Table of Contents
Social media refers to interactive digital platforms and applications designed to facilitate communication, content creation, and information sharing over the Internet. Social media addiction, in this context, is commonly defined as a compulsive or pathological engagement with these platforms, often leading to negative impacts on mental health and daily functioning.
What Is Social Media Addiction?
Social media addiction is popularly defined as a mental health condition 1 Karim, F., Oyewande, A. A., Abdalla, L. F., Chaudhry Ehsanullah, R., & Khan, S. (2020). Social Media Use and Its Connection to Mental Health: A Systematic Review. Cureus, 12(6), e8627. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.8627 in which a person experiences an uncontrollable and compulsive urge to use social media. Its main signs involve an obsessive preoccupation with internet activities as well as psychological dependence and withdrawal symptoms induced by the lack of social media use.
If a person spends more than 9 hours a day on social media, they are taken to be a “social media addict 2 Chegeni, M., Shahrbabaki, P. M., Shahrbabaki, M. E., Nakhaee, N., & Haghdoost, A. (2021). Why people are becoming addicted to social media: A qualitative study. Journal of education and health promotion, 10(1), 175. https://doi.org/10.4103/jehp.jehp_1109_20 ”. While it is not a formally recognized mental health disorder in psychiatric manuals, it has been included within the purview of impulse-control disorders and is considered a crippling health hazard that could mandate professional attention.
With the advent of the Internet in the 1990s, the term “Internet addiction disorder”(IAD) was coined by American psychiatrist Ivan K. Goldberg 3 Cash, H., Rae, C. D., Steel, A. H., & Winkler, A. (2012). Internet Addiction: A Brief Summary of Research and Practice. Current psychiatry reviews, 8(4), 292–298. https://doi.org/10.2174/157340012803520513 . He developed the term as a dig at the complexity and rigidity of the American Psychiatric Association’s (APA) Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM).
In later years, terms like “problematic internet use” and “pathological internet use” began to describe compulsive and maladaptive patterns of internet usage that significantly impair an individual’s physical and mental well-being.
With the rapid rise of social media platforms in the early 2000s, researchers and healthcare professionals increasingly recognized a link between excessive social media use and addictive behaviors.
Around this time, the term “social media addiction” began to emerge in common language, referring to a growing dependence on platforms such as Facebook, YouTube, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, and others.
Case Study
Arya, a 25-year-old woman, confessed that she couldn’t imagine life without social media. She spent an average of six to seven hours a day on Instagram, obsessively tracking likes, comments, follower counts, and other metrics.
Over the past couple of years, Arya had gradually withdrawn from activities unrelated to posting on Instagram or Twitter. Her interactions with family dwindled, and her daily routine began to revolve entirely around her online presence, rather than real-life priorities.
Recently, a steady drop in her Instagram followers triggered heightened distress. In an attempt to regain popularity, Arya began posting more frequently. She isolated herself in her room, constantly refreshing her feed and refusing to eat.
Convinced that losing weight would help her attract more likes, she began to restrict her food intake. Eventually, Arya started hallucinating the sound of notification alerts and became visibly agitated when they turned out to be imaginary.
As her mental and physical health sharply declined, Arya was admitted to the hospital. A psychiatric evaluation revealed that she was not only struggling with social media addiction but had also developed an eating disorder as a direct consequence of her compulsive online behavior.
Signs Of Social Media Addiction
The common social media addiction symptoms 4 Azizi, S. M., Soroush, A., & Khatony, A. (2019). The relationship between social networking addiction and academic performance in Iranian students of medical sciences: a cross-sectional study. BMC psychology, 7(1), 28. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-019-0305-0 include:
- Spending an excessive amount of time on social media platforms
- Constantly thinking about social media, even when offline
- Withdrawing from real-life activities, hobbies, or social interactions
- Obsessing over one’s online image, reputation, and digital persona
- Experiencing anxiety or restlessness when unable to check social media
- Preoccupying oneself with creating, planning, and curating posts
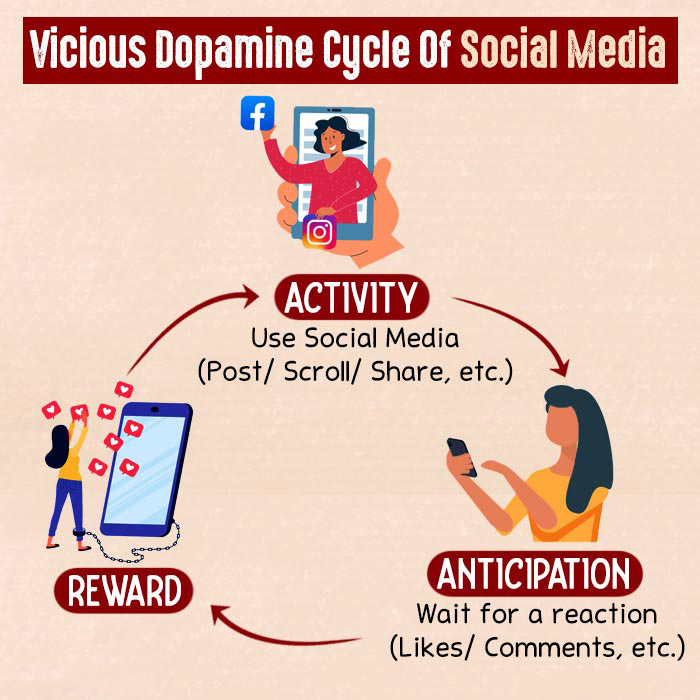
- Experiencing phantom notifications or “false alarms” from one’s device
- Fixating on interactions such as likes, comments, messages, and shares
- Neglecting responsibilities at work, school, or home due to social media use
- Repeatedly trying—and failing—to reduce screen time or limit usage
- Engaging in doomscrolling: compulsively consuming negative or distressing content
Causes Of Social Media Addiction
The common causes 5 Chegeni, M., Shahrbabaki, P. M., Shahrbabaki, M. E., Nakhaee, N., & Haghdoost, A. (2021). Why people are becoming addicted to social media: A qualitative study. Journal of education and health promotion, 10(1), 175. https://doi.org/10.4103/jehp.jehp_1109_20 of social media addiction involve:

- A lack of affection, emotional connection, or supportive social groups
- A strong need for external validation and approval
- The desire to expand and maintain a wide-reaching social influence
- The urge to reaffirm one’s identity within a peer group or community
- Seeking personal gratification or self-esteem boosts through online engagement
- Using social media as an escape from real-life stressors, such as family conflict or unsatisfying relationships
Social Media Addiction And Mental Health
Obsessive and excessive use of social media can severely impact mental health. Constant exposure to curated and often inauthentic portrayals of life, along with experiences like cyberbullying, online trolling, and relentless comparisons—both personal and professional—can lead to negative emotions such as diminished self-worth, low self-esteem, and dissatisfaction with one’s life or appearance.
Research 6 Aydin, S., Koçak, O., Shaw, T. A., Buber, B., Akpinar, E. Z., & Younis, M. Z. (2021). Investigation of the Effect of Social Media Addiction on Adults with Depression. Healthcare (Basel, Switzerland), 9(4), 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9040450 shows that social media addiction can trigger several mental health disorders and disabilities like:
- Self-esteem issues
- Depression [Read more]
- Anxiety [Read more]
- Fear of missing out (FOMO)
- Syndromes like ringxiety, selfitis 7 Ramesh Masthi, N. R., Pruthvi, S., & Phaneendra, M. S. (2018). A Comparative Study on Social Media Usage and Health Status among Students Studying in Pre-University Colleges of Urban Bengaluru. Indian journal of community medicine : official publication of Indian Association of Preventive & Social Medicine, 43(3), 180–184. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijcm.IJCM_285_17 , etc.
- Isolation and loneliness [Read more]
- Social withdrawal
- Behavioral disorders (linked to anger, frustration, etc.)
- Body dysmorphia
- Eating disorders [Read more]
- Substance use disorders
- Sleep disorders [Read more]
- Body aches and pain
- Obsessive-compulsive disorders [Read more]
- Self-harm and suicidal tendencies [Read more]

Social Media Addiction Statistics
Research 8 Montag, C., Lachmann, B., Herrlich, M., & Zweig, K. (2019). Addictive Features of Social Media/Messenger Platforms and Freemium Games against the Background of Psychological and Economic Theories. International journal of environmental research and public health, 16(14), 2612. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16142612 estimates that 12% of social media users 9 Hou, Y., Xiong, D., Jiang, T., Song, L., & Wang, Q. (2019). Social media addiction: Its impact, mediation, and intervention. Cyberpsychology: Journal of Psychosocial Research on Cyberspace, 13(1), Article 4. https://doi.org/10.5817/CP2019-1-4 have an addiction to social media. Studies have also found that:
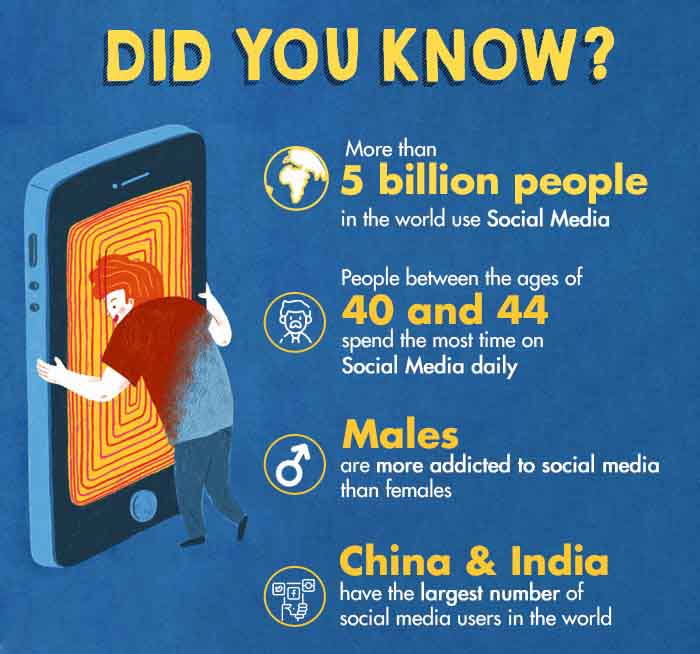
- More than 210 million people worldwide are affected by the Internet and social media addiction.
- Gen Z addicted to social media is aged 18–24 years and they usually use the social media sites of Instagram and Snapchat.
- An estimated 27% of children who spend 3 or more hours a day on social media exhibit symptoms of poor mental health.
- More males (66.4% 10 Ramesh Masthi, N. R., Pruthvi, S., & Phaneendra, M. S. (2018). A Comparative Study on Social Media Usage and Health Status among Students Studying in Pre-University Colleges of Urban Bengaluru. Indian journal of community medicine : official publication of Indian Association of Preventive & Social Medicine, 43(3), 180–184. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijcm.IJCM_285_17 ) are addicted to social media than females (33.6%).
- The risk of social media addiction gets lower as the age of the population increases. People above 60 years of age are most likely to escape this addiction.
- The occupational group 11 Aydin, S., Koçak, O., Shaw, T. A., Buber, B., Akpinar, E. Z., & Younis, M. Z. (2021). Investigation of the Effect of Social Media Addiction on Adults with Depression. Healthcare (Basel, Switzerland), 9(4), 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9040450 with the highest level of addiction is job seekers, followed by students and retirees.
Diagnosis Of Social Media Addiction
Clinical practice classifies social media addiction as an impulse-control disorder and it meets the criteria laid down for pathological behaviors such as gaming disorder, chronic gambling, sex addiction, workaholism, etc.
Although it is not formally recognized as a mental health disorder, screening tools like Social Media Addiction Scale 12 Shahnawaz, M., & Rehman, U. (2020). Social Networking Addiction Scale. Cogent Psychology, 7(1), 1832032. doi: 10.1080/23311908.2020.1832032 (SMAS) are used for detecting excessive social media use and addiction.
Treatment For Social Media Addiction
Much like other behavioral and conduct disorders, social media addiction carries the risk of frequent relapse and life-long prevalence. Although there is no medical treatment for this disorder, certain established therapeutic interventions could prove to be quite effective, such as:
- Cognitive behavioral therapy 13 Young K. S. (2007). Cognitive behavior therapy with Internet addicts: treatment outcomes and implications. Cyberpsychology & behavior : the impact of the Internet, multimedia and virtual reality on behavior and society, 10(5), 671–679. https://doi.org/10.1089/cpb.2007.9971 (CBT) [Read more]
- Group Motivation Enhancement Therapy 14 Manwong, M., Lohsoonthorn, V., Booranasuksakul, T., & Chaikoolvatana, A. (2018). Effects of a group activity-based motivational enhancement therapy program on social media addictive behaviors among junior high school students in Thailand: a cluster randomized trial. Psychology research and behavior management, 11, 329–339. https://doi.org/10.2147/PRBM.S168869
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy 15 Pluhar, E., Jhe, G., Tsappis, M., Bickham, D., & Rich, M. (2020). Adapting Dialectical Behavior Therapy for Treating Problematic Interactive Media Use. Journal of psychiatric practice, 26(1), 63–70. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRA.0000000000000439
Self-help coping strategies are usually the first step to managing social media and internet-related addictions. However, in extreme cases of social media addiction, it is recommended that a mental health professional (MHPs) be consulted.
Sometimes, excessive social media use can also lead to symptoms of eating disorders or body dysmorphic disorder (BDD). In such cases, it may be wise to consult a therapist and seek professional treatment.
Read More About Eating Disorders Here
How To Break Social Media Addiction
Overcoming social media addiction can be challenging, but with consistent effort, it’s entirely possible. Here are some effective strategies to help reduce your screen time and regain control:
- Monitor your usage: Keep track of how much time you spend online and aim to gradually cut back.
- Take a social media detox: Temporarily deactivate or uninstall your social media apps to give your mind a break.
- Disable non-essential notifications: Turn off alerts that aren’t work-related to minimize distractions and reduce the urge to check your phone.
- Set time limits: Establish a daily cap for social media use—consider using built-in phone features or dedicated apps to enforce it.
- Use apps to restrict access: Try digital well-being tools or time-limiting apps to help you stay accountable.
- Engage in offline hobbies: Pick up activities that keep you away from your phone, like painting, reading, or joining a local class.
- Avoid screen time before bed: Reducing exposure before sleep can significantly improve your sleep quality.
- Practice self-care: Activities like journaling, gardening, hiking, or meditating can ground you in the present moment.
- Limit phone use during key moments: Keep your phone away during work, meals, study sessions, or while spending time with loved ones.
- Prioritize real-life connections: Make time to connect with friends and family in person—it nurtures emotional well-being and reduces reliance on virtual validation.
Takeaway
Social media addiction is a serious mental health concern that can disrupt daily functioning, strain relationships, and diminish overall well-being. However, with timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment, its long-term effects can be effectively managed—paving the way for a healthier, more balanced, and fulfilling life.
At A Glance
- Social media addiction refers to an unhealthy and compulsive reliance on interactive platforms like Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and others. It is characterized by pathological use and a constant preoccupation with online interactions and internet-based activities.
- Key signs include psychological dependence, emotional distress when unable to access social media, and withdrawal-like symptoms. This addiction is often driven by underlying needs such as the desire for validation, personal gratification, or as a coping mechanism for real-life stressors and emotional discomfort.
- It is especially common among adolescents, young adults, and the broader adult population. Fortunately, social media addiction can often be effectively addressed through consistent self-help strategies and mindful digital habits.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What type of people are addicted to social media?
People with character traits 16 Peris, M., de la Barrera, U., Schoeps, K., & Montoya-Castilla, I. (2020). Psychological Risk Factors that Predict Social Networking and Internet Addiction in Adolescents. International journal of environmental research and public health, 17(12), 4598. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17124598 of neuroticism, conscientiousness, and agreeableness are particularly linked with social network addiction.
2. How long has social media addiction been around?
The notion of “Internet addiction disorder” was developed by Ivan K. Goldberg in 1995.
3. Is social media addiction genetic?
About two-thirds of a person’s social media habits are linked to genetic traits and learned psychosocial behavior.
4. What to do if your partner is addicted to social media?
If you think your partner is addicted to social media, communicate openly with them to address the issue. Discuss how much time you expect him/her to be on social media and listen to their thoughts on how they use or plan to use social networking sites. Help them come up with a plan to handle social media.
5. What can parents do to prevent social media addiction?
Parents need to be mindful of their children’s social media use. They must keep a check on the youngsters’ online activities and put a time limit on their online presence to curb this problem.
6. Who is more addicted to social media men or women?
Males 17 Su, W., Han, X., Yu, H., Wu, Y., & Potenza, M. N. (2020). Do men become addicted to internet gaming and women to social media? A meta-analysis examining gender-related differences in specific internet addiction. Computers in Human Behavior, 113, 106480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2020.106480 have been proposed to be more vulnerable to social media addiction than females.















