Table of Contents
Agoraphobia is an anxiety disorder in which a person is afraid of crowded places, such as public buses, malls, elevators, and other such situations that may cause them a panic attack.
What Is Agoraphobia?
Agoraphobia is a mental disorder 1 Balaram, K., & Marwaha, R. (2022). Agoraphobia. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554387/ involving an extreme fear of crowded, public, or enclosed spaces, such as markets, public vehicles, lines, malls, elevators, etc. People with this disorder usually avoid situations and places where they feel trapped or unable to escape and tend to remain within a certain “safe” radius.
The difference between people who may feel occasional discomfort in public places and people with agoraphobia is that the latter usually experience a fear that is out of proportion to the situation and that causes them significant distress and impairment.
Most agoraphobics tend to develop the condition after experiencing one or more panic attacks 2 Wittchen, H. U., Nocon, A., Beesdo, K., Pine, D. S., Hofler, M., Lieb, R., & Gloster, A. T. (2008). Agoraphobia and panic. Prospective-longitudinal relations suggest a rethinking of diagnostic concepts. Psychotherapy and psychosomatics, 77(3), 147–157. https://doi.org/10.1159/000116608 in a public place. As they become preoccupied with the possibility of such attacks in the future, they start to avoid situations that may trigger them.
Agoraphobia is a Greek term, derived from “agora” meaning place of assembly, and “phobia” meaning fear. The condition was not considered a distinct disorder until 2013 when the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5 3 American Psychiatric Association. (2013). DSM-5. Psychiatry.org; American Psychiatric Association. Available from: https://www.psychiatry.org/psychiatrists/practice/dsm ) finally included it as a separate diagnosis.
Agoraphobia affects almost 1.7% of adults. Moreover, around 30-50% of individuals 4 Agoraphobia – Mental Health Disorders. (n.d.). MSD Manual Consumer Version. Available from: https://www.msdmanuals.com/home/mental-health-disorders/anxiety-and-stress-related-disorders/agoraphobia with this disorder also suffer from panic disorder. The onset of agoraphobia usually happens by the age of 35. The condition begins in early adulthood and becomes less common with age. Agoraphobia is more commonly found in women than in men. It rarely occurs in children.

Case Example
Ever since her early teenage years, Aditi had disliked sitting in class. She would usually stay close to the door in classrooms and auditoriums, claiming that it made her feel safer. She had always tried to avoid events that involved a lot of people, as she would invariably end up having a panic attack in such situations.
After she joined college, Aditi’s situation significantly worsened. Her anxiety prevented her from attending regular classes and shopping for groceries, among other things.
Moreover, she would have at least 2 to 3 panic attacks in college every week. Every time Aditi entered the campus, she got intensely overwhelmed and felt like she had to escape.
.
At the age of 20, Aditi was diagnosed with agoraphobia.
How is Agoraphobia Different from Other Phobias?
Although technically called a ‘phobia’, agoraphobia differs from specific phobias 5 NIMH» Specific Phobia. (2020). Www.nimh.nih.gov. Available from: https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/statistics/specific-phobia . A specific phobia, such as a fear of elevators or malls, is usually restricted to a single situation or thing, whereas agoraphobia involves a fear of two or more public places.
Read More About Phobia Here
Agoraphobia vs. Social Anxiety
Another disorder that is often confused with agoraphobia is social anxiety disorder 6 National Collaborating Centre for Mental Health (UK. (2013). SOCIAL ANXIETY DISORDER. Nih.gov; British Psychological Society. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK327674/ . The basic difference between social anxiety disorder and agoraphobia is that the former involves intense fear of being judged by other people whereas the latter is to do more with particular places. However, the one thing common to both is the possibility and fear of panic attacks.
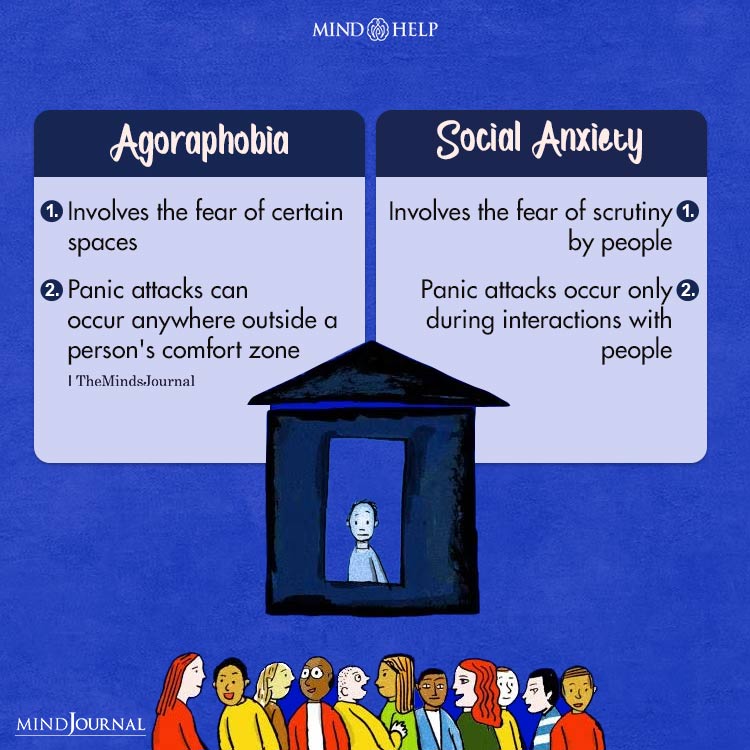
Read More About Social Anxiety Disorder Here
Symptoms Of Agoraphobia
Agoraphobia symptoms 7 Symptoms – Agoraphobia. (2021, February 12). Nhs.uk. Available from: https://www.nhs.uk/mental-health/conditions/agoraphobia/symptoms/ can manifest in the following ways:
Behavioral Symptoms
- Not leaving home for an extended period of time
- Trying not to go too far from home
- Avoiding situations and places where a panic attack might occur
- Limiting activities and socialization that might require going out
- Needing an accompanying person to go out with all of the time
Cognitive Symptoms
- Fear of being alone in a social gathering
- Fear of losing control or having a panic attack
- Fear of places that do not have an escape
- Constant worry and agitation
Physical Symptoms
Agoraphobia often comprises panic attacks, involving:
- Chest pain
- Rapid heartbeat
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness
- Trembling
- Choking
- Excessive sweating
- Chills, etc.
What Causes Agoraphobia?
Research is still ongoing to determine the causes of agoraphobia. However, several risk factors 8 Balaram, K., & Marwaha, R. (2020). Agoraphobia. PubMed; StatPearls Publishing. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554387/ have been implicated in its development, such as:
- Genetic predisposition
- Adverse childhood experiences
- Childhood trauma
- Parental overprotectiveness
- Traits related to avoidant and dependent personality 9 Bienvenu, O. J., Stein, M. B., Samuels, J. F., Onyike, C. U., Eaton, W. W., & Nestadt, G. (2009). Personality disorder traits as predictors of subsequent first-onset panic disorder or agoraphobia. Comprehensive psychiatry, 50(3), 209–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comppsych.2008.08.006

Agoraphobia Diagnosis
As laid down by the DSM 5 10 Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. (2016). Impact of the DSM-IV to DSM-5 Changes on the National Survey on Drug Use and Health. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (US). Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK519704/table/ch3.t10/ , in order to be diagnosed with agoraphobia, you would have a fear of at least two of the following persisting for a period of 6 months or more:
- Going out on public transportation such as a bus or train
- Being in open spaces such as a parking lot
- Being in enclosed spaces like an elevator or car
- Being in a crowd
- Being away from home alone
Moreover, the symptoms should be:
- Out of proportion in response to the actual situation
- Impair daily functioning or cause serious distress
- Triggered under the same circumstances
- Not caused by other general medical or mental conditions
A mental health professional usually takes a detailed history of the symptoms and other details related to the personal and family history of a person before arriving at a diagnosis. Certain psychometric assessments such as the Panic and Agoraphobia Scale 11 Bandelow B. (1995). Assessing the efficacy of treatments for panic disorder and agoraphobia. II. The Panic and Agoraphobia Scale. International clinical psychopharmacology, 10(2), 73–81. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004850-199506000-00003 may also be used to confirm the diagnosis.
Take Our Agoraphobia Test Here
Treatment For Agoraphobia
Early diagnosis and treatment of agoraphobia can ensure favorable outcomes. Agoraphobia treatment usually involves therapy, medication, or a combination of both.
Psychotherapy
The following therapy techniques are commonly adopted for the treatment of Agoraphobia:
A. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT is the standard treatment 12 Christoforou, M., Sáez Fonseca, J. A., & Tsakanikos, E. (2017). Two Novel Cognitive Behavioral Therapy-Based Mobile Apps for Agoraphobia: Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of medical Internet research, 19(11), e398. https://doi.org/10.2196/jmir.7747 method for agoraphobia. Cognitive techniques help a person identify the negative thoughts associated with public situations and behavioral experiments help them eventually overcome their fear.
Online or web-based CBT has been especially useful for people with intense agoraphobia who might fear going to therapy physically.
Read More About Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Here
B. Exposure Therapy
A behavioral therapy technique, exposure therapy is the gradual process of exposing the patient to situations or places they fear. This helps them overcome fears about being in an unsafe environment.
Virtual exposure therapy 13 APA PsycNet. (n.d.). Psycnet.apa.org. Retrieved October 11, 2022, from https://psycnet.apa.org/record/2008-01196-001 has recently been gaining popularity for the treatment of agoraphobia and related disorders.
Medications
Medications 14 Perna, G., Daccò, S., Menotti, R., & Caldirola, D. (2011). Antianxiety medications for the treatment of complex agoraphobia: pharmacological interventions for a behavioral condition. Neuropsychiatric disease and treatment, 7, 621–637. https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S12979 can help relieve the symptoms of Agoraphobia, especially panic attacks. A doctor may prescribe the following medicines for this condition:
- Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRI), such as paroxetine (Paxil) or fluoxetine (Prozac)
- Selective serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, like venlafaxine (Effexor) or duloxetine
- Tricyclic antidepressants, such as amitriptyline (Elavil) or nortriptyline (Pamelor)
- Anti-anxiety medications, such as alprazolam (Xanax) or clonazepam (Klonopin)
Self-Help Tips For Agoraphobia
A few modifications in daily life may also help the treatment process. Here are a few self-help tips 15 Treatment – Agoraphobia. (2021, February 12). Nhs.uk. Available from: https://www.nhs.uk/mental-health/conditions/agoraphobia/treatment/ for you to manage your agoraphobia better:
- Exercise regularly to increase the production of “happy” chemicals in the brain
- Eat a healthy diet that consists of whole grains, vegetables, and fruits
- Practice deep breathing exercises or meditation in order to reduce anxiety and fight the onset of panic attacks
- Avoid drugs and alcohol
- Limit caffeine intake
It is advisable not to take herbal or dietary supplements as these might interfere with the effectiveness of the prescribed medication.
Takeaway
Agoraphobia can be exhausting as it can make it difficult for you to engage in daily activities. However, research has found that agoraphobia symptoms improve with age.
Moreover, getting the right treatment and medication early can help accelerate the process of healing and ensure a good quality of life. Support from family and friends is also of paramount importance for a person suffering or recovering from agoraphobia.
At A Glance
- Agoraphobia is a mental disorder involving an intense fear of crowds or public places.
- Agoraphobia should not be confused with specific phobias or social anxiety disorder, as they are all distinct disorders.
- Symptoms of agoraphobia have behavioral, cognitive, and physical aspects.
- Certain factors such as childhood trauma, dependent and avoidant personality traits, and genetic predisposition can increase the risk of agoraphobia
- Agoraphobia can be treated with psychotherapeutic approaches such as cognitive behavioral therapy or medications such as anti-depressants and anti-anxiety medicines.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is agoraphobia an anxiety disorder?
Yes. Agoraphobia is classified as an anxiety disorder as it involves an intense fear/ anxiety of public places, crowds, or enclosed spaces.
2. Why are women more prone to agoraphobia?
Women are diagnosed with agoraphobia more frequently than men, which could be due to brain chemistry, hormonal fluctuations, or socio-cultural factors. However, the exact cause for this is not known.
3. How does agoraphobia affect relationships?
Agoraphobia can affect relationships in different ways. The fear of going out of the house and needing someone to accompany them at all times can make a person with agoraphobia quite dependent on others, which can be stressful for friends and folks at times. It can also affect social relationships that require going out to places the agoraphobic person is afraid of.
4. How to deal with a spouse with agoraphobia?
If your loved one is suffering from agoraphobia, you must encourage them to seek help from a mental health professional and try to support them throughout the treatment process. It might get stressful to live with someone who has agoraphobia. So, it is important for you to have a support system and take some time to engage in self-care as well.
5. Can you live a normal life with agoraphobia?
Agoraphobia can be quite a debilitating mental disorder. However, with help in the form of therapy and/ or medication, a person can indeed go on to live a normal life.















