- Irritability
- Sweating
- Sore throat and coughing
- Abdominal cramping
- nausea and vomiting
- Tingling in the hands and feet
How To Quit Smoking

Despite being aware of the serious health risks associated with nicotine, many people still start smoking and eventually become addicted. Smoking is both a psychological habit and a physical addiction.
While it may provide temporary relief or satisfaction, the long-term impact on a person’s physical and mental health is extremely harmful. Although quitting smoking can lead to mild or even severe withdrawal symptoms, it is essential to stop nicotine consumption to avoid life-threatening consequences.
Here are some effective strategies to help quit smoking:
- One needs to find and understand their personal reason to stop consuming nicotine. Choosing a reason that is strong enough often helps one to reduce the urge.
- Identifying the triggers and trying to avoid them completely.
- Understanding that withdrawal won’t happen overnight, and that your body will need a considerable amount of time to deal with withdrawal symptoms.
- Consulting with a health care professional and considering nicotine replacement therapy 72 Wadgave, U., & Nagesh, L. (2016). Nicotine Replacement Therapy: An Overview. International journal of health sciences, 10(3), 425–435. . This therapy will help you in coping with withdrawal symptoms.
- Whenever you feel a craving for smoking or any form of nicotine, give yourself 10 minutes, and then try to distract yourself for that period of time.
- Informing your loved ones that you are planning to quit smoking. Your family and friends can make the withdrawal easy for you by providing the right sort of care and support.
- Giving yourself a break, and spending time with the people you love. Doing things that make you happy, such as having your favorite food or indulging in your favorite hobbies.
- If you feel a craving for nicotine, chew sugarless gum or munch carrots or nuts to satisfy your craving.
- Get yourself habituated with regular physical activity. You can also try yoga or meditation 73 Khanna, S., & Greeson, J. M. (2013). A narrative review of yoga and mindfulness as complementary therapies for addiction. Complementary therapies in medicine, 21(3), 244–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctim.2013.01.008 or any kind of mindfulness practice.
- Eat healthy food and drink plenty of water. Add some fresh vegetables and fruits to your daily diet.
- Don’t be disappointed and try until you succeed in overcoming your cravings.
- If you find it extremely difficult to quit smoking, consider seeking medical help and treatment.
Takeaway
Smoking is a harmful habit that involves inhaling the smoke of burning tobacco. While it may initially create a temporary sense of relaxation or pleasure, over time, the body becomes less responsive to these effects, causing the individual to crave more nicotine.
This cycle slowly but steadily causes nicotine addiction, which ends up harming your mental and physical health in the long run.
Regular nicotine use has been linked to several severe psychological disorders. People often take up smoking for different reasons, such as peer pressure, the influence of tobacco advertisements, parental or sibling smoking, childhood exposure to substances, and more.
Whatever the reason may be, smoking significantly increases the risk of life-threatening diseases.
To protect their health, individuals should work toward quitting smoking and seek professional medical support if needed.
Smoking At A Glance
- Smoking is a harmful act where people burn various plant materials and inhale the smoke that reaches the brain within 10-20 seconds.
- Dried tobacco leaves are mostly used for smoking and nicotine is the most harmful substance in tobacco that causes addiction.
- Studies revealed that around 1 billion people regularly consume tobacco and it kills almost 1 million people every year worldwide.
- Nicotine addiction is associated with several life-threatening physical and physiological disorders, such as cancer, heart attack, respiratory diseases, depression, obsessive-compulsive disorder, panic attacks, schizophrenia, dementia, and many more.
- Smoking is also closely interconnected with three personality dimensions that include extraversion, neuroticism, and psychoticism.
- People may experience several mild to severe physical and psychological symptoms after they quit smoking.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What makes smoking addictive?
When you smoke a cigarette, or chew tobacco, the nicotine works towards releasing dopamine in your brain, which makes you happier and better. But only in the short-term.
2. What are 5 reasons why someone smokes?
The 5 biggest reasons why a person smokes are – peer pressure, trying to deal with stress and anxiety, coping with difficult situations, companionship, and to improve communication and attention span.
3. How many cigarettes a day is safe?
There are no safe number of cigarettes to be had in a day. Every cigarette you smoke has a detrimental effect on your mental and physical health.
















Absolutely informative. I am trying to quite myself and am going to challenge myself. It is time I really look after my health and that is something that cant be bought.